Fair Credit Reporting Act For Businesses
Description
How to fill out California Summary Of Fair Credit Reporting Act Rights?
When you need to finalize the Fair Credit Reporting Act For Businesses that adheres to your local state's statutes and guidelines, there can be various alternatives to choose from.
There's no requirement to examine each document to ensure it satisfies all the legal prerequisites if you are a US Legal Forms member.
It is a dependable service that can assist you in obtaining a reusable and current template on any topic.
Obtaining well-prepared official documents becomes simple with US Legal Forms. Furthermore, Premium users can also benefit from powerful integrated features for online PDF modification and signing. Try it today!
- US Legal Forms is the most extensive online collection with a compilation of over 85,000 ready-to-use papers for business and personal legal circumstances.
- All templates are confirmed to align with each state's regulations.
- For that reason, when downloading the Fair Credit Reporting Act For Businesses from our platform, you can be confident that you are maintaining a valid and updated document.
- Acquiring the necessary template from our site is remarkably straightforward.
- If you already have an account, simply Log In to the system, ensure your subscription is active, and save the selected file.
- Later, you can navigate to the My documents section in your profile and access the Fair Credit Reporting Act For Businesses at any time.
- If this is your first encounter with our website, please follow the instructions below.
- Browse the suggested page and verify it for alignment with your needs.
Form popularity
FAQ
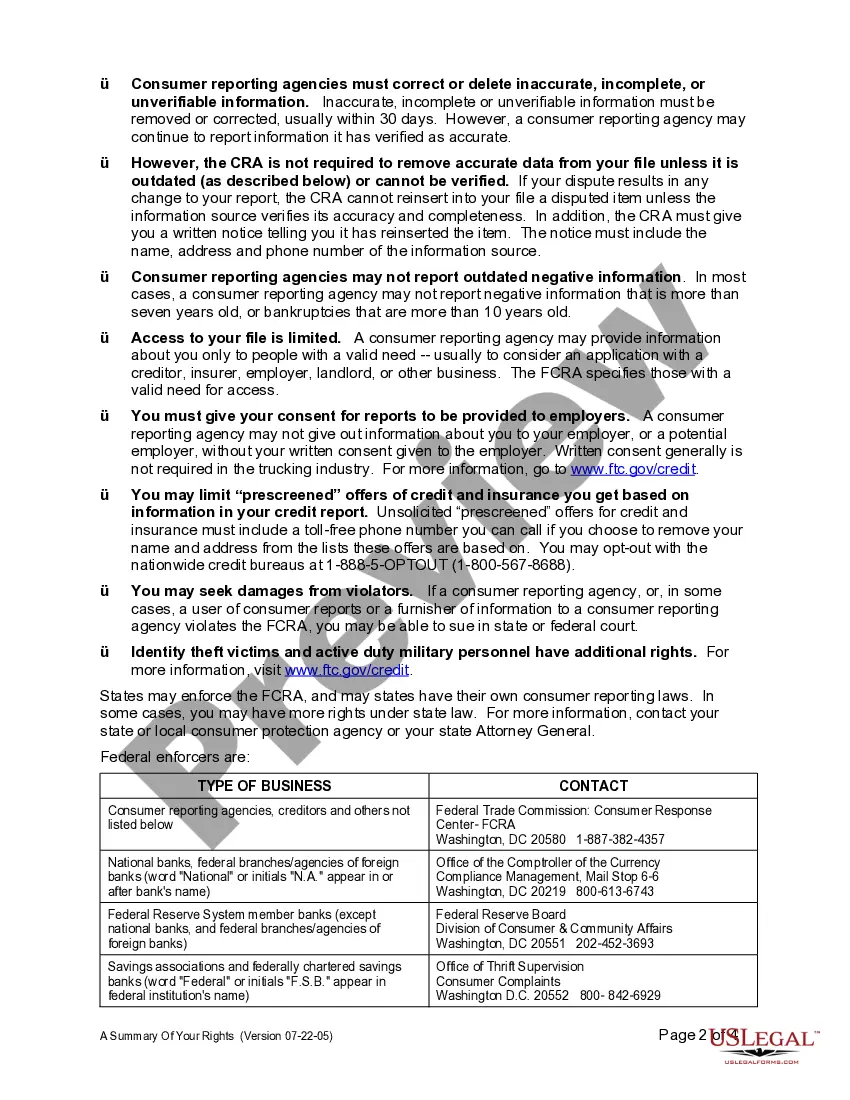
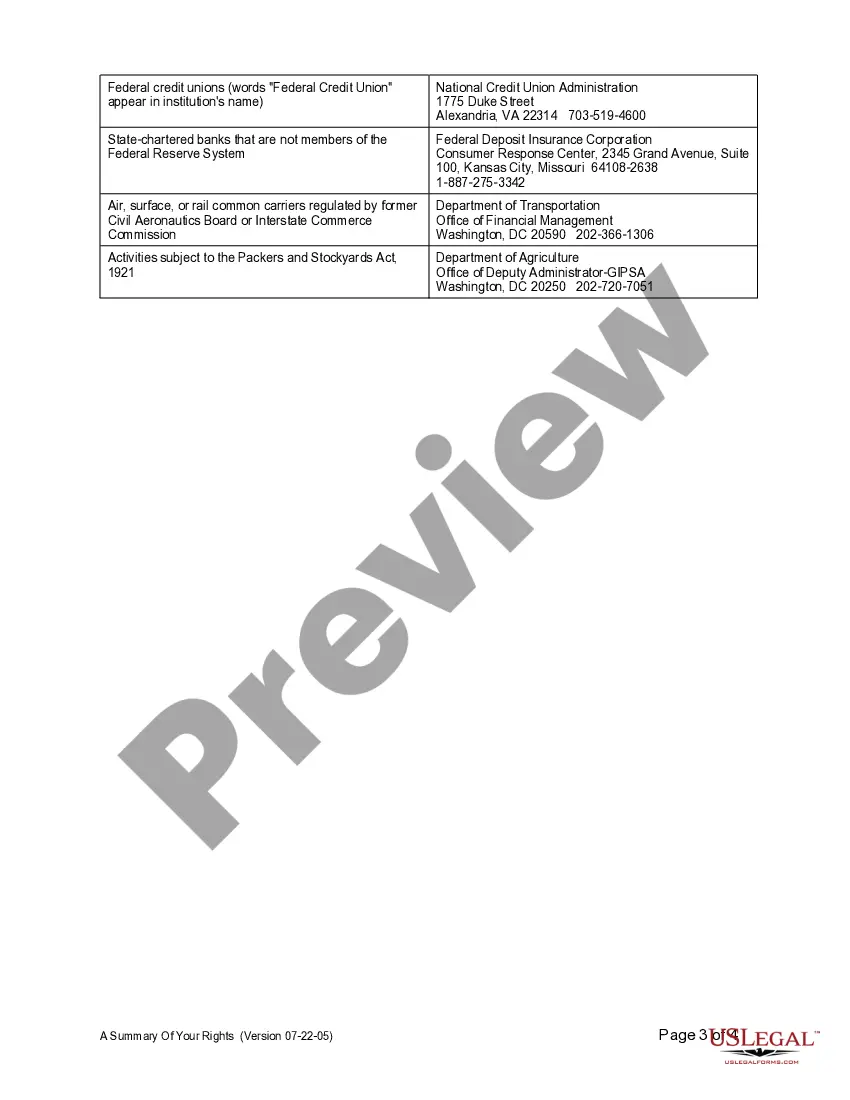
The Fair Credit Reporting Act for businesses applies to any entity that uses consumer credit reports for business purposes. This includes banks, credit unions, and employers who conduct background checks. Essentially, if you use credit reports to determine someone's creditworthiness or character, you must comply with the FCRA. Understanding these requirements helps businesses maintain compliance and protect consumer rights.
The Fair Credit Reporting Act for businesses mandates that credit bureaus maintain accurate and fair reporting practices. It also outlines the rights of consumers to access their credit reports and dispute inaccurate information. As a business, adhering to these requirements not only builds trust with your customers but also fosters a healthy credit ecosystem.
