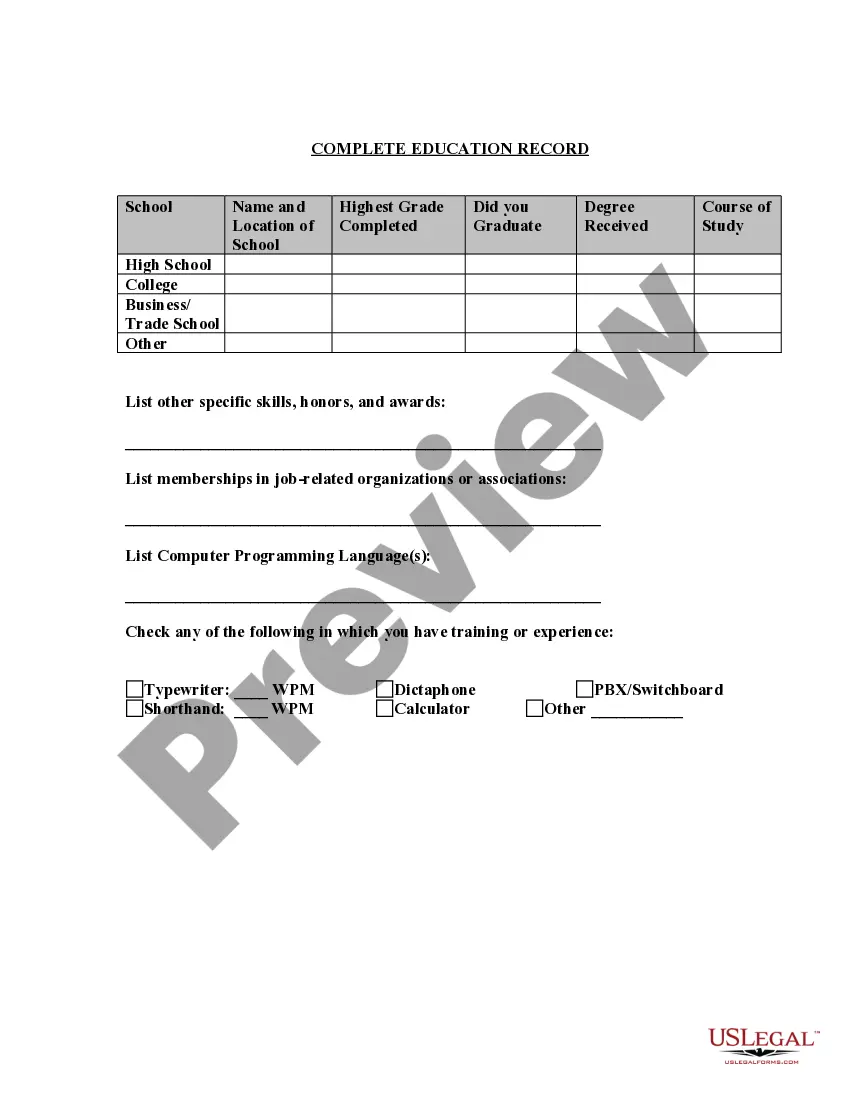
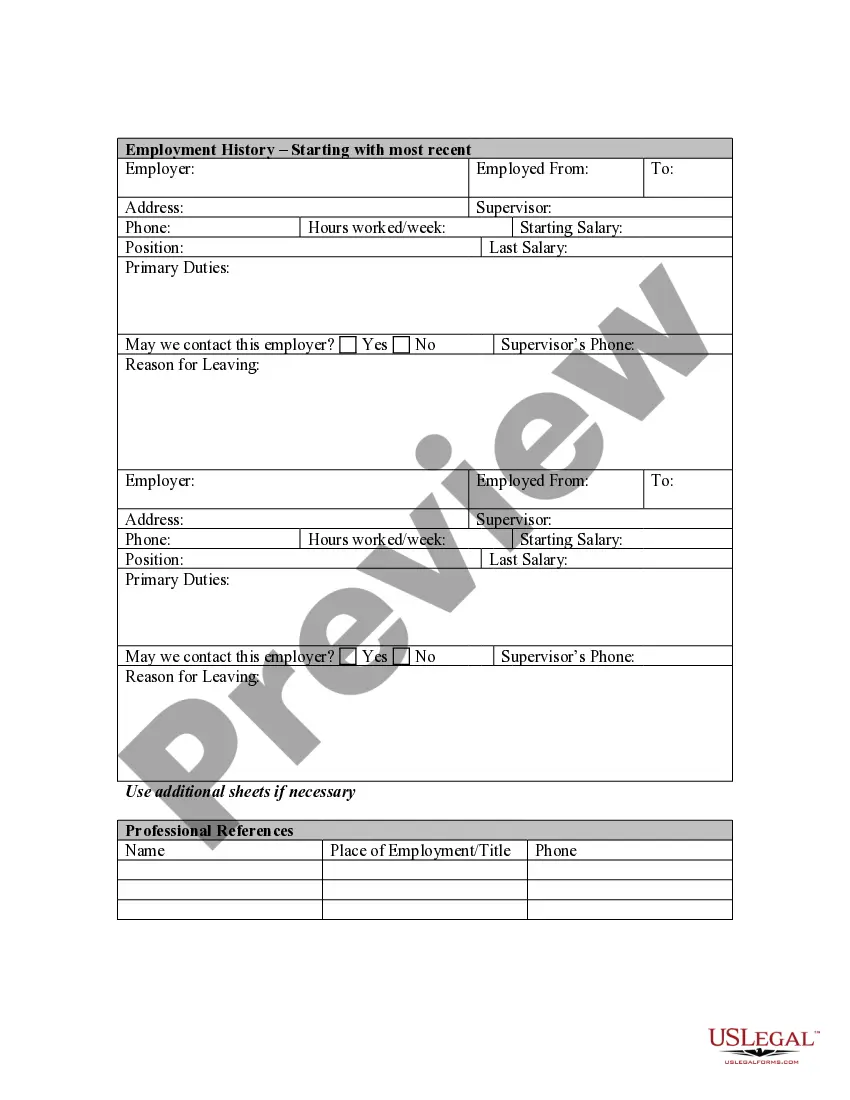
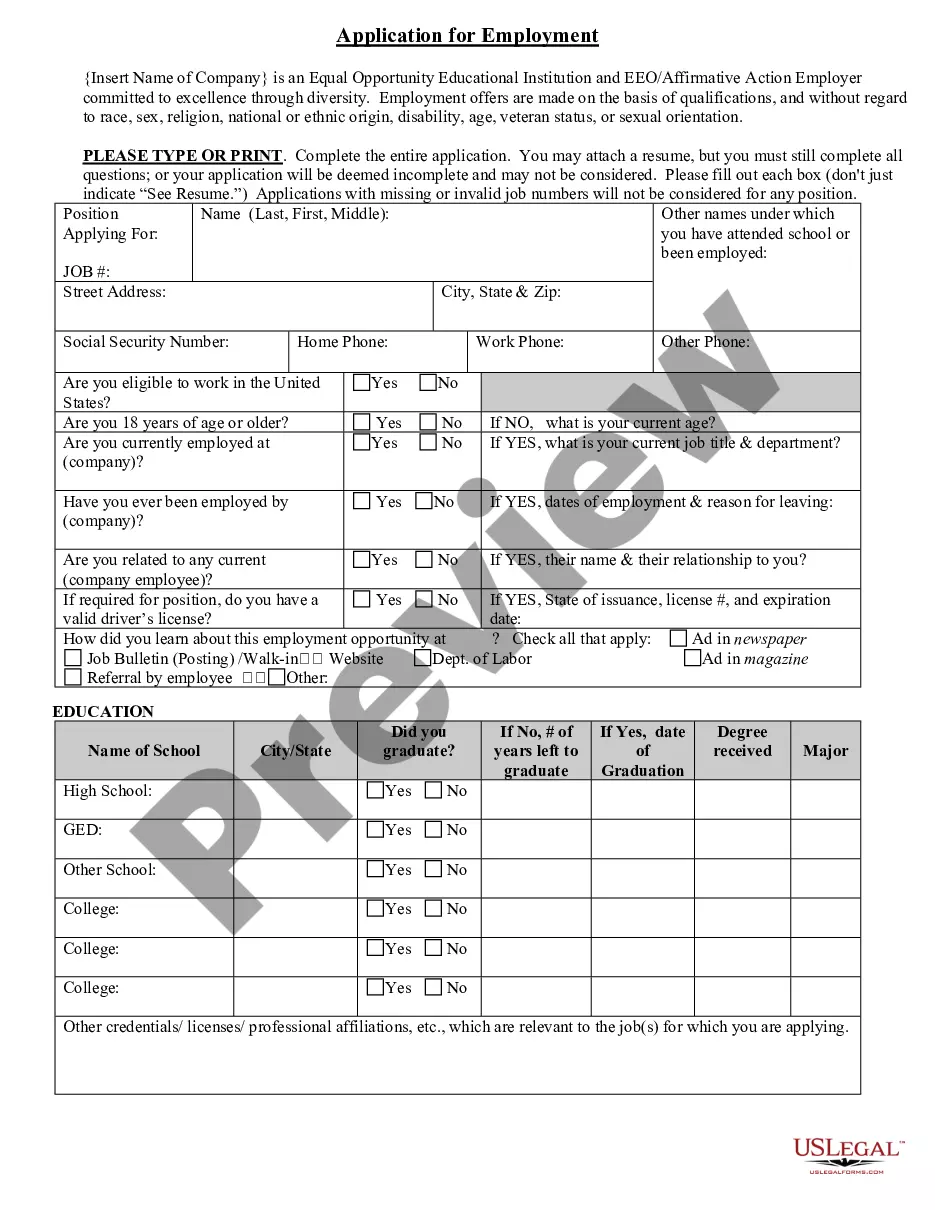
Oklahoma Application for Work or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position
Description
How to fill out Application For Work Or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, Or Nonexempt Position?
