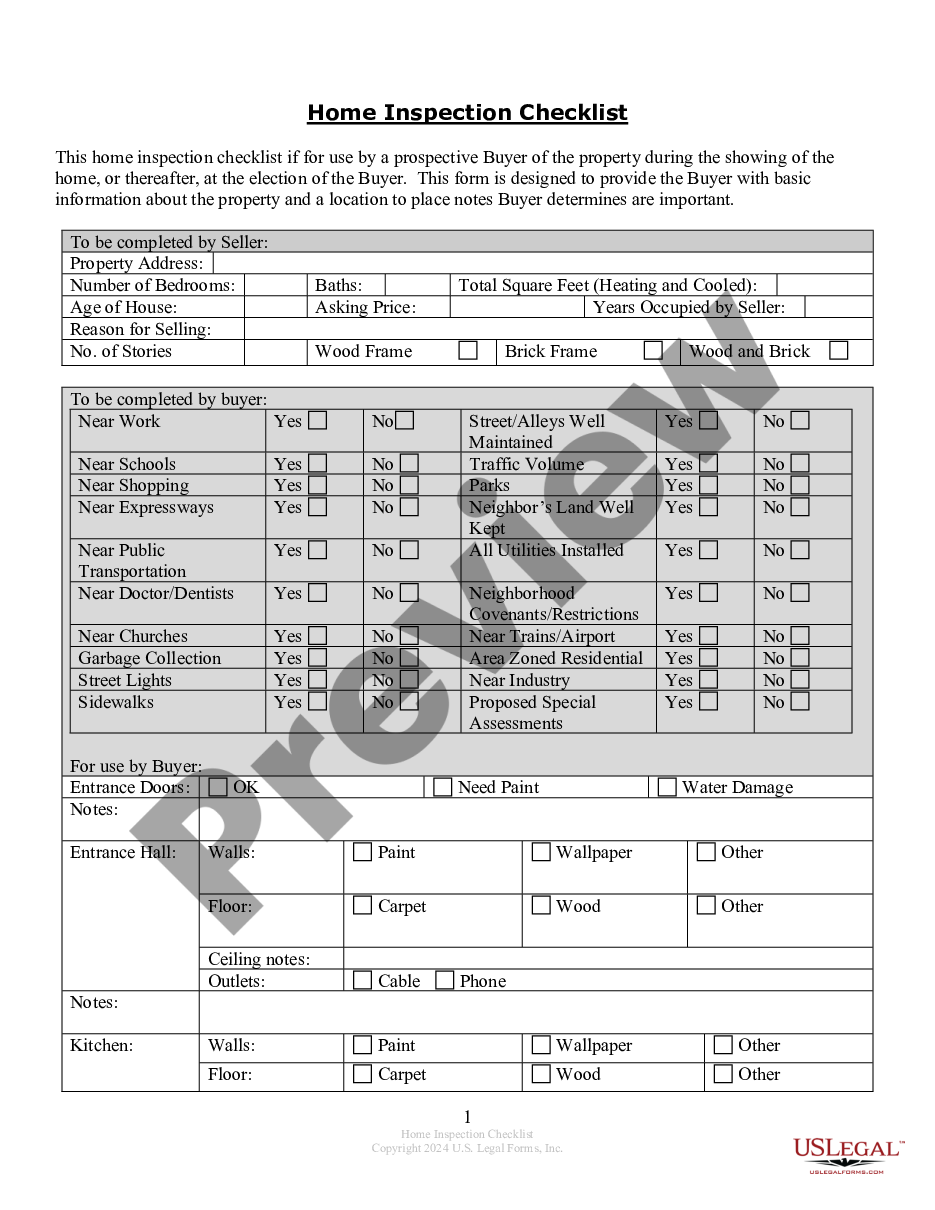
Extension Time In Pcr In Franklin
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
For qPCR, the target length is closer to 100 bp and for standard PCR, it is near 500 bp. If you know the positions of each primer with respect to the template, the product is calculated as: Product length = (Position of antisense primer-Position of sense primer) + 1.
Extension Time Extensions are normally performed at 68°C. As a general rule, use extension times of one minute per 1000 base pairs (e.g. 3 minutes for a 3 kb product) For products less than 1 kb, use 45-60 seconds. Products greater than 3 kb, or reactions using more than 30 cycles, may require longer extensions.
Elongation. The temperature for elongation depends on the polymerase used, with 68-72°C being most commonly used. The length of the amplicon is taken into account when determining the time needed for the elongation step with a general rule of thumb of 1 minute per kb to be synthesized.
How to Calculate PCR Test Hours? First, determine the total number of tests (T). Next, determine the time per test (t) in hours. Next, determine the number of testing machines (M). Finally, calculate the PCR test hours using the formula H = (T t) / M.
The extension time of PCR depends upon the synthesis rate of DNA polymerase and the length of target DNA. The typical extension time for Taq DNA Polymerase is 1 min/kb, whereas that of Pfu DNA polymerase is 2 min/kb.
Extension Time Extensions are normally performed at 68°C. As a general rule, use extension times of one minute per 1000 base pairs (e.g. 3 minutes for a 3 kb product) For products less than 1 kb, use 45-60 seconds. Products greater than 3 kb, or reactions using more than 30 cycles, may require longer extensions.
Elongation. The temperature for elongation depends on the polymerase used, with 68-72°C being most commonly used. The length of the amplicon is taken into account when determining the time needed for the elongation step with a general rule of thumb of 1 minute per kb to be synthesized.
If the annealing temperature is too low, non-specific products can be generated, leading to smeared bands on the gel. If the extension time is too long, secondary products can be formed, which can contribute to smearing.
Step 2, annealing: the temperature is lowered to enable the DNA primers to attach to the template DNA. Step 3, extending: the temperature is raised again and the new strand of DNA is made by the Taq polymerase enzyme. These three stages are repeated 20-40 times, doubling the number of DNA copies each time.
Extension is achieved by using the loosened nucleotides of each base to grow the complementary DNA strand. The end result is two double-stranded products of DNA. The temperature that is used during the extension phase is dependent on the DNA polymerase that is used.