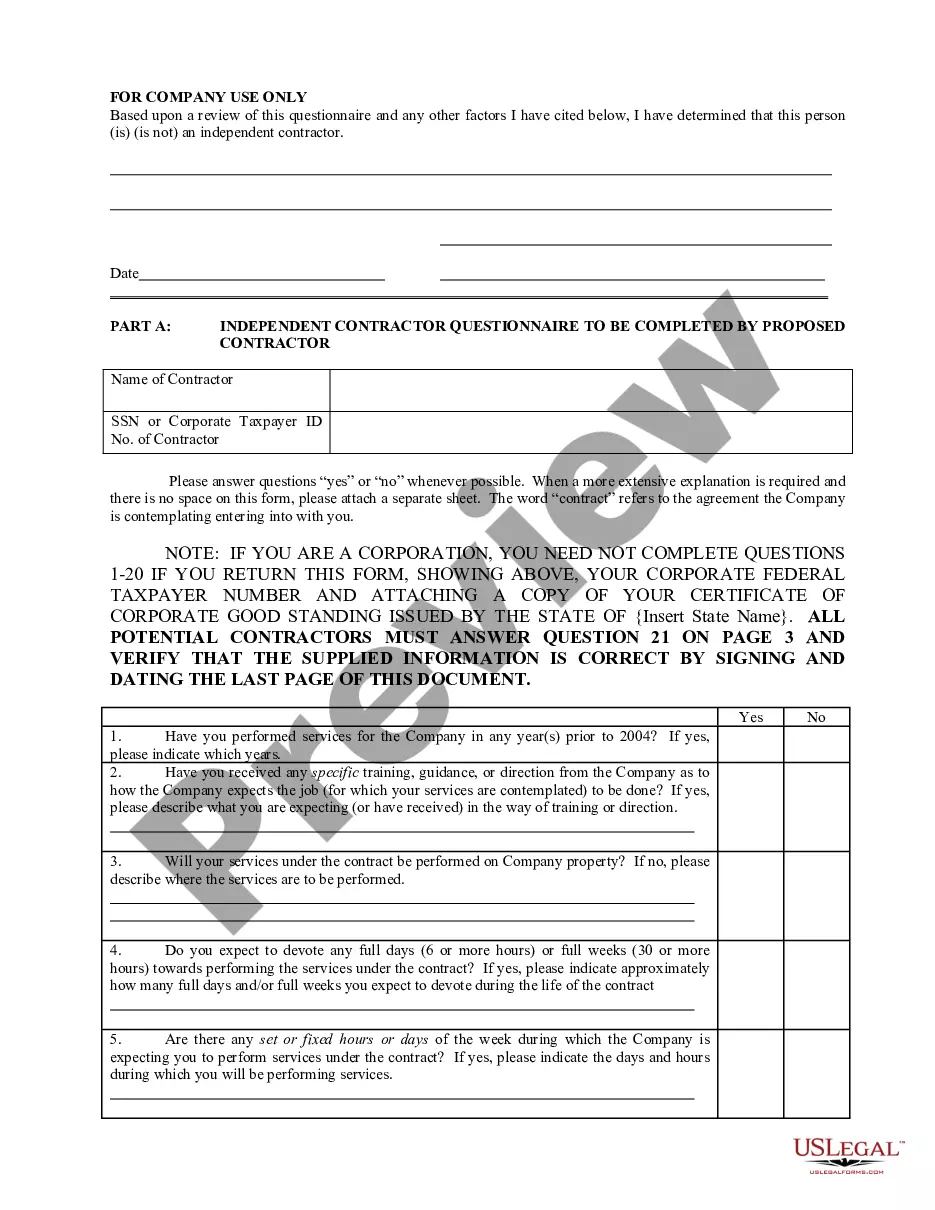
Bona Fide Purchaser With Notice
Description
How to fill out Texas Contract For Deed Notice Of Default By Seller To Purchaser Where Purchaser Paid 40 Percent Or Made 48 Payments?
