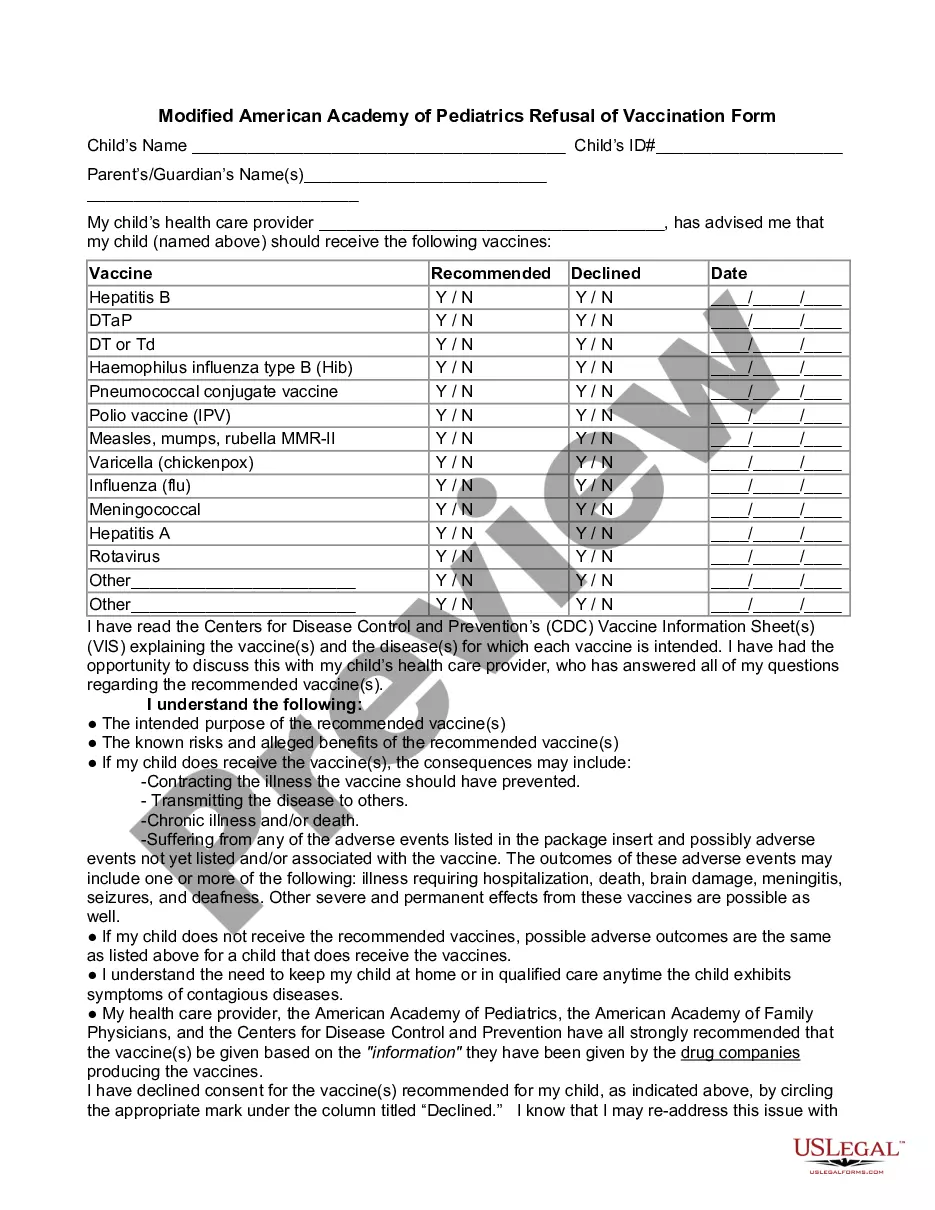
Minnesota Divorce with Foreclosure: A Comprehensive Overview Introduction: Minnesota divorce with foreclosure refers to the complex and often challenging situation that arises when a couple experiencing marital dissolution also faces the possibility of losing their jointly owned primary residence due to foreclosure. This scenario not only involves the legal aspects of divorce but also entails navigating the intricate foreclosure process in Minnesota. This article aims to provide a detailed description of Minnesota divorce with foreclosure, shedding light on various key aspects and offering guidance for those going through this difficult situation. Types of Minnesota Divorce with Foreclosure: 1. Marital Home Foreclosure during Divorce: — This type occurs when the couple's marital home faces foreclosure while their divorce is in progress or imminent. — It further intensifies the already stressful divorce process, as additional financial and legal issues must be addressed. 2. Foreclosure as a Divorce Settlement Outcome: — Sometimes, as part of the divorce settlement, one spouse may agree to give up their rights to the marital home, leading to foreclosure for the remaining spouse. — This situation requires careful negotiation, including exploring alternatives such as refinancing, short sale, or requesting a loan modification to avoid foreclosure. Key Considerations for Minnesota Divorce with Foreclosure: 1. Property Division: — One of the primary concerns in divorce with foreclosure is the division of property, particularly the marital home. — Both spouses need to determine who will retain the property, how the mortgage payments will be managed, and how any outstanding debts on the property will be addressed. — If foreclosure seems inevitable, the feasibility of selling the property or pursuing a short sale should be explored. 2. Financial Implications: — Divorce with foreclosure not only impacts the parties emotionally but also has significant financial consequences. — It is crucial to consider the potential tax implications, such as capital gains taxes or mortgage debt forgiveness, and seek advice from tax professionals. — Analyzing the sustainability of mortgage payments, preserving credit scores, and assessing the impact on individual financial situations are also important steps. 3. Legal Proceedings: — In Minnesota, divorce and foreclosure are dealt with separately in the legal system. — It is essential to engage competent legal counsel to navigate both processes, ensuring that the foreclosure does not compromise the divorce settlement terms and vice versa. — Effective communication and coordination between divorce attorneys and foreclosure attorneys are crucial to protect the parties' rights and interests. 4. Alternative Solutions: — To mitigate foreclosure risks during the divorce process, exploring alternative solutions is advisable. — Options include refinancing the mortgage, negotiating loan modifications, short sales, seeking assistance from foreclosure prevention programs, or considering bankruptcy (if appropriate). — A thorough evaluation of the available choices can help both parties make informed decisions regarding their financial stability and future. Conclusion: Minnesota divorce with foreclosure presents a unique set of challenges, combining the complexities of divorce proceedings with the threat of losing a jointly owned home. Navigating this situation requires a comprehensive understanding of legal and financial considerations. Seeking professional advice, coordinating with experts, and exploring alternative solutions play key roles in protecting the parties' interests and working towards a sustainable outcome within the legal framework.
Minnesota Divorce With Foreclosure
Description
How to fill out Minnesota Divorce With Foreclosure?
