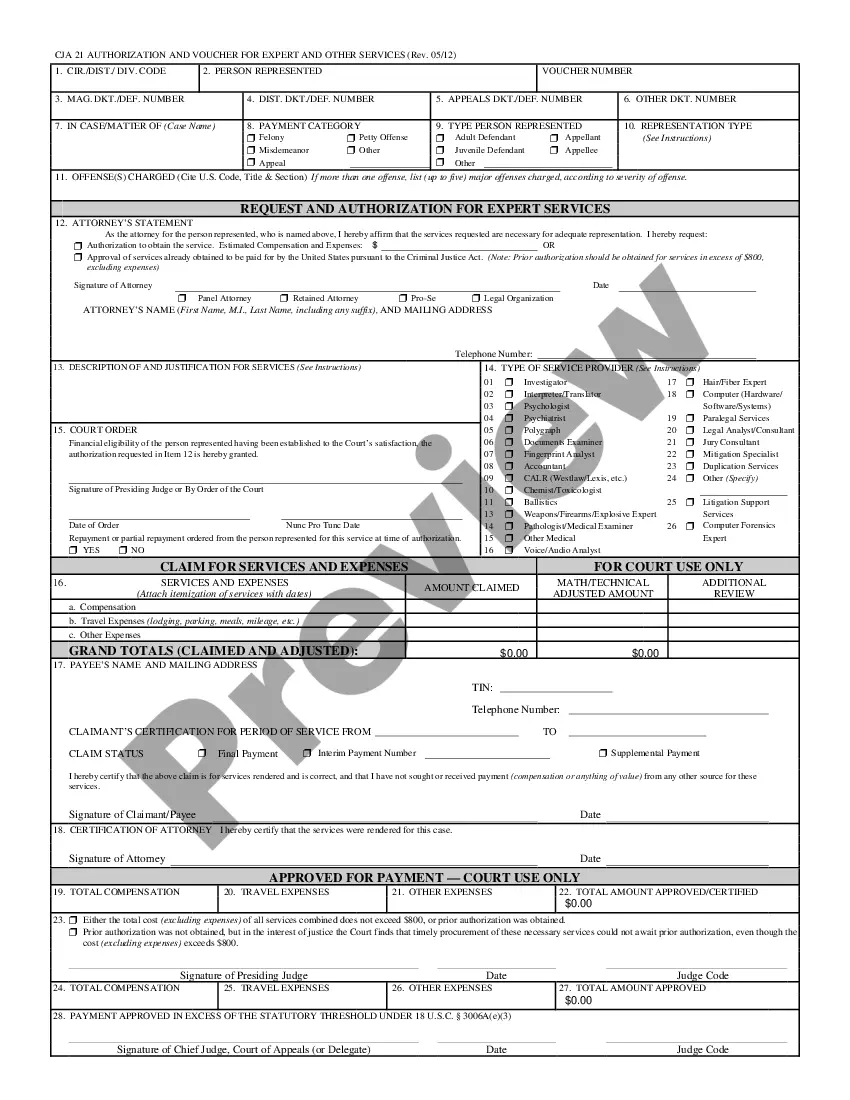
Types Of Torts In Kenya In King
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Tort law in Kenya encompasses a wide range of legal principles and rules that provide remedies to individuals who have suffered harm or injury due to the wrongful actions of others.
A negligence claim requires that the person bringing the claim (the plaintiff) establish four distinct elements: duty of care, breach, causation, and damages.
Torts fall into three general categories: Intentional torts (e.g., intentionally hitting a person); Negligent torts (e.g., causing an accident by failing to obey traffic rules); and. Strict liability torts (e.g., liability for making and selling defective products - see Products Liability).
The Four Elements of a Tort The accused had a duty, in most personal injury cases, to act in a way that did not cause you to become injured. The accused committed a breach of that duty. An injury occurred to you. The breach of duty was the proximate cause of your injury.
Four of them are personal: assault, battery, intentional infliction of emotional distress, and false imprisonment. The other three are trespass to chattels, trespass to property, and conversion.
Torts fall into three general categories: Intentional torts (e.g., intentionally hitting a person); Negligent torts (e.g., causing an accident by failing to obey traffic rules); and. Strict liability torts (e.g., liability for making and selling defective products - see Products Liability).
Tort requires a wrongful act, legal damage, and a legal remedy for a civil action. The absence of any of these elements means no tort has occurred.
The Four Elements of a Tort The accused had a duty, in most personal injury cases, to act in a way that did not cause you to become injured. The accused committed a breach of that duty. An injury occurred to you. The breach of duty was the proximate cause of your injury.
Four of them are personal: assault, battery, intentional infliction of emotional distress, and false imprisonment. The other three are trespass to chattels, trespass to property, and conversion.
A tort is an act or omission that causes legally cognizable harm to persons or property. Tort law, in turn, is the body of rules concerned with remedying harms caused by a person's wrongful or injurious actions.