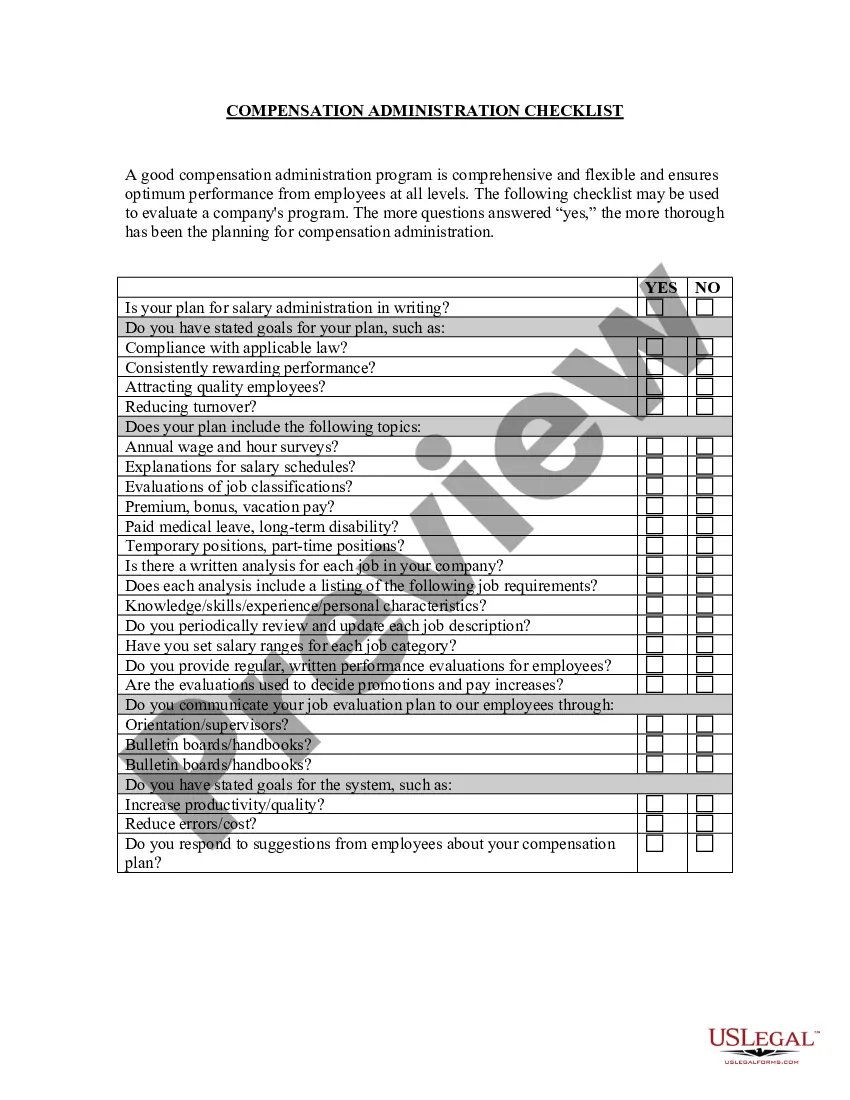
Travis Texas Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist
Description
How to fill out Equal Pay - Administration And Enforcement Checklist?
Do you require to swiftly create a legally-binding Travis Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist or perhaps any other document to manage your personal or business affairs.
You have two alternatives: engage a professional to compose a valid document for you or draft it entirely by yourself. The encouraging news is, there's a third alternative - US Legal Forms. It will assist you in obtaining expertly crafted legal documents without incurring excessive costs for legal services.
If the form doesn’t match your requirements, initiate the search again using the search bar at the top.
Select the plan that best fits your requirements and proceed to payment. Choose the format you prefer to receive your document in and download it. Print it out, complete it, and sign where indicated. If you have already created an account, you can simply Log In, find the Travis Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist template, and download it. To download the form again, just navigate to the My documents tab.
- US Legal Forms provides an extensive collection of over 85,000 state-compliant form templates, including the Travis Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist and various form packages.
- We offer paperwork for a variety of life situations: from divorce documents to real estate form templates.
- We have been in business for over 25 years, establishing an impeccable reputation among our clientele.
- Here's how you can join them and acquire the document you need without unnecessary complications.
- First and foremost, carefully ensure that the Travis Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist aligns with your state’s or county’s regulations.
- If the document includes a description, be sure to verify its purpose.
Form popularity
FAQ
Enforced by the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC), the law applies to employers with 20 or more employees and to federal government, interstate agencies, employment agencies and labor unions.
The Equal Pay Act 1970 was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that prohibited any less favourable treatment between men and women in terms of pay and conditions of employment. The Act was proposed by the then Labour government, and was based on the Equal Pay Act of 1963 of the United States.
The Equality Act 2010 gives both women and men the right to equal pay for equal work, with women and men being legally entitled to be paid at the same rate for like work, work rated as equivalent, and work of equal value.
Equal pay for equal work is the concept of labor rights that individuals doing the same work should receive the same remuneration. It is most commonly used in the context of sexual discrimination, in relation to the gender pay gap.
Here are five ways you can ensure equal pay on your team: Prevent salary disparities before making new hires.Review employee compensation on a regular basis.Separate compensation reviews from performance reviews.Disclose salary ranges for different positions and levels.Advocate for your people.
Equal pay for equal work eventually became law when John F. Kennedy signed the Equal Pay Act in 1963. His remarks on signing the bill echoed Stanley's from almost 20 years earlier: Our economy today depends upon women in the labor force.
An aggrieved individual may contact the Civil Rights Center (CRC) at: Phone: (202) 693-6500; Federal Relay Service TTY/TDD: (800) 877-8339; Video Relay (877) 708-5797; Email: CRC-INFORMAL-COMPLAINTS@DOL.GOV.
The Equal Pay Act requires that men and women in the same workplace be given equal pay for equal work. The jobs need not be identical, but they must be substantially equal. Job content (not job titles) determines whether jobs are substantially equal.
Equal pay here relates not only to basic pay but includes other benefits and allowances too. The Indian Constitution recognized the principle of 'Equal Pay for Equal Work' for both men and women, and 'Right to Work' through Article 39(d) and 41. These Articles are inserted as Directive Principles of State Policy.
18. Do I need to file a claim with the California Department of Fair Employment and Housing (DFEH)? The DFEH enforces the California Fair Employment and Housing Act, which prohibits discrimination based on sex, race, national origin, ancestry, in addition to other protected categories.