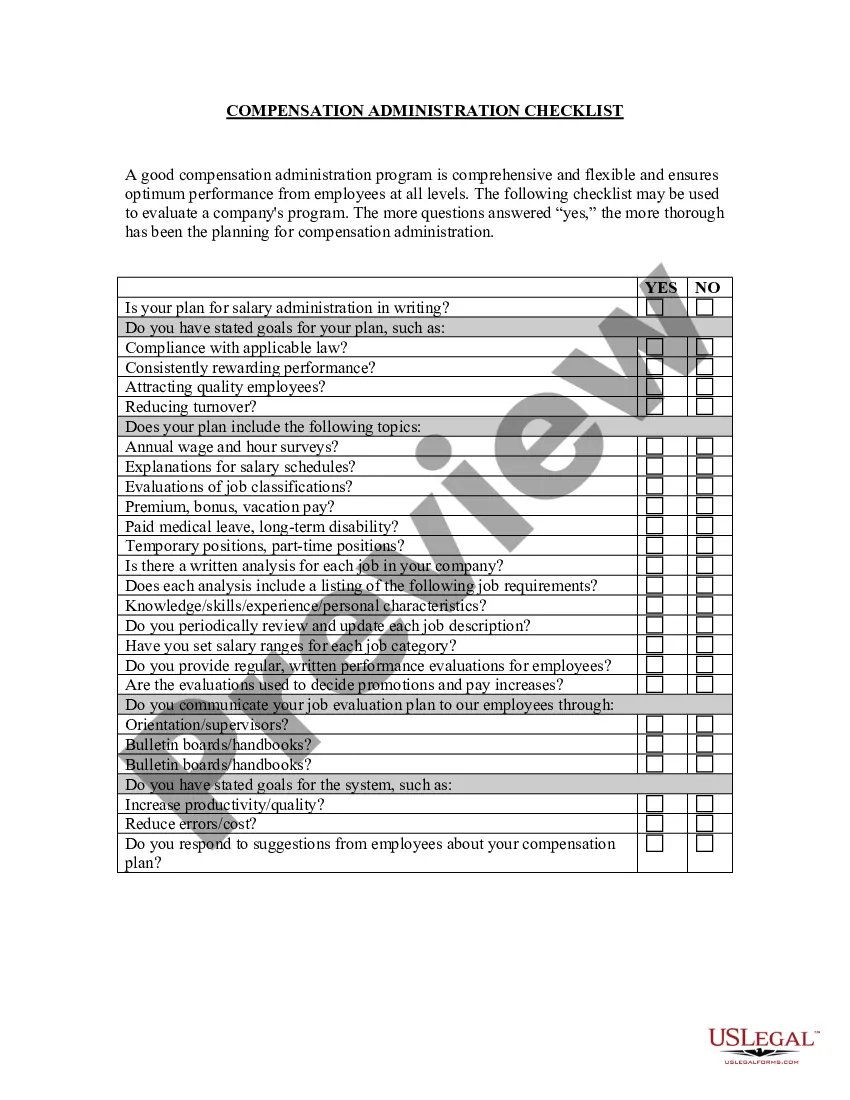
Oklahoma Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist
Description
How to fill out Equal Pay - Administration And Enforcement Checklist?
If you desire to total, acquire, or generate legal document templates, utilize US Legal Forms, the largest collection of legal forms, that is available online.
Employ the site's straightforward and user-friendly search to obtain the documents you require.
Various templates for commercial and personal purposes are organized by categories and states, or keywords.
Every legal document template you purchase is yours permanently.
You have access to every form you saved in your account. Go to the My documents section and select a form to print or download again.
- Use US Legal Forms to access the Oklahoma Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist with just a few clicks.
- If you are already a US Legal Forms customer, Log In to your account and select the Download button to retrieve the Oklahoma Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist.
- You can also find forms you previously saved in the My documents section of your account.
- If you are using US Legal Forms for the first time, follow the instructions below.
- Step 1. Ensure you have chosen the form for the correct city/state.
- Step 2. Use the Preview option to review the form’s content. Remember to read through the description.
- Step 3. If you are not satisfied with the form, utilize the Search field at the top of the screen to find alternate versions of the legal form template.
- Step 4. Once you have identified the form you need, click the Download now button. Choose the payment plan you prefer and enter your credentials to register for the account.
- Step 5. Process the transaction. You can use your credit card or PayPal account to complete the transaction.
- Step 6. Select the format of your legal form and download it to your device.
- Step 7. Fill out, modify and print or sign the Oklahoma Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist.
Form popularity
FAQ
In Oklahoma, it is not illegal to work seven days a week. However, certain regulations govern hours and wages to ensure fair treatment, as outlined in the Oklahoma Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist. Employers must still comply with state and federal laws regarding overtime and minimum wage standards. It is important for both employers and employees to be aware of these laws to maintain a fair and lawful working environment.
The 1 and 1/2 rule in Oklahoma refers to the overtime pay calculation for employees. According to this rule, employers must pay employees 1.5 times their regular pay rate for hours worked over 40 in a week. To ensure compliance with labor laws and protect your rights, review the Oklahoma Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist, which provides valuable insights into fair pay practices and employee rights.
Section 2 406 of the Oklahoma Employment Security Act addresses employer responsibilities and employee rights regarding employment security benefits. Understanding this section is crucial for workers seeking to know their entitlements under the law. The Oklahoma Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist can also help clarify how this section impacts your rights if you experience job loss or termination.
If you believe you have a case against your employer, you can file your complaint with the Oklahoma Employment Security Commission. It's essential to consult the Oklahoma Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist to ensure you gather the necessary documentation before filing. Additionally, consider reaching out to a legal professional who can guide you through the filing process and help protect your rights.
To file a claim for wrongful termination in Oklahoma, you should first gather all relevant evidence, such as documentation of your employment and any communications with your employer. Next, consult the Oklahoma Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist to understand your rights and the proper procedures to follow. You can file a complaint with the Oklahoma Employment Security Commission or seek legal advice from a local attorney who specializes in employment law.
The Oklahoma Administrative Code 380 30 1 7 outlines guidelines related to the enforcement of equal pay laws in the state of Oklahoma. This code provides a framework for employers to ensure compliance with the Oklahoma Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist. It covers various aspects of wage equality, including reporting requirements and employer responsibilities. Utilizing this code helps businesses foster fair pay practices while avoiding potential legal challenges.
Wrongful termination in Oklahoma occurs when an employee is fired for illegal reasons, such as discrimination or retaliation for whistleblowing. If an employee is let go in violation of a contract or an established public policy, this can also qualify. Being knowledgeable about your rights and protections under the Oklahoma Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist equips you to better address any potential wrongful termination claims.
Yes, Oklahoma does recognize non-compete agreements, but they must meet specific criteria to be enforceable. The agreement should protect legitimate business interests, like trade secrets or customer relationships, and be reasonable in geographic scope and duration. If you are concerned about how these agreements might affect your rights, refer to the Oklahoma Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist to understand your options and ensure you comply with state laws.
In Oklahoma, employers can typically go back a maximum of seven years on a background check for most employment purposes. However, certain positions may allow for a longer review period, especially in sensitive roles. This timeframe is important for employers to consider when conducting checks, as they must comply with the Fair Credit Reporting Act. Understanding your rights and the regulations surrounding Oklahoma Equal Pay - Administration and Enforcement Checklist can help ensure compliance.