Attorney Suing Client For Fees In Utah
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
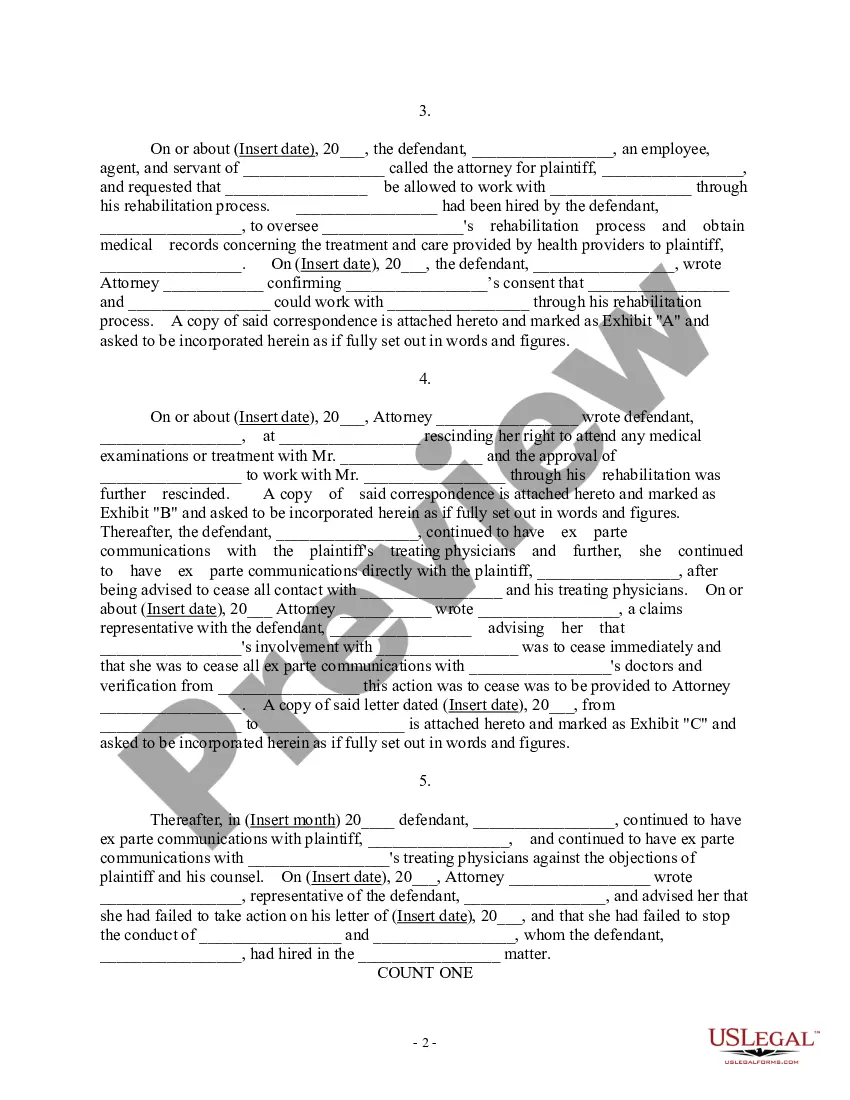
Code of Civil Procedure § 1021 codifies what is often called the "American Rule" of attorney's fees, the rule that says unless otherwise provided by statute, the measure and manner of paying attorney fees is left to the agreement of the parties.
In the U.S., each party in a legal case typically pays for their own attorney fees, under a principle known as the American rule.
Deciding whether to sue a client for unpaid fees and expenses requires a careful and in-depth analysis of the risks and benefits of bringing such a claim. Attorneys should be wary of the risk of a malpractice counterclaim, as well as the financial risks associated with a collection suit.
Attorney's fees (or attorneys' fees) Attorney's Fees/Attorneys' Fees, or Attorney fees are the amounts billed to a client for legal services performed on their behalf. Attorney fees may be hourly, contingent, flat, or hybrid. Nonrefundable fees are prohibited in some states.
Average Lawyer Hourly Rates by State StateAverage Hourly Rate 2023Average Hourly Rate 2022 Arkansas $242 $248 California $344 $358 Colorado $261 $271 Connecticut $342 $35047 more rows
How to Collect Court-Awarded Attorney Fees Step 1: Understand Your Judgment. Step 2: Locate the Debtor and Their Assets. Step 3: Determine the Best Method of Collection. Step 4: Initiate the Collection Process. Step 5: Enforce the Collection. Step 6: Address Any Challenges. Step 7: Complete the Collection and Close the Case.