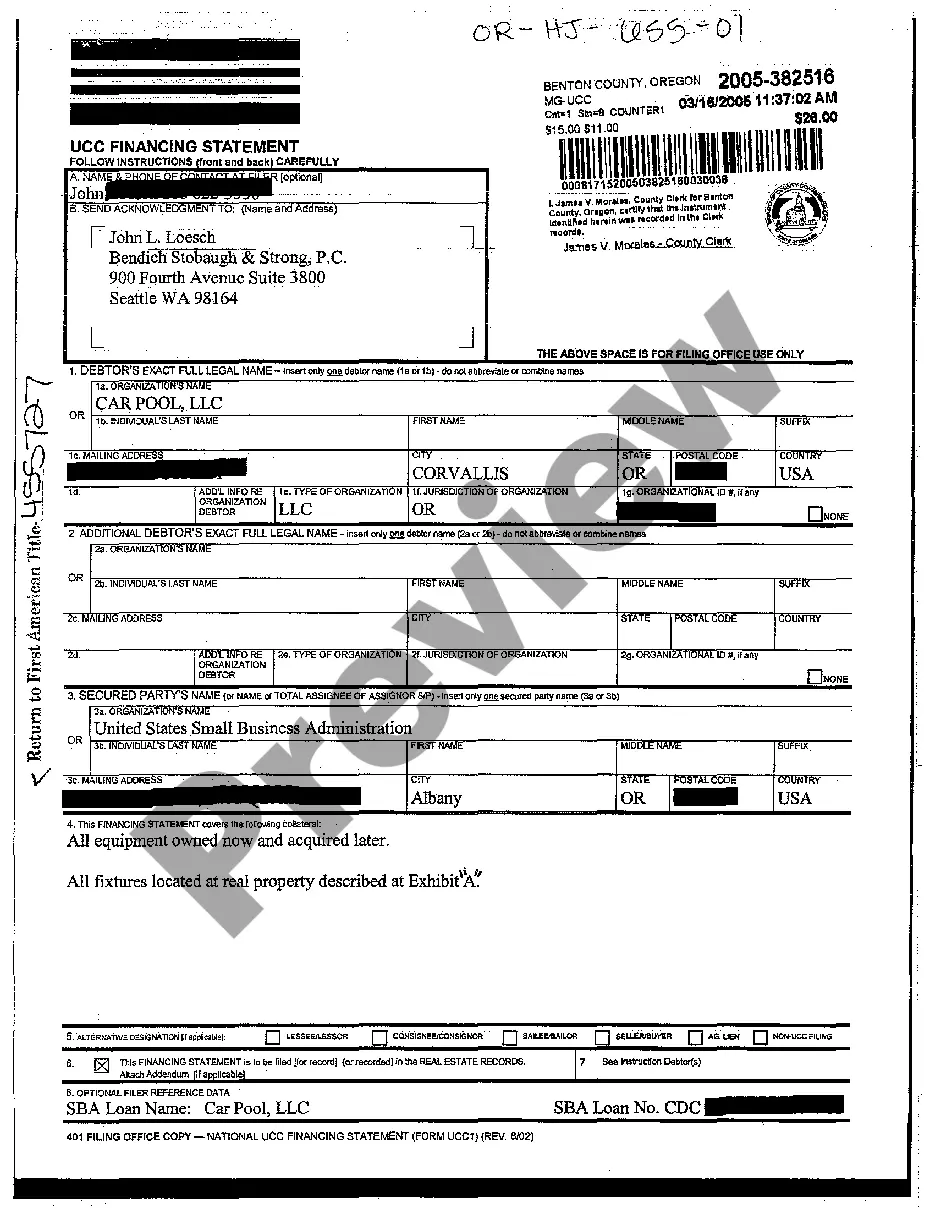
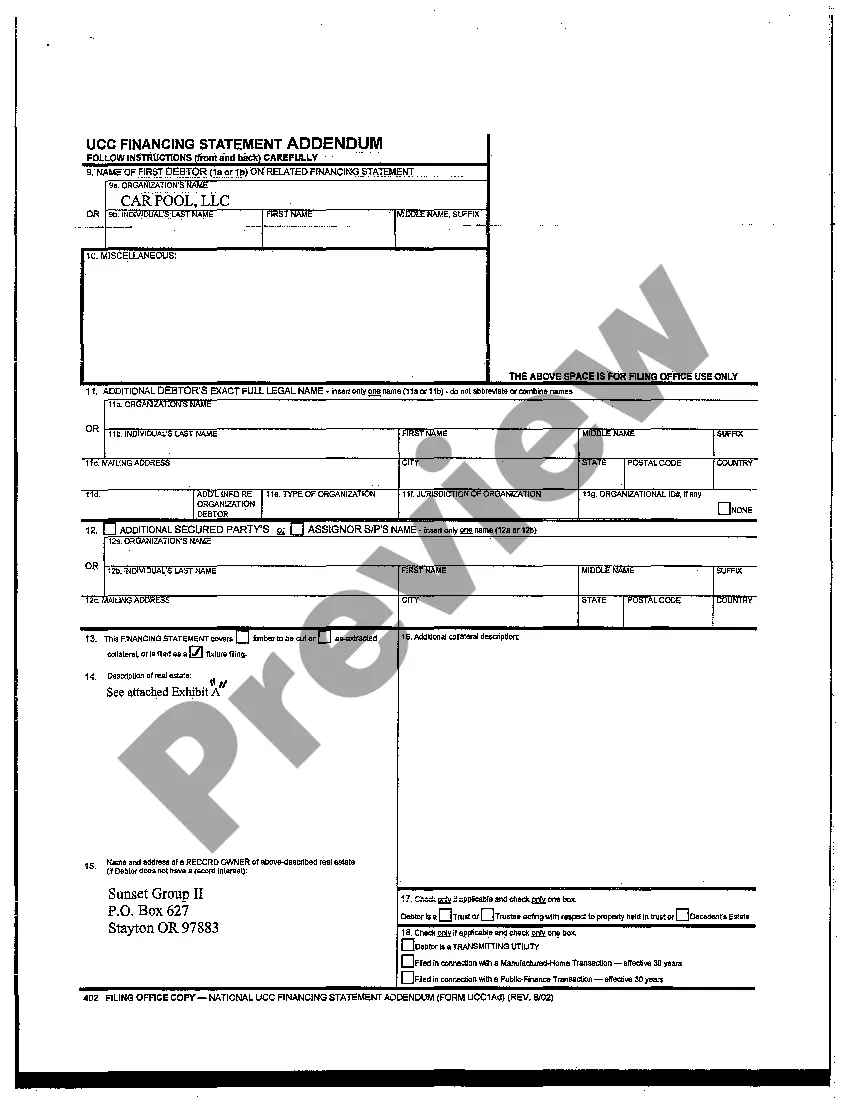
UCC filing, which stands for Uniform Commercial Code filing, is a legal process that establishes a publicly recorded notice of a secured party's interest in certain collateral provided by a debtor. It is generally used in the United States to secure loans and protect the interests of lenders. UCC filings are typically made with the Secretary of State's office in the state where the debtor is located. There are several types of UCC filings that can be made, each serving a specific purpose and involving different parties. Here are a few examples: 1. UCC-1 Financing Statement: This is the most common type of UCC filing and is used to establish a creditor's secured interest in collateral. It provides public notice that the creditor has a claim on the debtor's property and ensures priority in case of default or bankruptcy. 2. UCC-3 Amendment: This type of filing is used to modify or terminate an existing UCC-1 Financing Statement. It allows creditors to make changes to the original filing, such as adding or removing collateral, changing the debtor's name, or extending the expiration date of the filing. 3. UCC-5 Information Statement: This filing is used to provide additional information related to a previously filed UCC-1 Financing Statement. It helps interested parties gather more details about the secured transaction, such as the debtor's address change or the assignment of a secured party's interest. 4. UCC-11 Information Request: This filing allows anyone to request a search of the UCC records to obtain information about a particular debtor or collateral. It is often used by individuals or businesses to assess the existing security interests on a specific property before entering into a transaction. 5. UCC-1AD Additional Party: Sometimes, multiple parties may have an interest in the same collateral. In such cases, an additional secured party can file a UCC-1AD to be added to the original UCC-1 Financing Statement. Overall, UCC filing is a crucial process that helps establish and protect the rights of secured parties in commercial transactions. By making these filings, lenders ensure that their interests are disclosed to the public and have a higher chance of recovering their investment in case of default.
