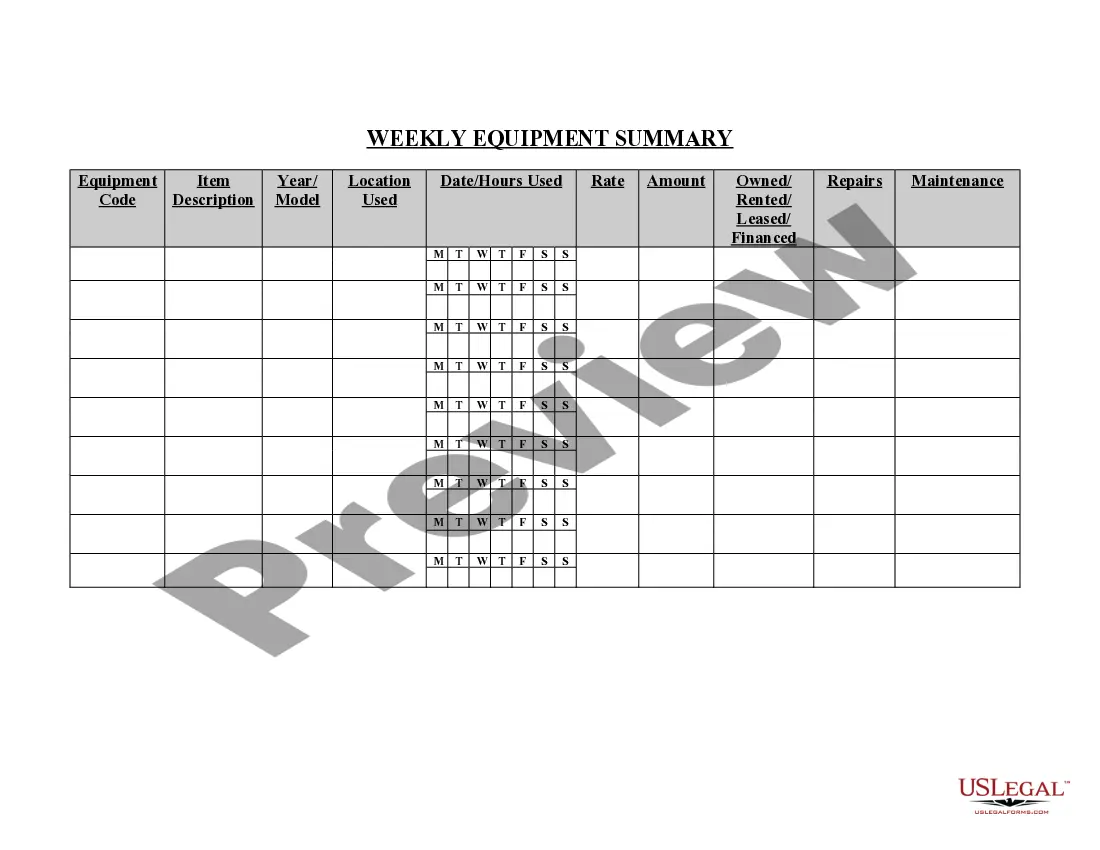
Contract Law For Dummies In Massachusetts
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
To form a contract, the parties must mutually agree to the terms and conditions of their promises. This is often referred to as “mutuality” or a “meeting of the minds.” When an agreement is mutual, it means that the parties communicated to each other their agreement to the same terms and conditions.
A contract is an agreement between parties, creating mutual obligations that are enforceable by law. The basic elements required for the agreement to be a legally enforceable contract are: mutual assent, expressed by a valid offer and acceptance; adequate consideration; capacity; and legality.
To be legally binding a contract must include an offer, acceptance, and consideration. The contract should be in writing. There is no requirement for the involvement of a third person.
There are four essential elements of forming a contract: offer, acceptance, consideration, and intention to create legal relations. Beyond this, the terms of the contract must also be unambiguous, and the parties must have the mental capacity to agree.
7 Essential Elements of A Contract Offer. For there to be a contract, there must first be an offer by one party and an acceptance by the other. Acceptance. Acceptance is the agreement to the specific conditions of an offer. Consideration. Intention to create legal relations. Authority and capacity. Certainty.
Both parties must clearly understand and agree to the terms outlined in the contract. Additionally, consideration, or something of value exchanged between the parties, must be present to support the contract's validity. Moreover, legality and the capacity of the parties involved are essential components to consider.
To understand that, you need to know about the 5 essential elements of a valid contract: offer, acceptance, consideration, mutual intent, capacity and legality. Understanding these 5 fundamental elements of a contract can help you protect your interests and avoid potential legal disputes.
To be legally enforceable, an agreement must contain all of the following criteria: An offer and acceptance; Certainty of terms; Consideration; An intention to create legal relations; Capacity of the parties; and, Legality of purpose.
Lesson Summary. A contract is a legal agreement between two or more parties in which they agree to each other's rights and responsibilities. Offer, acceptance, awareness, consideration, and capacity are the five elements of an enforceable contract.
A contract is a legally binding agreement between parties to create mutual obligations that businesses and individuals use to protect their interests. Contracts outline the specific terms of engagement for a transaction. They can also dictate legal consequences if a party tries to break the agreement.