Finding a go-to place to access the most recent and relevant legal samples is half the struggle of working with bureaucracy. Choosing the right legal documents requirements accuracy and attention to detail, which is the reason it is crucial to take samples of Minnesota Divorce With Foreclosure only from trustworthy sources, like US Legal Forms. An improper template will waste your time and hold off the situation you are in. With US Legal Forms, you have very little to worry about. You can access and check all the details concerning the document’s use and relevance for your situation and in your state or county.
Take the following steps to complete your Minnesota Divorce With Foreclosure:
- Make use of the catalog navigation or search field to find your sample.
- Open the form’s description to ascertain if it matches the requirements of your state and county.
- Open the form preview, if there is one, to ensure the form is the one you are searching for.
- Get back to the search and find the correct document if the Minnesota Divorce With Foreclosure does not match your requirements.
- When you are positive about the form’s relevance, download it.
- If you are a registered user, click Log in to authenticate and gain access to your selected forms in My Forms.
- If you do not have an account yet, click Buy now to obtain the template.
- Pick the pricing plan that suits your preferences.
- Go on to the registration to finalize your purchase.
- Finalize your purchase by choosing a transaction method (bank card or PayPal).
- Pick the file format for downloading Minnesota Divorce With Foreclosure.
- Once you have the form on your gadget, you may alter it using the editor or print it and finish it manually.
Remove the hassle that accompanies your legal documentation. Explore the extensive US Legal Forms collection to find legal samples, check their relevance to your situation, and download them on the spot.
Form popularity
FAQ
Table of Contents Step 1: Give it an accurate name. Step 2: Mention all parties involved. Step 3: Describe your services or product with all rights, guarantees, and restrictions. Step 4: State the contract duration and make deadlines clear. Step 5: Include the price, services, payment conditions, and penalties.
NOW, THEREFORE, the parties hereby agree as follows: 1) Purchase. The Seller agrees to sell, and the Institution agrees to buy, the Collection for a total purchase price of __________ (?Purchase Price?).
A sale agreement should include all important details regarding the exchange. This includes aspects such as payment method and date, expected or actual delivery date, price and order quotes, and the date the order was submitted. The sale agreement letter should take both parties' interests into consideration.
Example: 'X' sold 10 bags of Wheat to 'Y' against payment of Rs. 3,000. Example: 'X' agrees to sell 10 bags of wheat to 'Y' for Rs. 3,000 after getting the stock.
An LOI stands for Letter of Intent. In commercial real estate, a Letter of Intent is a preliminary agreement that is negotiated between a tenant and landlord or buyer and seller.
An agreement to sell is a promise in future that the property will be transferred to the rightful owner, while the sale deed is the actual transfer of property ownership to the buyer.
How to write a letter of agreement Title the document. Add the title at the top of the document. ... List your personal information. ... Include the date. ... Add the recipient's personal information. ... Address the recipient. ... Write an introduction paragraph. ... Write your body. ... Conclude the letter.
The difference between a sale and an agreement to sell is that a sale transfers ownership of goods immediately, while an agreement to sell only promises to transfer ownership at a future date or upon certain conditions.