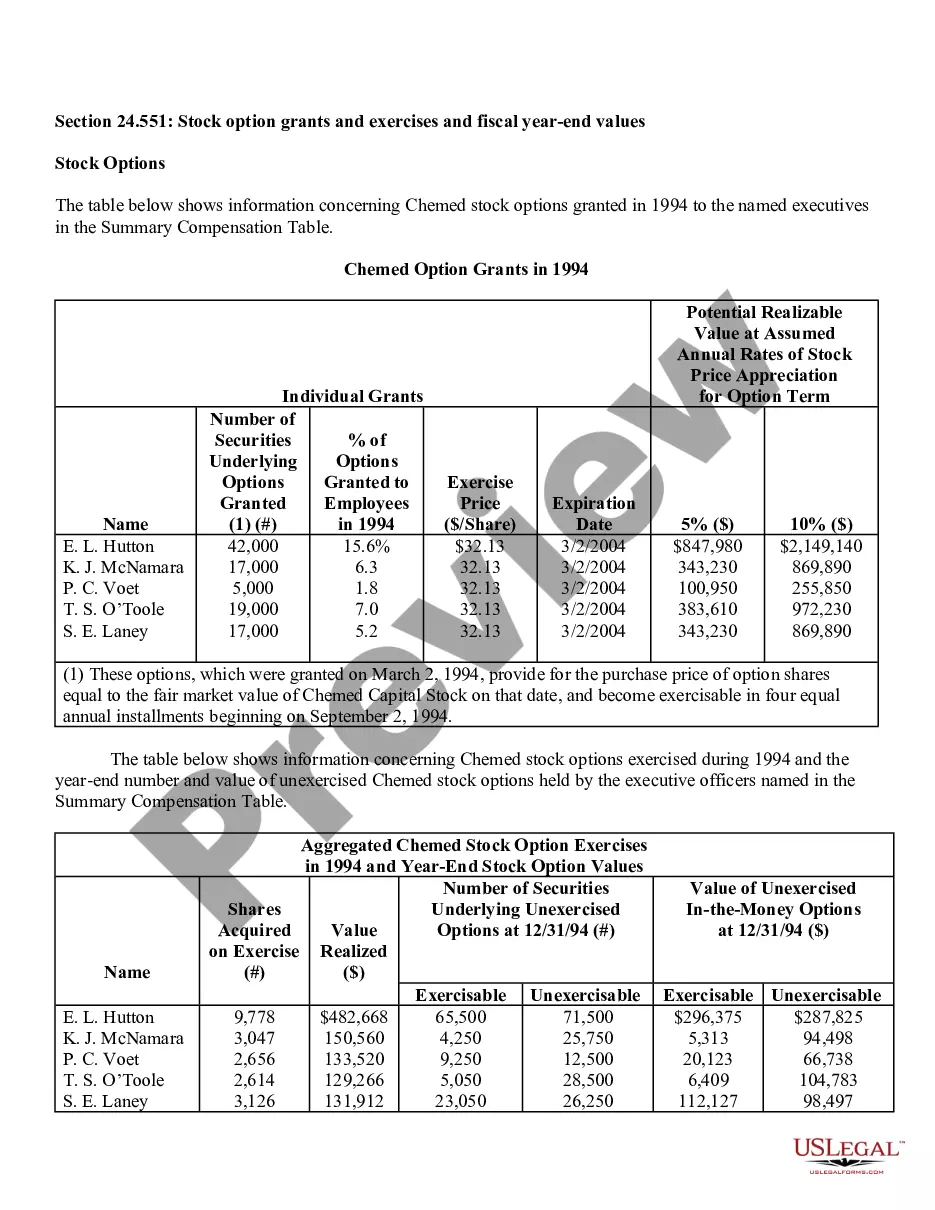
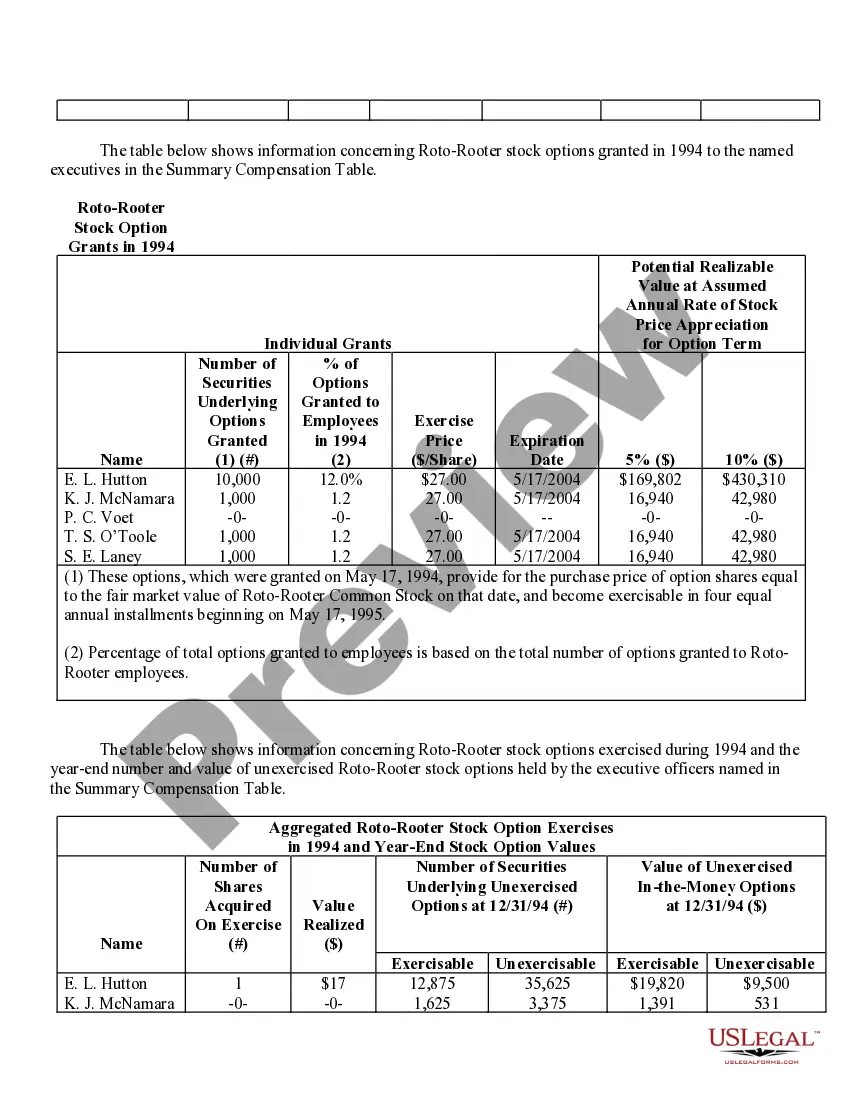