Ucc Filing Example
Description
How to fill out Ucc Filing Example?
The Ucc Filing Example you see on this page is a multi-usable legal template drafted by professional lawyers in line with federal and local laws. For more than 25 years, US Legal Forms has provided individuals, organizations, and attorneys with more than 85,000 verified, state-specific forms for any business and personal situation. It’s the quickest, simplest and most trustworthy way to obtain the documents you need, as the service guarantees the highest level of data security and anti-malware protection.
Obtaining this Ucc Filing Example will take you just a few simple steps:
- Browse for the document you need and review it. Look through the file you searched and preview it or review the form description to verify it fits your needs. If it does not, make use of the search option to get the right one. Click Buy Now when you have found the template you need.
- Sign up and log in. Choose the pricing plan that suits you and register for an account. Use PayPal or a credit card to make a quick payment. If you already have an account, log in and check your subscription to proceed.
- Get the fillable template. Pick the format you want for your Ucc Filing Example (PDF, DOCX, RTF) and download the sample on your device.
- Complete and sign the document. Print out the template to complete it by hand. Alternatively, use an online multi-functional PDF editor to quickly and precisely fill out and sign your form with a legally-binding] {electronic signature.
- Download your papers one more time. Utilize the same document once again whenever needed. Open the My Forms tab in your profile to redownload any previously downloaded forms.
Subscribe to US Legal Forms to have verified legal templates for all of life’s circumstances at your disposal.
Form popularity
FAQ
How Much Does an Uncontested Divorce Cost in Louisiana? As a rule, an uncontested divorce is a lot cheaper than a traditional, contested divorce. That's because many couples can get through the uncontested divorce process without hiring lawyers to represent them?which leads to big savings on the normal cost of divorce.
An Article 103 divorce is a type of divorce in Louisiana that is filed after the spouses have lived separate and apart for at least the required period of time. For an Article 103 divorce, the children must reach the age of 18 before the petition for divorce is filed.
Divorce Filing Fees in Louisiana If you can't afford to pay the filing fees, you can ask the judge to waive the fees by filing an affidavit with the court to proceed in forma pauperis (IFP). If the court grants your request, the court allows you to have your fees deferred until the end of the case.
Generally, after couples have been living spearate and apart for the mandatory amount of time, an uncontested simple divorce will take between 2 weeks and 6 months depending upon the court in the parish you are filing.
What are the basic steps for filing for divorce? First, you must meet the residency requirements of the state in which you wish to file. Second, you must have ?grounds? (a legally acceptable reason) to end your marriage. Third, you must file divorce papers and have copies sent to your spouse.
Divorce Filing Fees and Typical Attorney Fees by State StateAverage Filing FeesOther Divorce Costs and Attorney FeesLouisiana$150 to $250Average fees: $10,000Maine$120Average fees: $8,000+Maryland$165Average fees: $11,000Massachusetts$200Average fees: $12,000+48 more rows ?
The divorce petition should be printed and signed before a notary public since the court clerk cannot notarize it. Additional fees may apply. The filing spouse must also make two photocopies of the original papers. An average filing fee to start a divorce in Louisiana is $250.
A judge can grant a no-fault divorce if you and your spouse have lived separate and apart continuously for at least: 180 days if you and your spouse do not have a child together under 18 years old; or. 365 days if you and your spouse do have a child together under 18 years old.