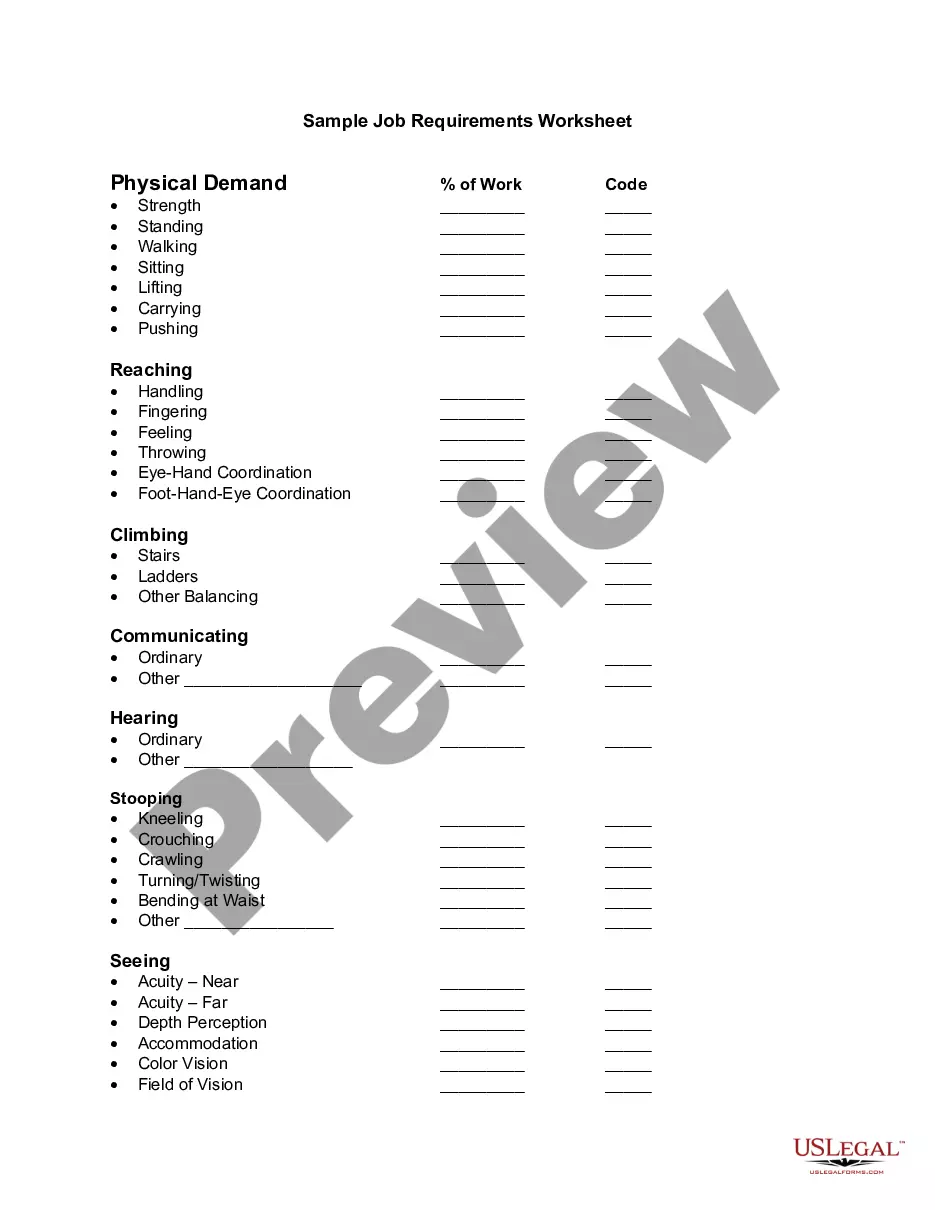
Contingency Contract In The Classroom In Travis
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Contingent contracts, similar to other forms of contracts, are usually an official written document that has been signed by both parties (although they can be created verbally).
32. Contingent contracts to do or not to do anything if an uncertain future event happens cannot be enforced by law unless and until that event has happened. If the event becomes impossible, such contracts become void.
The 3 Types of Group Contingencies. Group contingencies can be a powerful tool in ABA, using group dynamics to motivate behavior change. Let's explore the three main types: independent, dependent, and interdependent.
Example of a Contingency Contract One straightforward example might be a child who agrees with their parent that if they get an A in a particular class, they will get a new bicycle. Of course, the contract may be verbal, and it may be between family members.
Contracts for the Rotating Site changes as the operation rotates, and from C.C. Barrenland, must be unlocked by clearing the respective operation with a certain threshold of Risk: Clearing the operation for the first time unlocks all Level 1 Contracts. Clearing the operation with Risk 2 unlocks all Level 2 Contracts.
A contingency clause is a contract provision that requires a specific event or action to take place in order for the contract to be considered valid. If the party that's required to satisfy the contingency clause is unable to do so, the other party is released from its obligations.
A contingency plan in the educational context is a comprehensive strategy designed to prepare educational institutions for unforeseen events that could disrupt normal operations. Imagine a scenario where a sudden natural disaster forces a school to close physically.
Examples of contingency plans in business could include: Strategies to ensure minimal operational disruption during crises, such as unexpected market shifts, regulatory compliance changes, or severe staff shortages.
A contingency plan involves anticipating and planning for an alternate delivery of course material and communication with students when technology is not available.