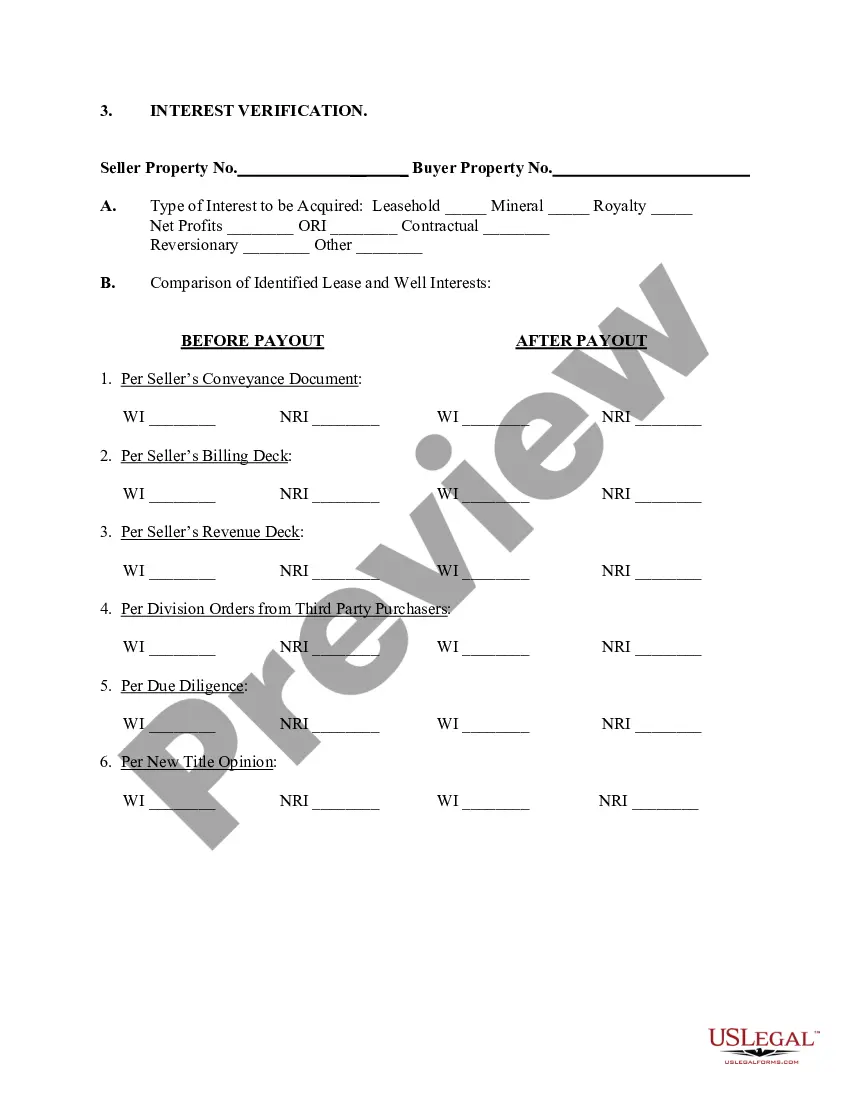
Payoff Statement Template With Ebitda In Texas
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
What Factors Influence EBITDA Multiples? Industry and Sector. Company Size and Market Position. Profitability and Margins. Growth Prospects. Risk Factors. Market Conditions and Sentiment. Competitive Landscape. M&A Activity.
EBITDA isn't normally included on a company's income statement because it isn't a metric recognized by Generally Accepted Accounting Principles as a measure of financial performance.
Small Inventory write-offs are typically expensed as COGS and therefore will negatively impact the EBITDA.
EBITDA (pronounced "ee-bit-dah") is a standard of measurement banks use to judge a business' performance. It stands for earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortisation.
EBITDA isn't normally included on a company's income statement because it isn't a metric recognized by Generally Accepted Accounting Principles as a measure of financial performance.
EBITDA = Operating Income + Depreciation + Amortization Being a non-GAAP computation, one can select which expense they want to add to the net income. For instance, if an investor wants to check how a company's financial standing can be affected by debt, they can exclude only depreciation and taxes.
Here's how to calculate EBITDA in Excel: Start a new Excel file and label the first worksheet "EBITDA". Input your company's figures for profit or loss, interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization. Use the formula: EBITDA=Net Income+Interest+TaxExpense+Depreciation/Amortization
EBITDA does not appear on income statements but can be calculated using income statements. Gross profit does appear on a company's income statement. EBITDA is useful in analysing and comparing profitability. Gross profit is useful in understanding how companies generate profit from the direct costs of producing goods.
Each taxable entity formed as a corporation, limited liability company (LLC), limited partnership, professional association and financial institution that is organized in Texas or has nexus in Texas must file Form 05-102, Texas Franchise Tax Public Information Report (PIR) annually to satisfy their filing requirements.
How Are Texas LLCs Taxed? If you own a single-member LLC, it will be taxed as a sole proprietorship (aka “disregarded entity”) by default. If you have multiple LLC members, you'll be taxed as a partnership by default.