This Handbook provides an overview of federal laws addressing employer-employee rights and obligations. Information discussed includes wages & hours, discrimination, termination of employment, pension plans and retirement benefits, workplace safety, workers' compensation, unions, the Family and Medical Leave Act, and much more in 25 pages of materials.
Labour Laws In Pakistan In Bexar
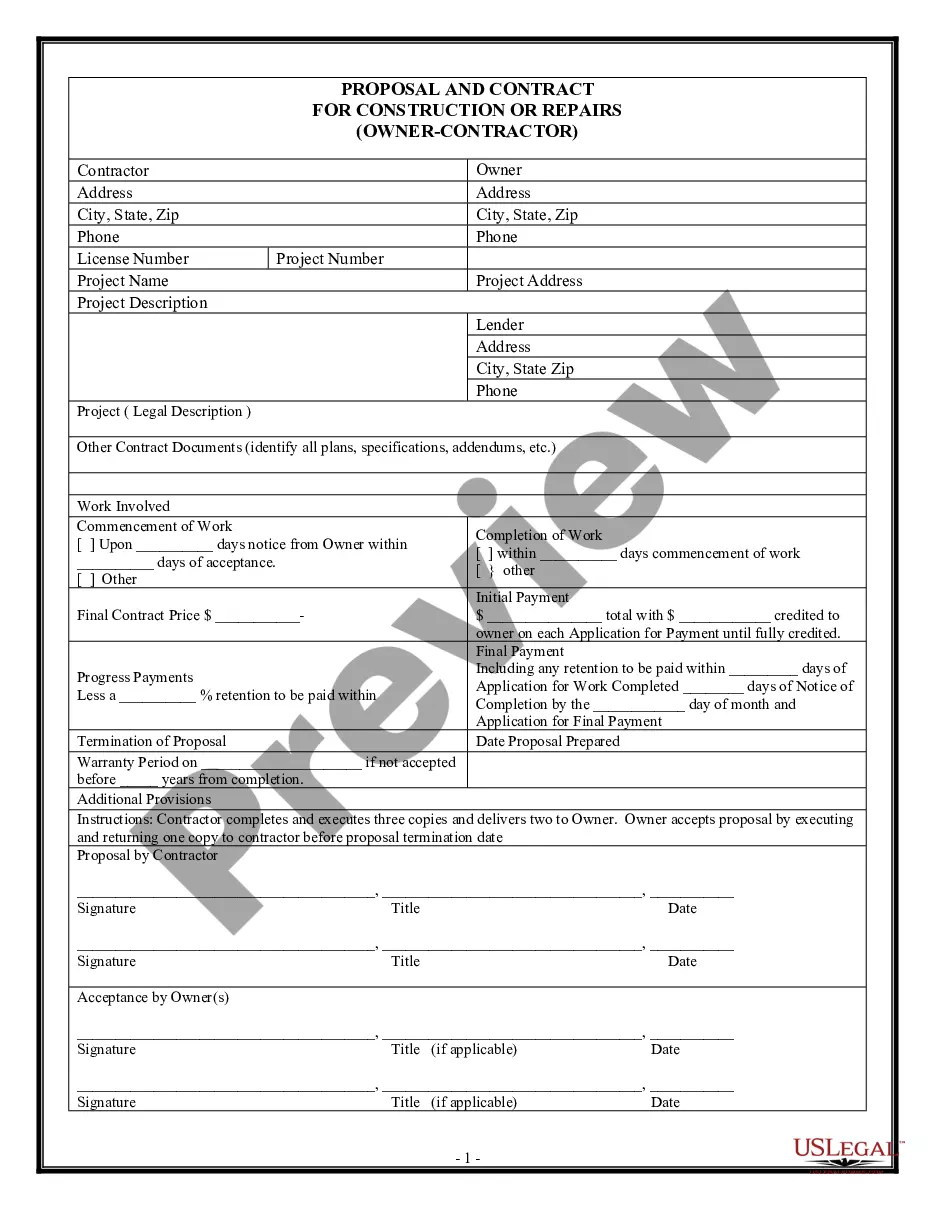
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Basic Conditions of Employment Act (BCEA) This Act relates to the working conditions of employees by providing standard / basic conditions of employment. Some terms covered by the Act include leave, overtime, hours of work, etc.
The maximum normal working time allowed (section 9 BCEA) is 45 hours weekly. This is 9 hours per day (excluding lunch break) if the employee works a five-day week, and 8 hours per day (excluding lunch break) if the employee works more than 5 days per week.
The sources of labour law The Labour Relations Act 66 of 1995 (LRA) NB: this law was amended in 2002. Text of the Labour Relations Amendment Act, 2002. The Occupational Health and Safety Act 85 of 1993 (OHSA) The Compensation for Occupational Injuries and Diseases Act 130 of 1993 (COIDA).
Unfair labor practices by unions include forcing workers to join or contribute to a union against their will, engaging in coercive tactics during collective bargaining, disrupting work without lawful cause, or discriminating against employees for not joining the union.
Under federal and provincial laws (except those of Balochistan), for workers and non-managers, an employer is bound to give at least one month of prior notice (or wage equivalent to an average of three months' wages in lieu of notice) to terminate the employee without cause.
The two compulsory wall charts that must be displayed are the Basic Conditions of Employment Act (Act 75 of 1997), as amended, and the Employment Equity Act (Act 55 of 1998), as amended.
No. When they say remote, they mean remote within whatever country they're hiring for. Employment laws vary greatly from one country to the next. They will not just hire anyone from any country to fill a remote position because they would have to deal with all of the specific laws in South Africa just to employ you.
Article 11 prohibits slavery and forced and child labour; Article 17 grants freedom of association and the right to form unions; Article 18 permits the practice of lawful profession or occupation and to conduct any lawful trade or business; Article 25 grants equality before the law and prohibition of discrimination on ...