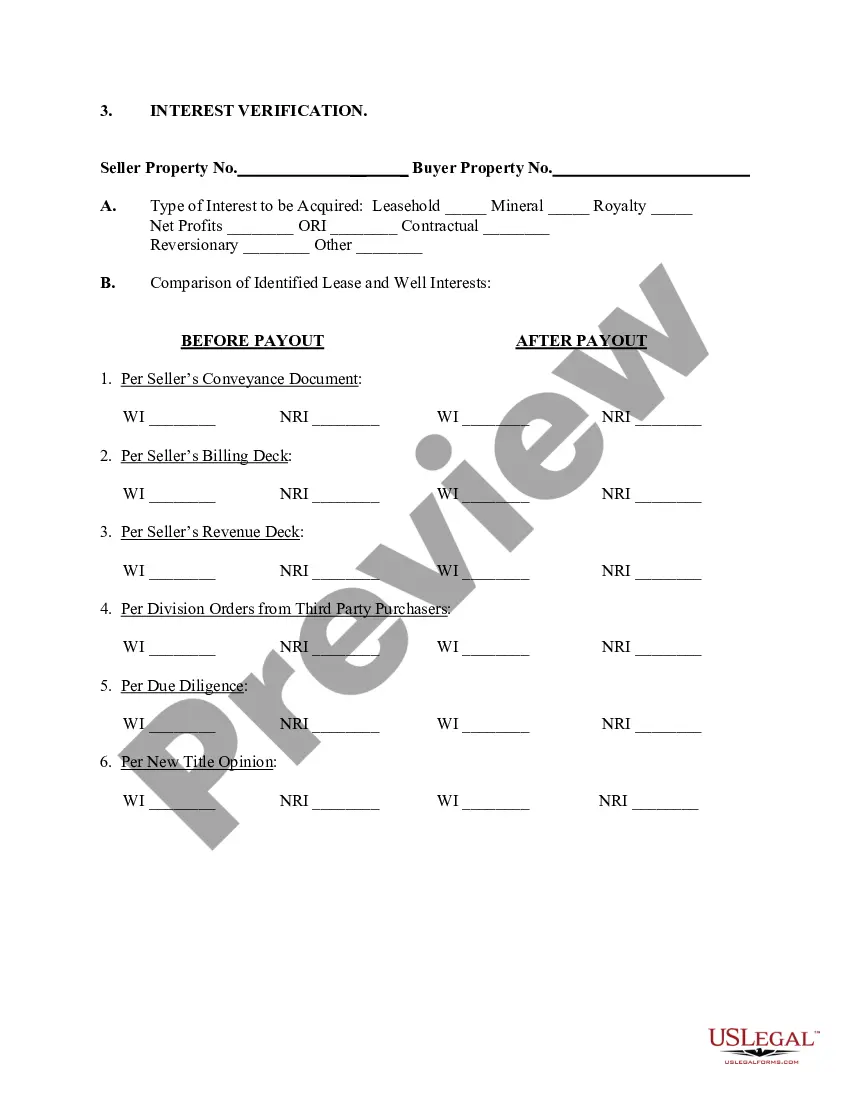
Patent Trademark Application With Priority Date In Ohio
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
The priority date for a trademark is established when the application is filed and remains fixed. It does not expire or change unless the application is abandoned or withdrawn. The priority date serves as a permanent reference point for determining the order of rights and protecting the trademark.
Priority date refers to the earliest filing date in a family of patent applications.
A trademark priority date is the earliest a trademark can be registered with the US Trademark Office (USPTO). This date is usually the date of first use or first filing. A trademark registration date is an actual day on which the mark is officially registered with the USPTO.
What is a priority date and why does it is matter? A. Priority date refers to the earliest filing date in a family of patent applications. If the earliest-filed patent application for a particular invention was a provisional application, then the filing date of the provisional is your priority date.
The priority date for a trademark is established when the application is filed and remains fixed. It does not expire or change unless the application is abandoned or withdrawn. The priority date serves as a permanent reference point for determining the order of rights and protecting the trademark.
The timeline for trademark registration in India varies, but on average, it takes around 1 to 2 years. Factors like application scrutiny, objections, and legal procedures can influence the duration.
Trademark Priority: Determining Who Was First Trademark rights in the US generally belong to the one who was first to use the mark in commerce. Whoever was first to sell goods or services under a particular mark will typically be deemed the rightful trademark owner. This is known as trademark priority.
What is claiming priority? Claiming priority back-dates your protection, whether you have a registered design, a patent or a trade mark. Claiming priority from your first application for something means you don't have to file for protection in multiple places at the outset, with all the fees that would entail.
The five primary requirements for patentability are: (1) patentable subject matter; (2) utility; (3) novelty; (4) non-obviousness; and (5) enablement. Like trademarks, patents are territorial, meaning they are enforceable in a specific geographic area.