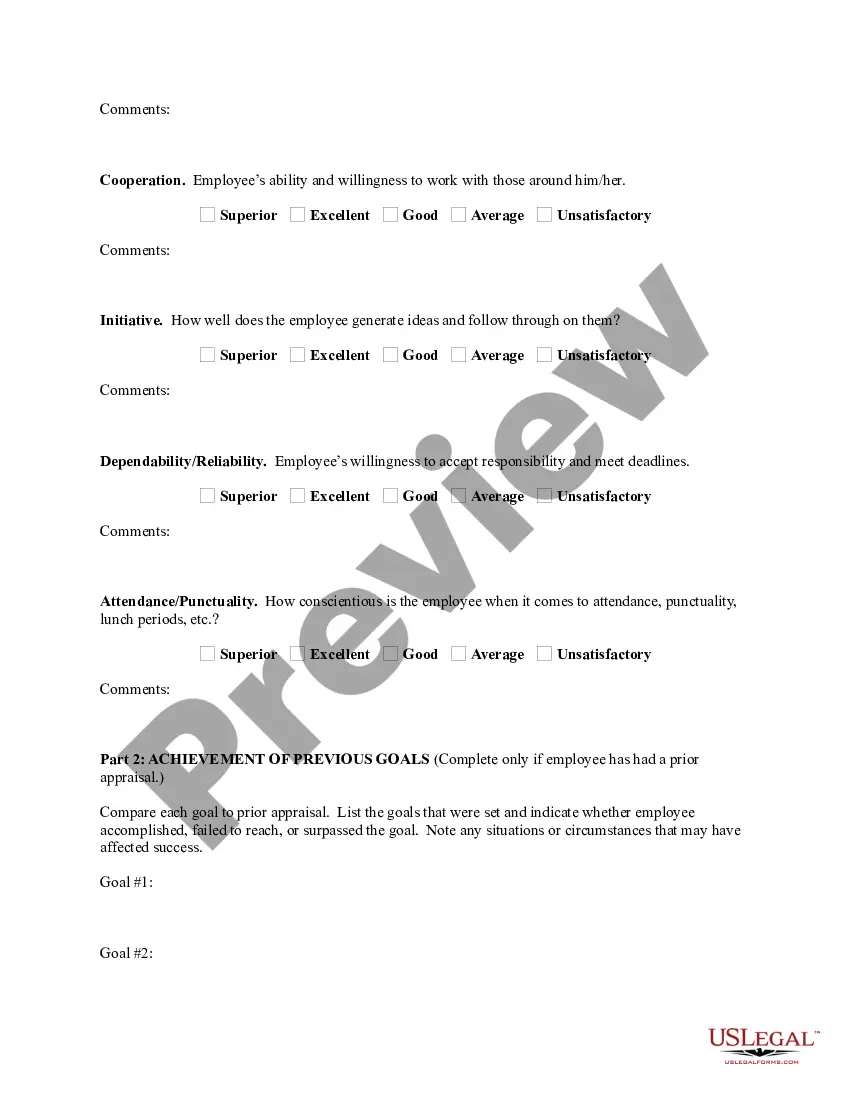
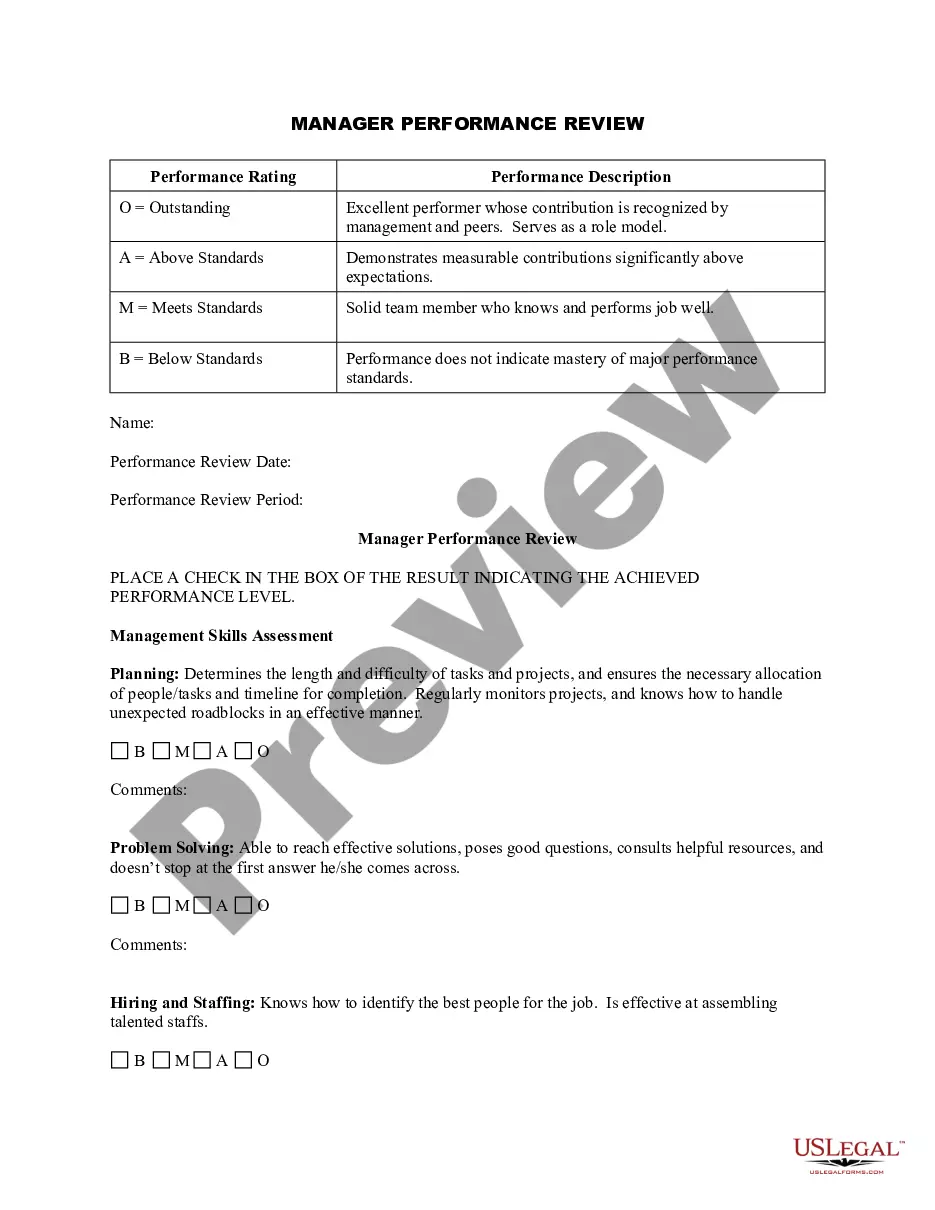
Oregon Performance Evaluation for Nonexempt Employees
Description
How to fill out Performance Evaluation For Nonexempt Employees?
If you wish to finalize, acquire, or print legal document templates, utilize US Legal Forms, the most significant collection of legal forms available online.
Take advantage of the site's straightforward and user-friendly search function to find the documents you need.
A selection of templates for commercial and specific applications are organized by categories and jurisdictions, or by keywords.
Every legal document template you purchase is yours indefinitely.
You have access to all forms you downloaded in your account. Navigate to the My documents section and select a form to print or download again.
- Leverage US Legal Forms to obtain the Oregon Performance Assessment for Nonexempt Employees in just a few clicks.
- If you are currently a US Legal Forms customer, sign in to your account and hit the Acquire button to access the Oregon Performance Assessment for Nonexempt Employees.
- You can also view forms you previously downloaded from the My documents section of your account.
- If you are using US Legal Forms for the first time, please follow the steps below.
- Step 1. Ensure you have chosen the form for the correct region/country.
- Step 2. Utilize the Preview option to review the form's content. Be sure to read the description.
- Step 3. If you are dissatisfied with the form, use the Search box at the top of the page to find alternative versions of the legal form template.
- Step 4. Once you have found the form you need, click on the Buy now button. Select the payment plan you desire and enter your details to register for the account.
- Step 5. Complete the transaction. You can use your Visa or MasterCard or PayPal account to finalize the purchase.
- Step 6. Choose the format of the legal document and download it to your device.
- Step 7. Fill out, modify, and print or sign the Oregon Performance Assessment for Nonexempt Employees.
Form popularity
FAQ
Nonexempt: An individual who is not exempt from the overtime provisions of the FLSA and is therefore entitled to overtime pay for all hours worked beyond 40 in a workweek (as well as any state overtime provisions). Nonexempt employees may be paid on a salary, hourly or other basis.
