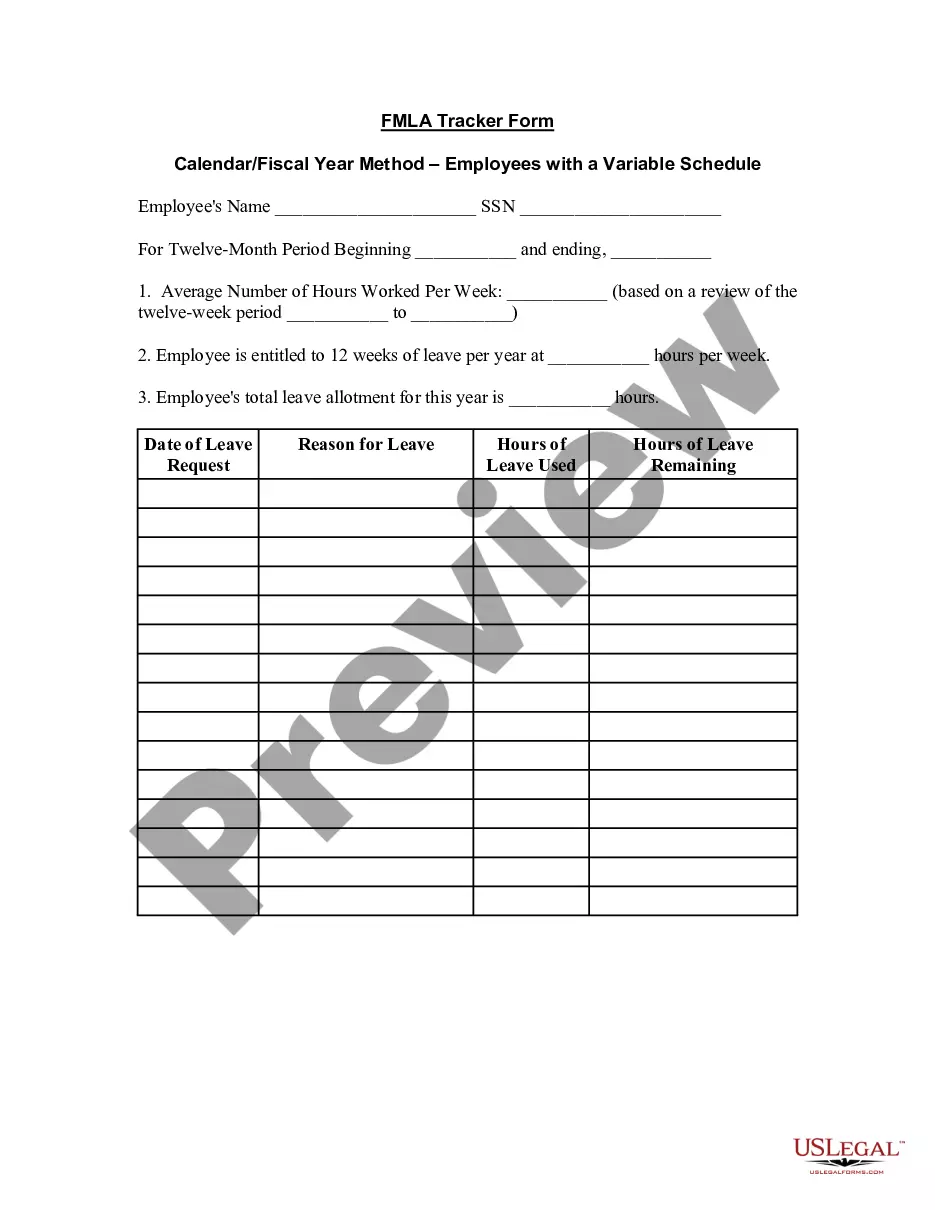
Contract Law Without Foundations In Montgomery
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
A contract is an agreement between parties, creating mutual obligations that are enforceable by law. The basic elements required for the agreement to be a legally enforceable contract are: mutual assent, expressed by a valid offer and acceptance; adequate consideration; capacity; and legality.
Mutual assent, expressed through a valid offer and acceptance, lies at the foundation. Both parties must clearly understand and agree to the terms outlined in the contract. Additionally, consideration, or something of value exchanged between the parties, must be present to support the contract's validity.
The contract is initially an agreement when the person to whom the offer is made indicates his acceptance of the same. In other words, an agreement is the foundation of a contract.
In contract law, legal purpose is the requirement that the object of, or reason for, the contract must be legal. There must be a legal reason and purpose for the contract to be implemented; for example, the policyowner must have an insurable interest in the insured.
A legally enforceable contract must include an offer, acceptance, consideration, capacity, legality, and mutual assent. Understanding different types of contracts and situations where they may be deemed unenforceable is key to navigating contract law.
The basic elements required for the agreement to be a legally enforceable contract are: mutual assent, expressed by a valid offer and acceptance; adequate consideration; capacity; and legality.
To understand that, you need to know about the 5 essential elements of a valid contract: offer, acceptance, consideration, mutual intent, capacity and legality. Understanding these 5 fundamental elements of a contract can help you protect your interests and avoid potential legal disputes.
The main principles which govern: •entry into a contract •the terms of a contract; the principal policies and values underpinning contract rules; existing areas of debate about what the law is and what it ought to be.
A person may file a claim for breach of contract in any court with proper venue and jurisdiction unless the contract states where the claim should be filed. Generally, any civil court of general jurisdiction would have jurisdiction over a lawsuit alleging breach of contract.
If you decide to pursue a claim for breach of contract, you will need evidence of the breach. It is therefore crucial to collate and retain all relevant evidence. You should take photographs of any defective goods as soon as they are received. If possible, speak to witnesses and make a note of their recollection.