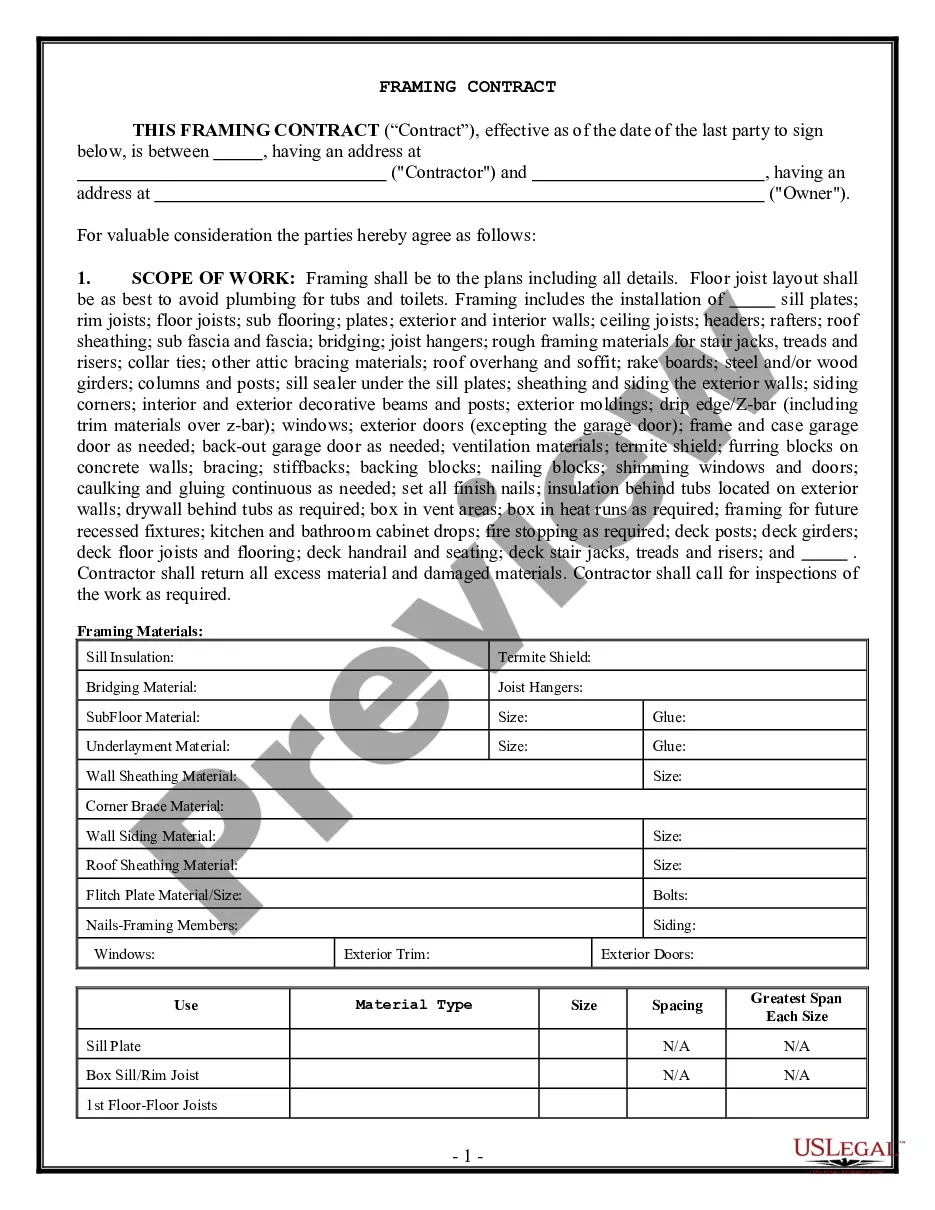
Tort Negligence Liability For Dummies In Michigan
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
When someone fails to exercise an expected degree of care, and that failure results in an injury, that person is said to be negligent. Michigan negligence laws recognize "comparative negligence," in which recovery of damages is reduced proportionately to the plaintiff's own negligence.
A tort is a civil wrong that leads to physical harm, damage to property, or damage to reputation. The four key elements of a tort claim are duty, breach of duty, causation, and damages. In order to hold someone liable for a tort, you must be able to demonstrate that all four of these elements exist.
Personal injury tort liability occurs when a person's negligent or intentional actions cause harm or injury to another individual. In these cases, the injured party may be entitled to compensation for medical expenses, lost wages, pain and suffering, and other damages.
Most civil lawsuits for injuries allege the wrongdoer was negligent. To win in a negligence lawsuit, the victim must establish 4 elements: (1) the wrongdoer owed a duty to the victim, (2) the wrongdoer breached the duty, (3) the breach caused the injury (4) the victim suffered damages.
No person can be held liable in tort unless the act or omission with which he or she is charged was a breach of a duty owing by that person to the plaintiff or to a class to which the plaintiff belongs, and the plaintiff has suffered individual damage therefrom.
Damage to your car (include your license plate where possible in the photo so it can be confirmed that you are the registered/titled owner of the vehicle) The at-fault driver's proof of auto insurance card. The at-fault driver's driver's license. The license plate of the vehicle that the at-fault driver was driving.
Tort liability is predicated on the existence of proximate cause, which consists of both: (1) causation in fact, and (2) foreseeability. A plaintiff must prove that his or her injuries were the actual or factual result of the defendant's actions.
In tort states, drivers must carry liability insurance to cover the property damage and injuries they cause to others in an accident. Tort states do not require drivers to carry additional coverages, like personal injury protection and medical payments coverage.