Installment Contract Agreement With Irs In Maricopa
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
While the IRS typically doesn't allow taxpayers to have two separate installment agreements, adding a new tax debt to an existing installment plan is possible. However, taxpayers must act swiftly before the IRS assesses the new tax balance and potential default occurs, triggering enforcement actions.
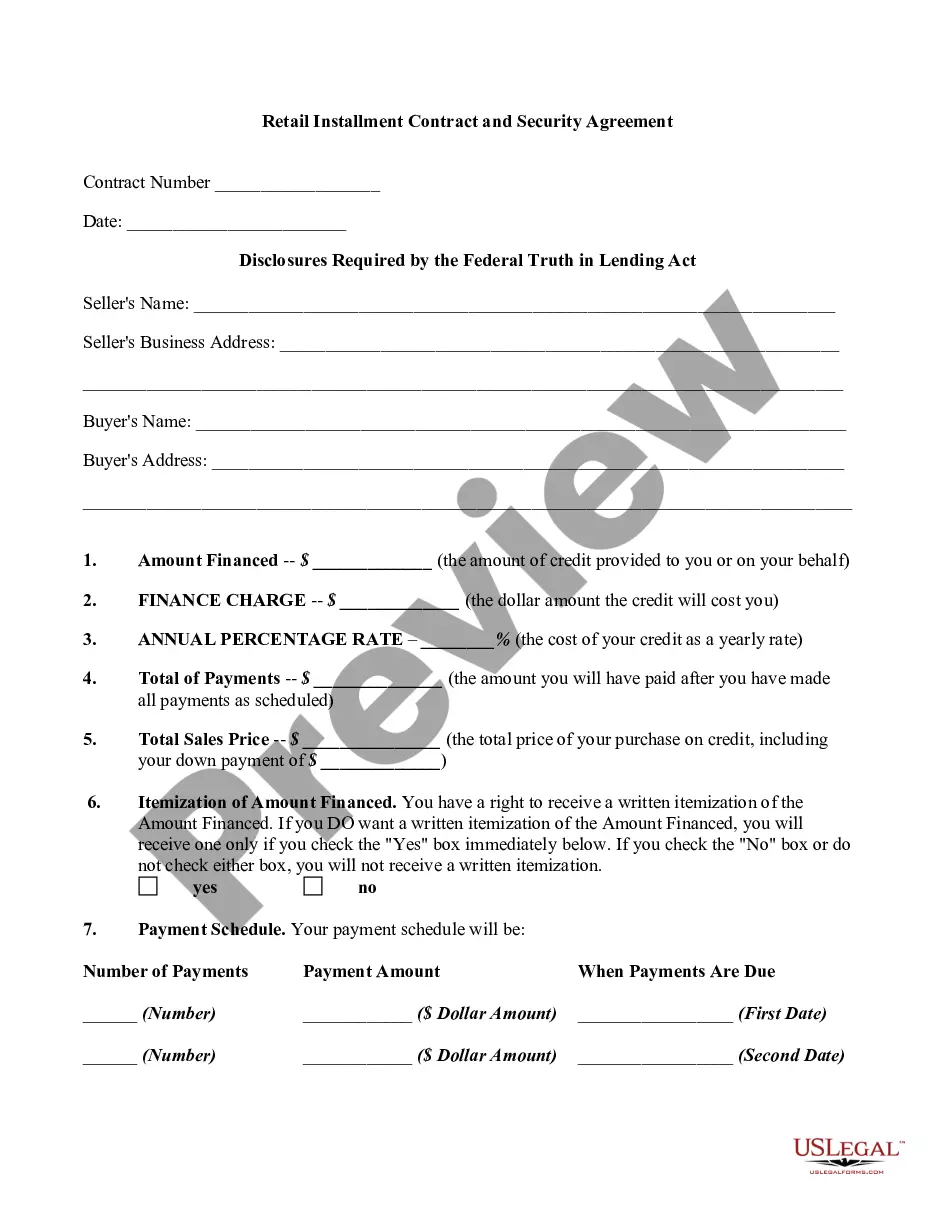
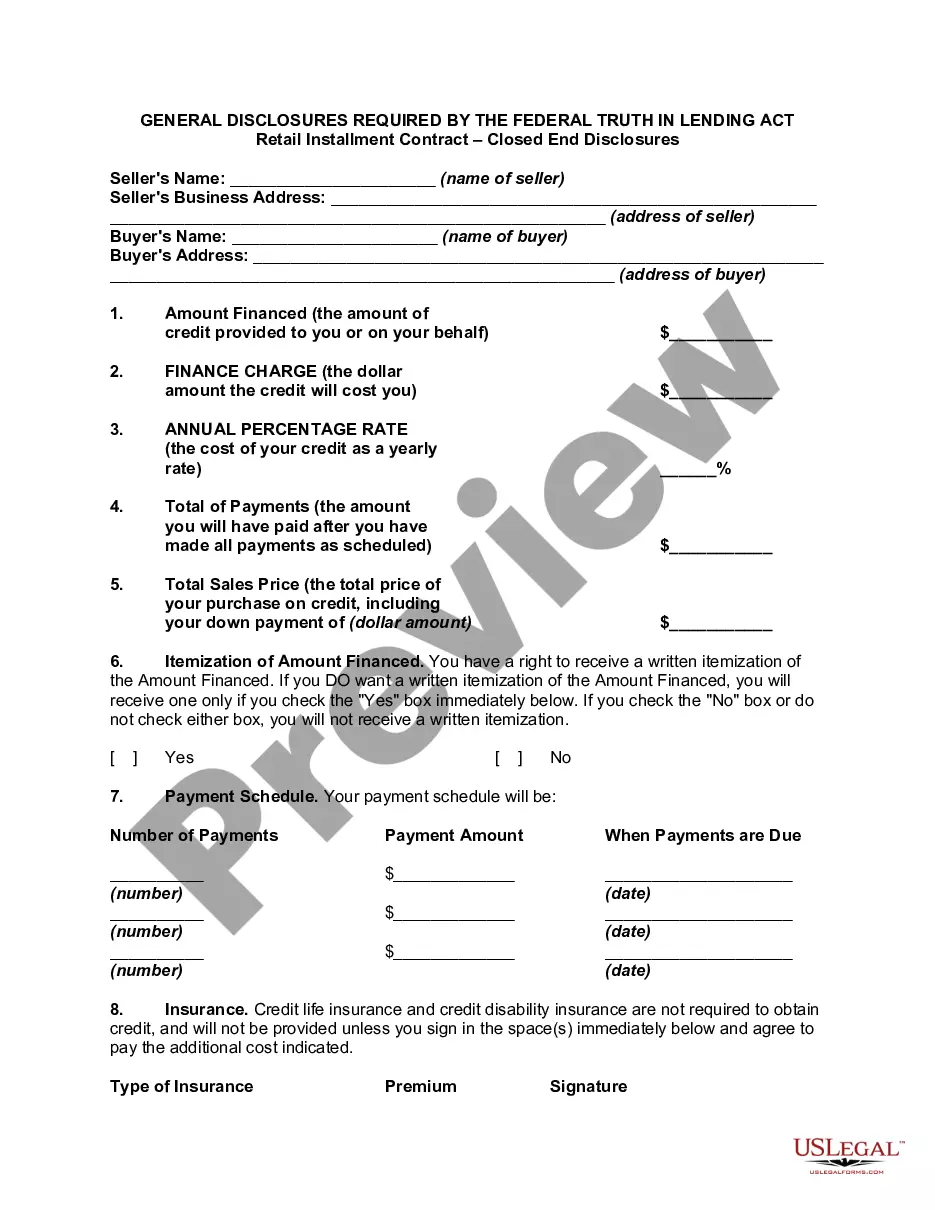
A payment plan agreement, also known as an installment agreement, is a written legal document that allows one party to make smaller payments over time to payoff a larger debt.
What does the principal debt mean? An instalment sale agreement between you and a credit provider allows you to buy a vehicle or asset using the principal debt, which you repay by means of regular instalments over an agreed period, with fees and interest.
Essentially, Form 9465 is a request form used to apply for a payment plan, and Form 433-D is the direct debit installment agreement form that is used to establish the actual agreement once the IRS has approved the payment plan. 433 d form allows the IRS to take payments directly from a taxpayer's bank account.
If you are unable to revise an existing installment agreement online, call us at 800-829-1040 (individual) or 800-829-4933 (business).
If you don't qualify for an IA through OPA, you may also request an IA by submitting Form 9465, Installment Agreement Request, with the IRS. When you request an IA using the form, generally, you'll receive a response from the IRS within 30 days notifying you of whether the IA request was approved or rejected.
WHY THE IRS REJECTS INSTALLMENT AGREEMENT REQUESTS. The IRS typically rejects an installment agreement request for one of three reasons. If the IRS determines that your living expenses do not fall under the category of “necessary,” your agreement will more than likely be rejected.