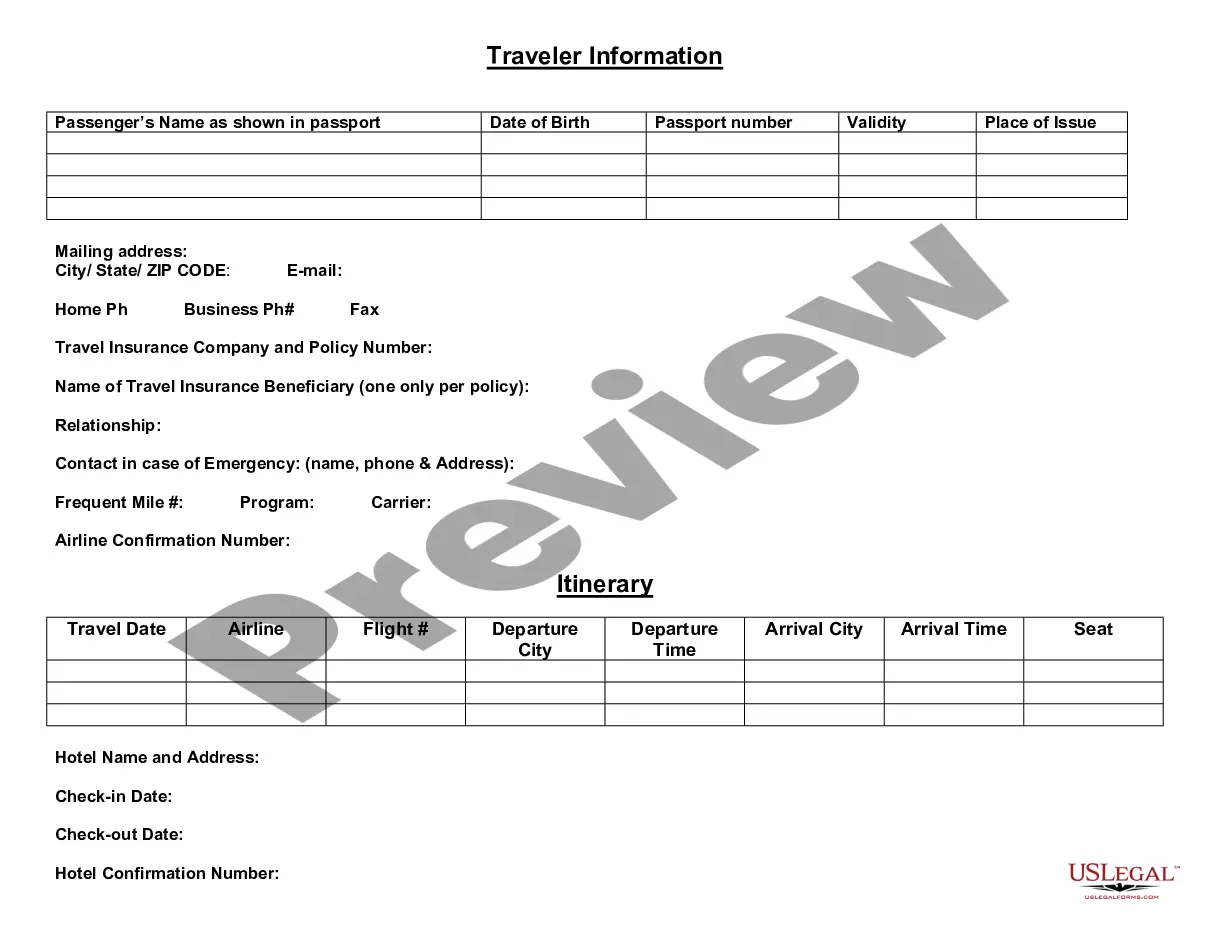
This form is a Petition For Writ Of Habeas Corpus By Person In State Custody based on Lack of Voluntariness of confession and Ineffective Assistance of Counsel. Adapt to your specific circumstances. Don't reinvent the wheel, save time and money.
Petition For Writ Of Habeas Corpus (form Hc-001) In San Diego
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
The "Great Writ" of habeas corpus is a fundamental right in the Constitution that protects against unlawful and indefinite imprisonment. Translated from Latin it means "show me the body." Habeas corpus has historically been an important instrument to safeguard individual freedom against arbitrary executive power.
All prisoners may file a writ of habeas corpus. However, judges receive a flood of habeas corpus petitions each year, including some that inmates prepare without the assistance of a lawyer. Strict procedures govern which petitions judges may consider.
Today, habeas corpus is mainly used as a post-conviction remedy for state or federal prisoners who challenge the legality of the application of federal laws that were used in the judicial proceedings that resulted in their detention.
The court must rule on a petition for writ of habeas corpus within 60 days after the petition is filed. (B) If the court fails to rule on the petition within 60 days of its filing, the petitioner may file a notice and request for ruling.
Habeas Corpus petitions are filed in a California court by inmates or, more specifically, their attorneys, claiming they have been unlawfully detained or imprisoned. It is considered a last legal resort after other legal remedies and appeals have been exhausted.
Habeas corpus is one of the earliest common law writs. In its simplest form a writ of habeas corpus requires that a person who is in custody be brought before a judge or court and that they be able to challenge that custody. The writ of habeas corpus is used to attack an unlawful detention or illegal imprisonment.
(a) Writs of habeas corpus may be granted by the Supreme Court, any justice thereof, the district courts and any circuit judge within their respective jurisdictions. The order of a circuit judge shall be entered in the records of the district court of the district wherein the restraint complained of is had.
State every ground (reason) that supports your claim that you are being held in violation of the Constitution, laws, or treaties of the United States. Attach additional pages if you have more than four grounds. State the facts supporting each ground. Any legal arguments must be submitted in a separate memorandum.
For example, if an individual was convicted on the basis that their skin color matched that of the perpetrator ing to eyewitnesses, but there is no other evidence against them, then the individual can appeal for habeas corpus in order to be freed from imprisonment.
If an inmate meets all the requirements to file a petition for writ of habeas corpus, they will file their petition in the superior court in the court of conviction. Within 60 days, the court will review the petition to determine if the inmate raised a prima facie case entitling them to relief.