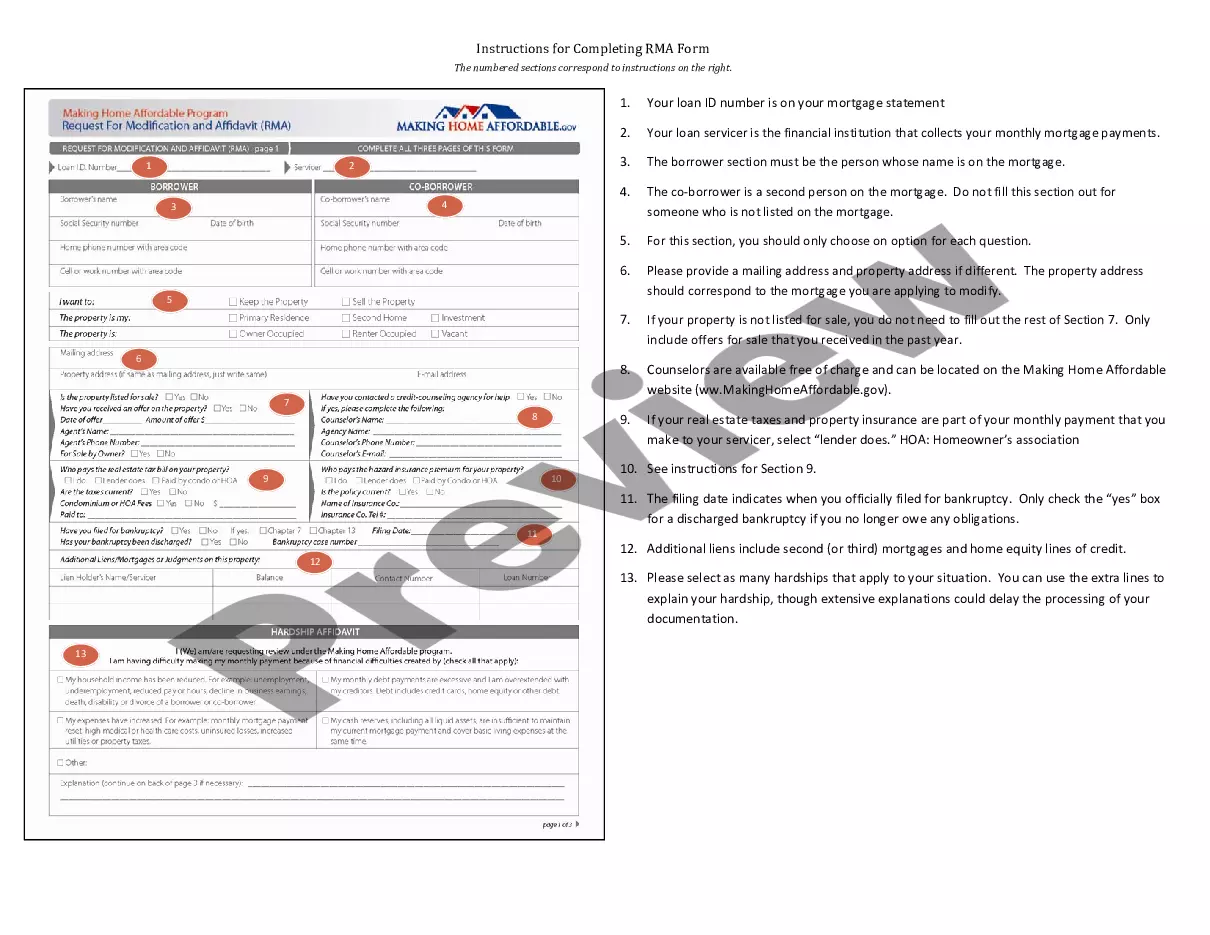
Simple Agreement For Future Equity Template In Suffolk
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
A SAFE is an investment contract between a startup and an investor that gives the investor the right to receive equity of the company on certain triggering events, such as a: Future equity financing (known as a Next Equity Financing or Qualified Financing), usually led by an institutional venture capital (VC) fund.
An SAFT is an investment contract between investors who provide capital and developers who issue the s after specific conditions are met. An SAFE is a contract where investors provide capital in exchange for equity in a company at a future date.
Introduced by Y Combinator in 2013, the Simple Agreement for Future Equity (SAFE) has become the go-to structure for pre-seed and seed-stage startups looking to raise capital fast and with minimal legal friction. But while SAFE notes are often considered founder-friendly, they're not without trade-offs.
A simple agreement for future equity (SAFE) is a financing contract that may be used by a startup company to raise capital in its seed financing rounds. The instrument is viewed by some as a more founder-friendly alternative to convertible notes.
The Discount Rate is calculated as 100% minus the percent discount the SAFE investors are entitled to. For example, if SAFE investors are entitled to a discount of 20% (they can buy Standard Preferred Stock 20% cheaper than subsequent investors), the Discount Rate is 80% = 100% - 20%.
An equity discount rate range of 12% to 20%, give or take, is likely to be considered reasonable in a business valuation. This is about in line with the long-term anticipated returns quoted to private equity investors, which makes sense, because a business valuation is an equity interest in a privately held company.
They are accounted for as equity on the balance sheet. When the Simple Agreement for Future Equity converts to preferred stock, the accounting entries are that the SAFE entry is removed and the amount is credited to preferred equity (ignoring any APIC implications).
The SAFE discount is derived by dividing the valuation cap by the typical equity financing valuation and then removing that value from one (representing no discount). In this case, $2 million / $4 million = 0.5 and 1 – 0.5 = 0.5 would be the mathematical representations. Discounts often vary from 0% to 20%.
For example, if a SAFE has a valuation cap of $10 million, and your startup's next financing round values the company at $15 million, the SAFE investor's equity will be calculated based on the $10 million cap, not the $15 million valuation.
An equity discount rate range of 12% to 20%, give or take, is likely to be considered reasonable in a business valuation. This is about in line with the long-term anticipated returns quoted to private equity investors, which makes sense, because a business valuation is an equity interest in a privately held company.