Ohio Chapter 7 Individual Debtors Statement of Intention - Form 8 - Post 2005
Description
How to fill out Chapter 7 Individual Debtors Statement Of Intention - Form 8 - Post 2005?
Discovering the right legitimate file template could be a have a problem. Obviously, there are a lot of themes available online, but how would you discover the legitimate form you require? Utilize the US Legal Forms website. The assistance gives a large number of themes, including the Ohio Chapter 7 Individual Debtors Statement of Intention - Form 8 - Post 2005, which can be used for enterprise and private requirements. Each of the forms are inspected by specialists and satisfy federal and state demands.
When you are already signed up, log in to the bank account and click the Acquire switch to find the Ohio Chapter 7 Individual Debtors Statement of Intention - Form 8 - Post 2005. Make use of bank account to look from the legitimate forms you might have purchased formerly. Proceed to the My Forms tab of your bank account and have an additional copy in the file you require.
When you are a fresh user of US Legal Forms, allow me to share simple guidelines so that you can follow:
- Initially, make certain you have chosen the right form to your town/area. You can look through the form while using Review switch and browse the form explanation to guarantee this is basically the right one for you.
- In the event the form is not going to satisfy your requirements, take advantage of the Seach industry to find the proper form.
- When you are certain that the form would work, select the Acquire now switch to find the form.
- Opt for the prices strategy you desire and enter in the necessary info. Make your bank account and pay money for the order utilizing your PayPal bank account or credit card.
- Opt for the data file format and obtain the legitimate file template to the device.
- Comprehensive, modify and print and signal the acquired Ohio Chapter 7 Individual Debtors Statement of Intention - Form 8 - Post 2005.
US Legal Forms may be the largest catalogue of legitimate forms in which you can discover numerous file themes. Utilize the service to obtain skillfully-made files that follow status demands.
Form popularity
FAQ
A chapter 7 bankruptcy case does not involve the filing of a plan of repayment as in chapter 13. Instead, the bankruptcy trustee gathers and sells the debtor's nonexempt assets and uses the proceeds of such assets to pay holders of claims (creditors) in ance with the provisions of the Bankruptcy Code.
Filing for Chapter 7 bankruptcy will wipe out your mortgage obligation. Still, if you aren't willing to pay the mortgage, you'll have to give up the home because your lender's right to foreclose doesn't go away when you file for Chapter 7.
In a chapter 7 case, however, a discharge is only available to individual debtors, not to partnerships or corporations. 11 U.S.C. § 727(a)(1). Although an individual chapter 7 case usually results in a discharge of debts, the right to a discharge is not absolute, and some types of debts are not discharged.
That being said, here's what you're not allowed to do with a Chapter 7: Lie under oath about your financial or property assets. Keep property that must be used to discharge your debts. Miss payments to certain creditors in order to keep your home.
The consequences of a Chapter 7 bankruptcy are significant: you will likely lose property, and the negative bankruptcy information will remain on your credit report for ten years after the filing date.
Chapter 11 is the chapter used by large businesses to reorganize their debts and continue operating. Corporations, partnerships, and limited liability companies cannot use chapter 13 to reorganize and must cease business operations if a chapter 7 bankruptcy is filed.
A Chapter 7 bankruptcy wipes out mortgages, car loans, and other secured debts. But if you don't continue to pay as agreed, the lender will take back the home, car, or other collateralized property using the lender's lien rights.
Whether the trustee can take money you receive after filing your case depends on whether you were entitled to the money at the time your case was filed and how it was listed on your forms, if at all.
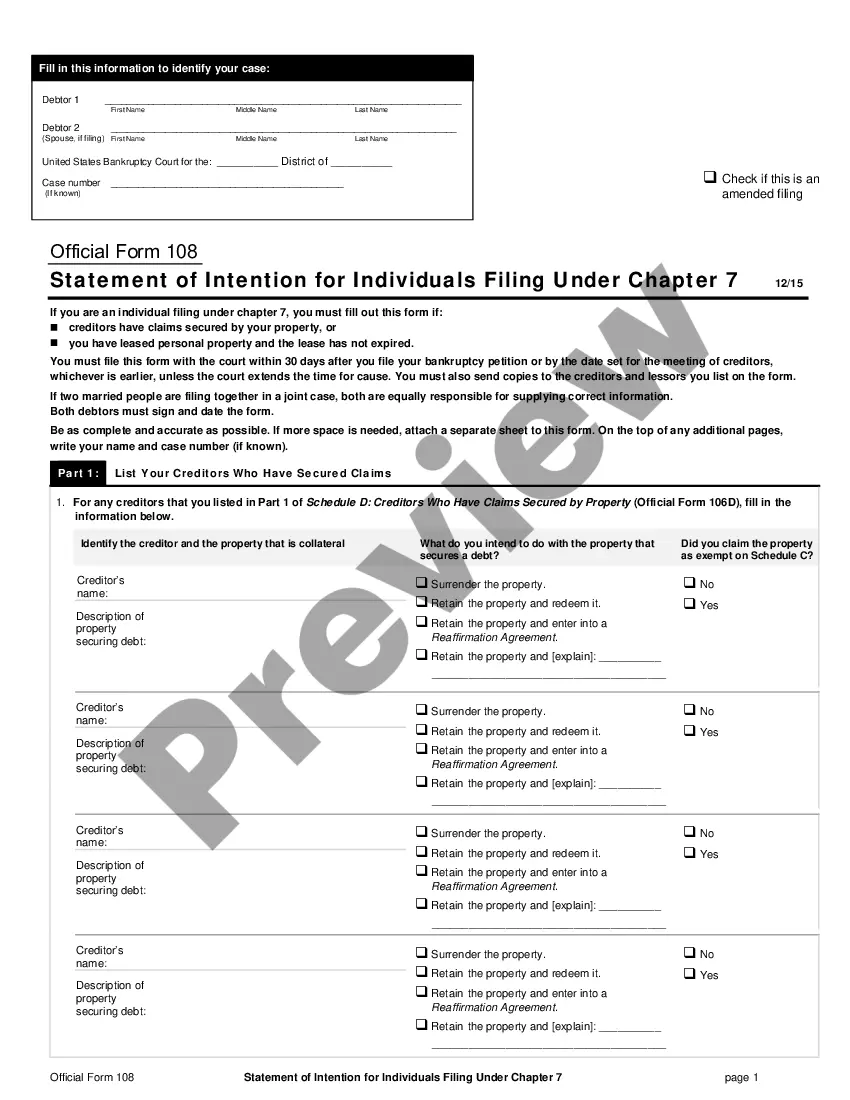
When you file for Chapter 7 bankruptcy, you will have to complete a form called the Statement of Intention for Individuals Filing Under Chapter 7. On this form, you tell the court whether you want to keep your secured and leased property?such as your car, boat, or home?or let it go back to the creditor.
A Notice of Intention to Make a Proposal (commonly referred to as "NOI") is a procedure under the Bankruptcy and Insolvency Act (?BIA?) that allows financially troubled corporations the opportunity to restructure their affairs.