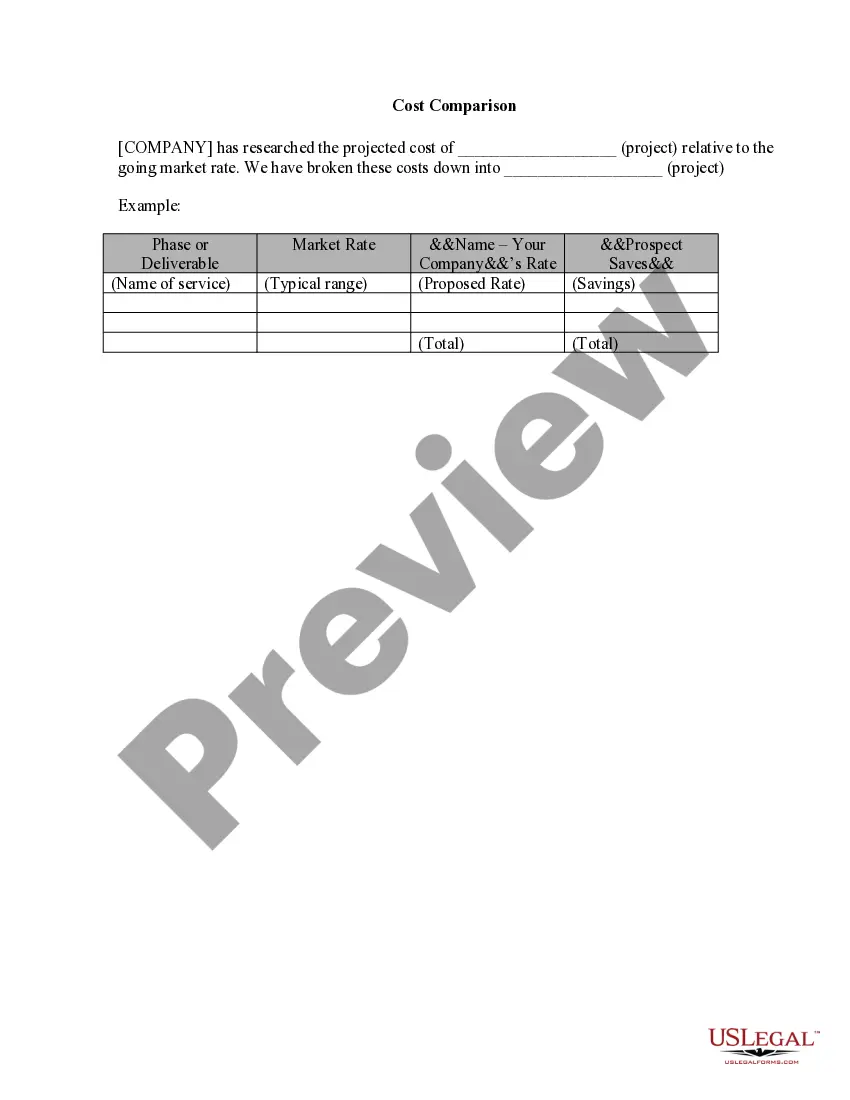
This is a multi-state form covering the subject matter of the title.
Pregnancy Discrimination At Work Examples In King
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Pregnancy has been a protected class for a while in the United States. The PWFA went into effect on June 27, 2023. On April 15, 2024 the EEOC issued its final regulation to carry out the law. So, no. US employers are not allowed to deny employment if you are pregnant IF YOUR EMPLOYER HAS MORE THAN 15 EMPLOYEES.
Average Pregnancy Discrimination Settlement in California Complexity of CaseAverage California Pregnancy Discrimination Settlement Minor Approximately: $50,000 – $100,000 Moderate Approximately: $100,000 – $250,000 High Approximately: $250,000 – $1,000,000
If your employer treats you unfavourably because of your pregnancy, for example, by ending your contract, extending your probation period, taking account of pregnancy-related sickness or suddenly raising performance issues that had not previously been mentioned, you are protected by pregnancy discrimination law.
Proving pregnancy discrimination requires more than a victim's claim. There must be evidence that the employer acted against the individual exclusively based on their pregnancy. That evidence must be clear, inarguable, and documented.
Violations have involved a variety of fact patterns, including: refusing to hire, failing to promote, demoting, or firing pregnant workers after learning they are pregnant; discharging workers who take medical leave for pregnancy-related conditions (such as a miscarriage);
Proving pregnancy discrimination requires more than a victim's claim. There must be evidence that the employer acted against the individual exclusively based on their pregnancy. That evidence must be clear, inarguable, and documented.
Proving pregnancy discrimination requires more than a victim's claim. There must be evidence that the employer acted against the individual exclusively based on their pregnancy. That evidence must be clear, inarguable, and documented.
To successfully win a pregnancy discrimination claim, an employee must provide evidence showing that her pregnancy was a substantial motivating reason for an adverse employment (such as a demotion, a write up and, of course, a termination) and that other employees in similar situations were treated differently.
Violations have involved a variety of fact patterns, including: refusing to hire, failing to promote, demoting, or firing pregnant workers after learning they are pregnant; discharging workers who take medical leave for pregnancy-related conditions (such as a miscarriage);