The FLSA includes these job categories as exempt: professional, administrative, executive, outside sales, and computer-related. The details vary by state, but if an employee falls in the above categories, is salaried, and earns a minimum of $684 per week or $35,568 annually, then they are considered exempt.
Almost all Oregon employers are subject to the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), and the minimum salary to qualify for exemption under that law is $684 per week or $35,568 annually (allowing up to 10% of the salary basis threshold to be met with nondiscretionary bonuses/incentives, including commissions, paid at least
Salary level test. Employees who are paid less than $23,600 per year ($455 per week) are nonexempt. (Employees who earn more than $100,000 per year are almost certainly exempt.)
Employees who are paid less than $23,600 per year ($455 per week) are nonexempt. (Employees who earn more than $100,000 per year are almost certainly exempt.)
Can I Sue My Oregon Employer for not Giving Me a Full 30-Minute Lunch break? Generally Yes, our lawyers can sue for short lunch breaks. Currently it appears that an employee who was provided a short lunch break can sue their employer for failing to pay wages.
The law prohibits employers from inquiring about job applicants' salary history. Do not discourage employees from discussing compensation with one another. The law protects employees who want to discuss their compensation with one another.
Oregon law requires an employer-paid rest period of not less than 10 minutes for every segment of four hours or major part thereof (two hours and one minute through four hours) worked in one work period. This time must be taken in addition to and separately from required meal periods.
All salaried employees must be paid overtime unless they meet the test for exempt status as defined by federal and state laws. CAUTION: Misclassification of salaried employees as exempt creates liability for unpaid overtime. It is the employer´s burden to prove exempt status of employees.
Federal law allows employers to pay for the breaks provided by employers. The law, however, does not make it compulsory for employers to provide break time. Oregon and a few other states differ in this aspect. They require employers to allow rest and meal breaks and pay for the time.