- Log in to your account if you're an existing user, and download the desired template by clicking the Download button. Ensure your subscription is current; renew it if necessary.
- For new users, start by reviewing the Preview mode and detailed form description to select the appropriate template that aligns with your local jurisdiction.
- If adjustments are needed, utilize the Search tab to find alternative templates that suit your requirements.
- Proceed to purchase the document by clicking the Buy Now button, then select your preferred subscription plan. You'll need to create an account for full access.
- Complete your transaction by providing payment information, either via credit card or PayPal.
- Finally, download your form and save it for completion. Access it anytime from the My Forms section of your profile.
By following these steps, you will leverage the benefits of US Legal Forms, which offers a robust collection of forms, a user-friendly interface, and access to expert legal assistance, ensuring your documents are both accurate and compliant.
Start simplifying your legal documentation process today with US Legal Forms and ensure your legal needs are met efficiently!
Form popularity
FAQ
The bona fide purchaser doctrine safeguards those who buy property without knowledge of any existing claims or defects. This legal principle ensures that purchasers are treated fairly when they follow proper procedures, such as conducting due diligence before acquisition. It's vital for individuals entering real estate transactions to understand this doctrine, as it plays a significant role in securing their rights.
The key elements of a bona fide purchaser with notice include paying a valuable consideration, acquiring property in good faith, and having no actual notice of outstanding claims. Furthermore, the purchaser must also demonstrate that they acted without negligence in their inquiry. These components establish a solid foundation for the defense of the purchaser's rights in land dealings.
A party that has actual notice of a claim or defect in the title cannot be protected as a bona fide purchaser with notice. Additionally, a party who is a close relative of the seller may be denied this protection. Thus, it is essential to conduct thorough due diligence to identify potential issues. Understanding these limitations helps you navigate the complexities of land transactions.
A bona fide purchaser is someone who buys property in good faith, without knowledge of any existing claims or defects in the title. To achieve this, they must conduct their due diligence, which includes obtaining necessary notices and understanding the surrounding circumstances. For those entering the real estate market, ensuring you qualify as a bona fide purchaser with notice can greatly impact your ownership rights and security.
Inquiries in real estate refer to the process of questioning or investigating information related to property ownership, rights, or claims. Buyers often need to make inquiries to ensure that they have a clear title and to identify any possible issues. For a bona fide purchaser with notice, making thorough inquiries is essential to safeguard their investment and rights in the property.
Inquiry notice refers to a legal concept where a person is presumed to have knowledge of any facts that a reasonable investigation would have revealed. This means that if you are a bona fide purchaser with notice, and there are obvious signs indicating potential claims or interests, you are expected to investigate. This concept protects the interests of existing claimants and emphasizes the importance of due diligence in property transactions.
Inquiry notice and actual notice serve different purposes in property law. Actual notice refers to explicit awareness of rights or claims, while inquiry notice suggests a responsibility to investigate further due to circumstances that could alert a reasonable person. For a bona fide purchaser with notice, recognizing this difference can impact the security of their property title and ownership claims.
The three types of notices are actual notice, constructive notice, and inquiry notice. Each plays a crucial role in real estate transactions. Actual notice involves direct knowledge of a fact, constructive notice occurs through legal means or public records, and inquiry notice arises when a reasonable person should investigate further. Understanding these types of notice is essential for a bona fide purchaser with notice.
A notice jurisdiction is a legal area where the laws recognize types of notice that affect property ownership. An example is a state that enforces constructive notice through record-keeping, meaning once a deed is recorded, it becomes public knowledge. Understanding the rules of notice jurisdiction helps a bona fide purchaser with notice make informed decisions.
The three types of property law include real property law, personal property law, and intellectual property law. Real property law governs land and anything attached to it, while personal property law addresses movable items. Intellectual property law involves creations of the mind, such as inventions and artistic works, which can also intersect with concepts of notice.