Registering your business with credit bureaus involves submitting application forms and essential business documentation. You'll also need to provide details about the type of credit you will be reporting. Using services like US Legal Forms can guide you through the registration process, ensuring you meet all Fair Credit Reporting Act for businesses requirements.
To become a reporting company, you must establish a relationship with a credit bureau by registering as a data furnishers. This step includes providing necessary business information and understanding your obligations under the Fair Credit Reporting Act for businesses. Once approved, you can start reporting customer credit behavior, which can enhance your business credibility.
To report an issue related to the Fair Credit Reporting Act for businesses, you should contact the credit bureau that provided the report. Clearly outline the discrepancies in writing, providing any supporting documents. Following the proper channels ensures your concerns are addressed effectively.
To comply with the Fair Credit Reporting Act for businesses, ensure your reporting is accurate and fair, and only provide relevant information. Regularly review your credit reporting practices to align with FCRA requirements. Additionally, consider using platforms like US Legal Forms to access resources and templates that can help streamline your compliance efforts.
Various entities can report to credit bureaus, including lenders, credit card issuers, and businesses that extend credit. Your company can also report if it offers credit terms to customers. Understanding the Fair Credit Reporting Act for businesses is vital, as it outlines how to report and the responsibilities involved.
An LLC typically starts without a credit score upon formation, as it needs to establish a credit history. Initially, businesses must apply for trade lines and credit accounts to build their score. The Fair Credit Reporting Act for businesses enables proper reporting of this information, which contributes to a positive credit profile over time.
All businesses that use consumer credit reports for various purposes must comply with the Fair Credit Reporting Act. This encompasses lenders, insurance companies, employers, and landlords, among others. Ensuring adherence to the FCRA helps maintain trust and protects both consumers and businesses.
Under the Fair Credit Reporting Act for businesses, any disputes regarding inaccuracies in a credit report must be investigated promptly. If a consumer reports an error, the business is required to verify the information and correct any inaccuracies. Investigating these claims not only protects consumers but also ensures compliance with the Act.