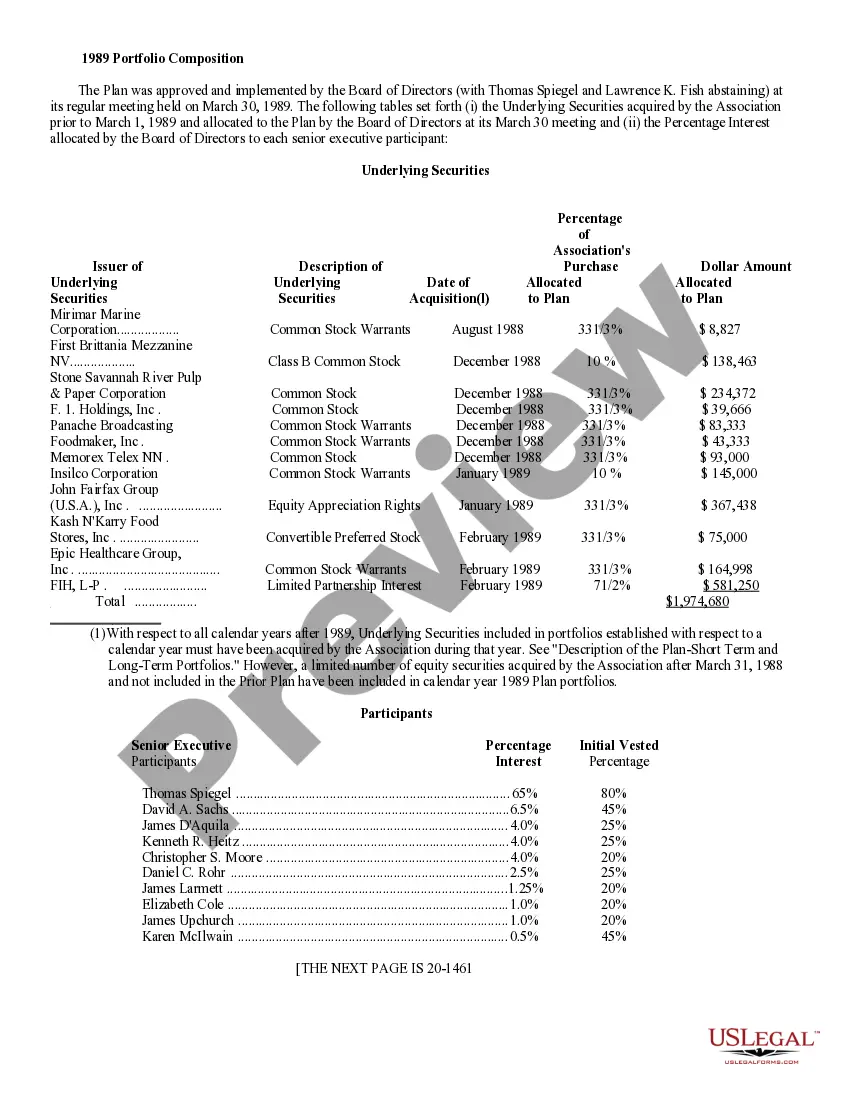
San Diego California Approval of deferred compensation investment account plan
Description
How to fill out Approval Of Deferred Compensation Investment Account Plan?
Laws and regulations vary across the nation in every field.
If you're not a lawyer, navigating through a multitude of rules while drafting legal documents can be challenging.
To prevent expensive legal fees when setting up the San Diego Approval of deferred compensation investment account plan, it's essential to have a validated template that is applicable in your area.
This is the simplest and most cost-effective method to access current templates for any legal requirements. Find them quickly and organize your documentation efficiently with US Legal Forms!
- That's where the US Legal Forms platform proves to be beneficial.
- US Legal Forms is a reliable online repository with over 85,000 state-specific legal templates, trusted by millions.
- It's an excellent resource for professionals and individuals seeking do-it-yourself templates for various personal and business needs.
- All documents are reusable; once you acquire a sample, it remains available in your profile for later access.
- Therefore, if you possess an account with an active subscription, you can simply Log In and re-download the San Diego Approval of deferred compensation investment account plan from the My documents section.
- For newcomers, there are a few additional steps to obtain the San Diego Approval of deferred compensation investment account plan.
- Assess the page content to confirm you have located the suitable sample.
- Utilize the Preview option or review the form description if it’s provided.
Form popularity
FAQ
Unlike a 401k with contributions housed in a trust and protected from the employer's (and the employee's) creditors, a deferred compensation plan (generally) offers no such protections. Instead, the employee only has a claim under the plan for the deferred compensation.
Money saved in a 457 plan is designed for retirement, but unlike 401(k) and 403(b) plans, you can take a withdrawal from the 457 without penalty before you are 59 and a half years old. This is a very important rule that often times goes overlooked with the 457 plan.
For example, the Internal Revenue Code (IRC) allows for 401(k) withdrawals to begin penalty-free after age 59½but the IRC also requires that you start taking distributions at age 72. By contrast, there are no IRC age restrictions on distributions from a deferred compensation plan.
An eligible deferred compensation plan under IRC Section 457(b) is an agreement or arrangement (which may be an individual employment agreement) under which the payment of compensation is deferred (whether by salary reduction or by nonelective employer contribution).
Qualified plans allow employees to put their money into a trust that's separate from your business' assets. An example would be 401(k) plans. Nonqualified deferred compensation plans let your employees put a portion of their pay into a permanent trust, where it grows tax deferred.
A deferred compensation plan withholds a portion of an employee's pay until a specified date, usually retirement. The lump sum owed to an employee in this type of plan is paid out on that date. Examples of deferred compensation plans include pensions, 401(k) retirement plans, and employee stock options.
A deferred comp plan is most beneficial when you're able to reduce both your present and future tax rates by deferring your income. Unfortunately, it's challenging to project future tax rates. This takes analysis, projections, and assumptions.
Typically, Fidelity says, you and your employer agree on when withdrawals can start. It may be five years, 10 years or not until you reach retirement. If you retire early, get fired or quit for another job before the due date, your employ gets to claw back some of that compensation as a penalty.
Some 401(a) plans have mandatory contributions that specify exactly how much employees must invest in the plan. Government entities administer 457(b) plans for employees and all contributions are made on a pre-tax basis. 457(b) plans are designed to supplement other retirement income rather than provide the bulk of it.
Deferred compensation is a portion of an employee's compensation that is set aside to be paid at a later date. In most cases, taxes on this income are deferred until it is paid out. Forms of deferred compensation include retirement plans, pension plans, and stock-option plans.