Workplace Discrimination In The Philippines In Clark
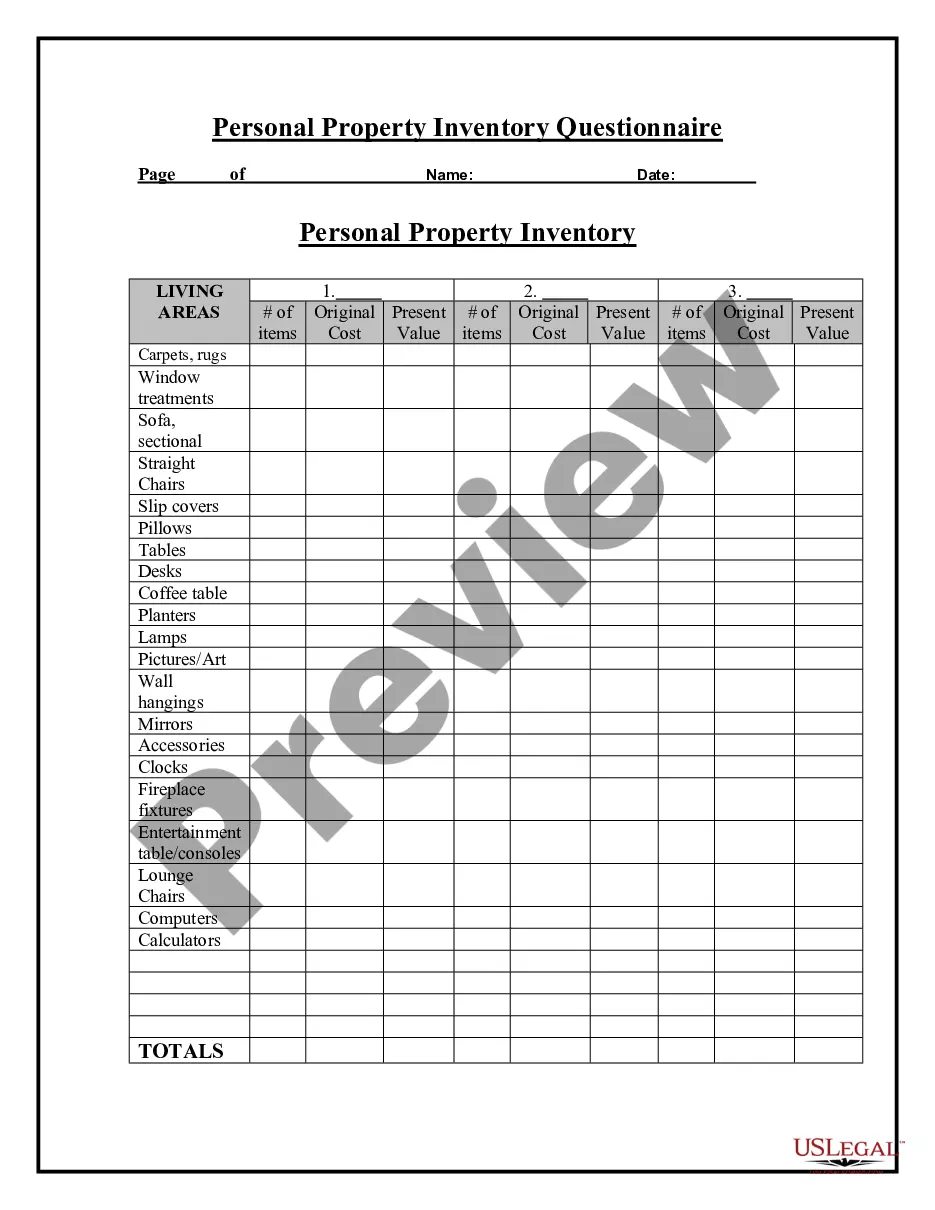
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
SEC. 7. Penalty. – Any violation of this Act shall be punished with a fine of not less than fifty thousand pesos (P50,000.00) but not more than five hundred thousand pesos (P500,000.00), or imprisonment of not less than three (3) months but not more than two (2) years, or both, at the discretion of the court.
Examples of Employment Discrimination Failure to hire. Harassment. Quid pro quo: Conditioning employment or promotion on sexual favors. Hostile Work Environment: Continuous actions and comments based on protected characteristics that create an uncomfortable and hostile workplace. Job assignment. Compensation.
The Labor Code of the Philippines is a legal code that establishes labour practices and employment standards, including hiring, working conditions, wages, and employee benefits, to protect workers' rights.
However, discrimination is a state of mind and, therefore, notoriously hard to prove. Sophisticated employers are well aware that discrimination is illegal. Thus, most cases are established through circumstantial evidence.
A written complaint to OSPI must include the following information: A description the conduct or incident—use facts (what, who and when) An explanation of why you believe unlawful discrimination has taken place. Your name and contact information, including a mailing address.
Employees have the legal right to file complaints against former employers for violations of labor laws. Complaints can be filed with DOLE or the NLRC, depending on the nature of the dispute. Proper documentation and timely filing are essential to ensure that employees' rights are upheld under Philippine labor law.
282 Termination by Employer. — An employer may terminate an employment for any of the following causes: (a) Serious misconduct or willful disobedience by the employee of the lawful orders of his employer or representative in connection with his work.
2. Government Agencies and Jurisdictions A. Department of Trade and Industry (DTI) B. National Labor Relations Commission (NLRC) C. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) D. Environmental Management Bureau (EMB) E. Office of the Ombudsman. A. Consumer Complaints. B. Labor Complaints. C. Corporate Misconduct.
Basic rules keep your letter to the point. You need to give enough detail for your employer to be able to investigate your complaint properly. keep to the facts. never use abusive or offensive language. explain how you felt about the behaviour you are complaining about but don't use emotive language.
Employers are also required to provide fair wages and benefits, safe and healthy working conditions, and access to social security and other benefits. Additionally, workers are protected against discrimination, harassment, and forced labor.