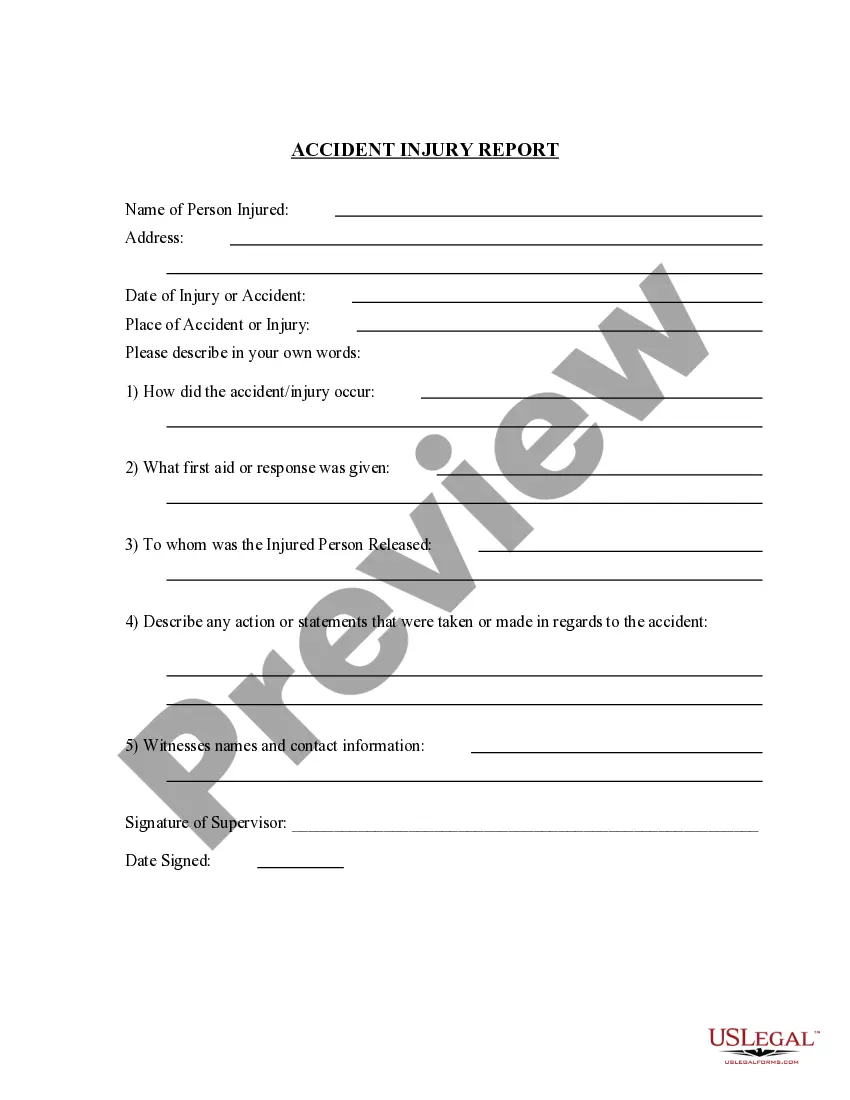
Accident With Trauma In Minnesota
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Blunt force trauma frequently occurs in auto accidents. It is usually due to an impact with the steering wheel or other object within the vehicle and can cause damage to the head, lungs, abdomen and chest.
During a car accident, a series of events can unfold that can cause lasting emotional trauma, including life-altering injuries, the threat of death, and the death of someone else. Emotional trauma is a natural response to such a dramatic chain of events. It is a function of the brain's complex survival mechanisms.
PTSD can develop immediately after the accident or even months or years later. Additionally, while some individuals find that their PTSD symptoms ease within a few days to a month, others might struggle with lasting effects that don't go away on their own and may need some help to work through.
(a) The driver of any motor vehicle involved in a collision the driver knows or has reason to know results in bodily injury to or death of another, or damage to any vehicle driven or attended by another, shall give the driver's name, date of birth, mailing address or email address, and the registration plate number of ...
Absolutely. Report the severe PTSD to the insurance reps, get an official diagnosis and official treatment, and if you have to get an accident lawyer to do it, make sure all treatment, both physical and mental health, comes out of the insurance of the at fault person.
To be able to make a PTSD claim, you need to be suffering PTSD due to someone else's negligence. You must also show that you have incurred financial loss as a direct result of this. If you can satisfy these two points, there's a good chance that you could make a claim for PTSD compensation.
Even minor accidents can lead to psychological distress and lingering trauma, such as: Mood swings, causing feelings of anger, frustration and guilt. High levels of stress and anxiety that don't go away. Difficulty sleeping, including insomnia and recurring nightmares.
Minnesota uses a comparative fault system and modified comparative negligence, meaning drivers cannot collect any damages from other parties if they are 51 percent or more at fault for the incident. You can recover damages if your fault does not exceed the other driver's.
In the event of a not-at-fault accident, meaning an accident you did not cause, the claim will be handled based on the state's fault laws. Remember that a not-at-fault accident and no-fault accidents are two separate things; not-at-fault accidents happen in both no-fault and tort states.