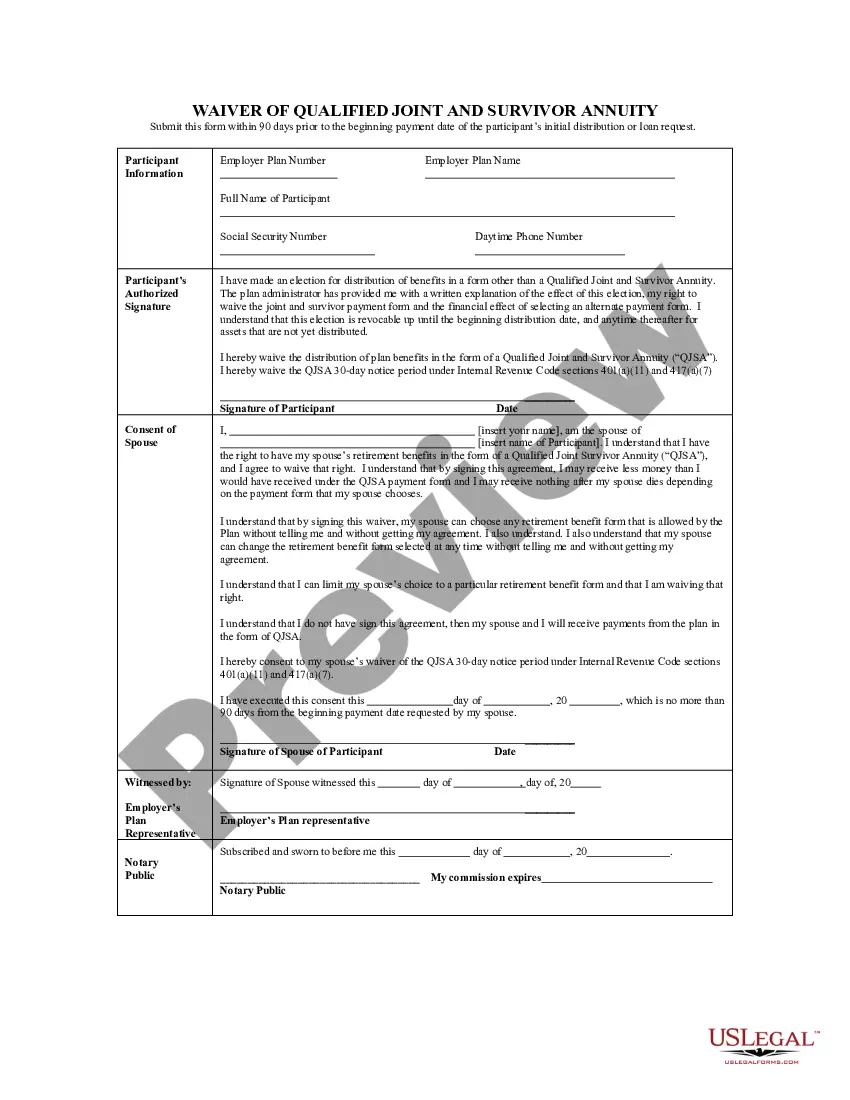
Types Of Torts In Canada In Bexar
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
While mass tort claims can be incredibly effective, they can also take years to reach a settlement or go through the trial process. Mass tort claims can take anywhere from a few weeks to a few years.
What is a Tort Claim? A tort is a wrongful act or the failure to act resulting in injury to another person. If the injured party can prove the act or omission was the result of negligence, courts can award compensation in an effort to make the victim whole again.
In the vast majority of tort cases, litigants settled the complaint without going to trial. Therefore, details of tort settlements are unknown.
To file a claim, complete these steps: Complete Standard Form 95. Explain in detail what happened, using additional pages if necessary. Attach all documents that support your claim, which may include the following. Submit the completed Standard Form 95 and supporting documents to the OPM Office of the General Counsel.
Torts fall into three general categories: Intentional torts (e.g., intentionally hitting a person); Negligent torts (e.g., causing an accident by failing to obey traffic rules); and. Strict liability torts (e.g., liability for making and selling defective products - see Products Liability).
Negligence is by far the most common type of tort. Negligence occurs when a person fails to act carefully enough and another person gets hurt as a result. For this type of case, a person must owe a duty to another person. Then, they must fail in their duty to act reasonably.
Generally, intentional torts are harder to prove than negligence, since a plaintiff must show that the defendant did something on purpose.
The time frame for these cases varies for each situation. However, you can generally expect them to take years to fully resolve, with some mass tort lawsuits lasting for decades. A mass tort lawsuit lawyer can help you review the factors that impact the length of these legal claims.
More simply, a tort claim is a right to sue an individual or entity to recover damages for injuries caused by their actions. It's a civil action where an injured party, the plaintiff, can sue the responsible party, the defendant, to recover damages. Damages in tort cases can be both economic and non-economic.
What is Tort Law in Canada? Torts are roughly equivalent to extra-contractual civil liability in civil law . While common law and civil law often have practical similarities, there are significant theoretical differences. Torts can be understood as legal wrongs that result in civil liability.