If you need to finish, obtain, or create legal document templates, utilize US Legal Forms, the largest array of legal forms, available on the web.
Take advantage of the site's user-friendly and convenient search function to locate the documents you require.
Various templates for business and personal purposes are categorized by type and jurisdiction, or by keywords.
Step 3. If you are dissatisfied with the form, use the Search box at the top of the screen to find alternative versions of the legal form.
Step 4. Once you have located the form you require, click the Buy now button. Select the pricing plan you prefer and enter your details to sign up for an account.
- Utilize US Legal Forms to quickly find the Oklahoma Application for Employment or Work - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position.
- If you are already a US Legal Forms customer, Log In to your account and select the Download option to access the Oklahoma Application for Employment or Work - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position.
- You can also retrieve forms you have previously downloaded from the My documents section of your account.
- If you are using US Legal Forms for the first time, adhere to the guidelines below.
- Step 1. Confirm that you have selected the form for the appropriate city/state.
- Step 2. Utilize the Review feature to inspect the content of the form. Always remember to read the description.
Form popularity
FAQ
In Oklahoma, salaried employees must meet specific criteria to be classified as exempt. Generally, they should perform professional, executive, or administrative duties and earn a salary above a threshold set by federal or state regulations. When filling out your Oklahoma Application for Work or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position, it's essential to understand how these rules apply. Correctly classifying your position can influence your eligibility for overtime and other benefits.
An exempt employee is an employee who does not receive overtime pay or qualify for minimum wage. Exempt employees are paid a salary rather than by the hour, and their work is executive or professional in nature.
Who is eligible for overtime pay? To qualify as an exempt employee one who does not receive overtime pay staff members must meet all the requirements under the duties and salary basis tests.
Nonexempt: An individual who is not exempt from the overtime provisions of the FLSA and is therefore entitled to overtime pay for all hours worked beyond 40 in a workweek (as well as any state overtime provisions). Nonexempt employees may be paid on a salary, hourly or other basis.
"Non-exempt" means an employee who is covered by the minimum wage and overtime provisions of FLSA or is granted special non-exempt status.
Tips For Drafting Job Descriptions for Exempt EmployeesAccuracy is King. The job description must be accurate.Accuracy Does Not Mean Exhaustion.Strong Verbs, Clear Impact.Focus on Exempt Functions.Don't Shy Away From Degree Requirements.Assist With Can Diminish a Role.Consider Requiring Acknowledgement.
Employees who do not meet the requirements to be classified as exempt from the Minimum Wage Act are considered nonexempt. Nonexempt employees may be paid on a salary, hourly or other basis. Employees who do not qualify for an exemption but are paid on a salary basis are considered salaried nonexempt.
An exempt employee is not entitled overtime pay by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). These salaried employees receive the same amount of pay per pay period, even if they put in overtime hours. A nonexempt employee is eligible to be paid overtime for work in excess of 40 hours per week, per federal guidelines.
An exempt employee is not entitled overtime pay by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). These salaried employees receive the same amount of pay per pay period, even if they put in overtime hours. A nonexempt employee is eligible to be paid overtime for work in excess of 40 hours per week, per federal guidelines.
An exempt employee must be paid at least $23,600 per year ($455 per week), be paid on a salary basis, and perform exempt job duties. Page 2. Exempt job duties consists of three typical categories. The three categories are executive, professional and administrative.