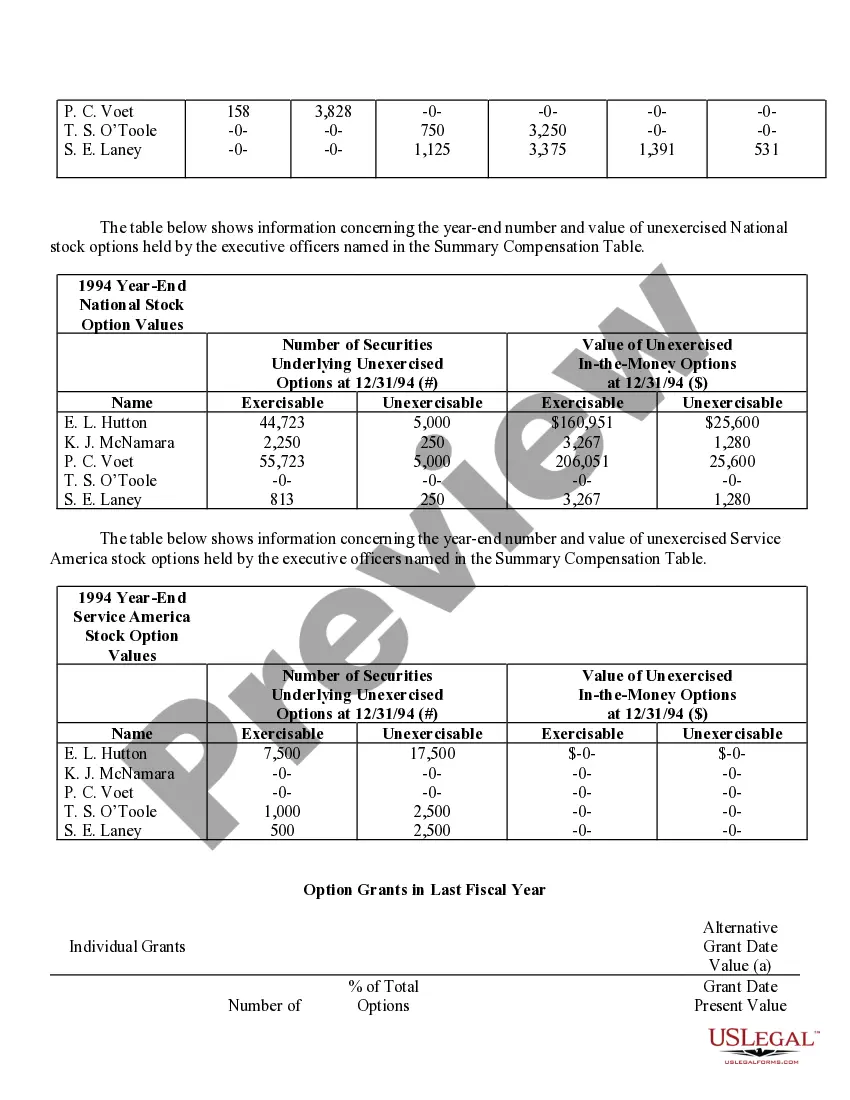
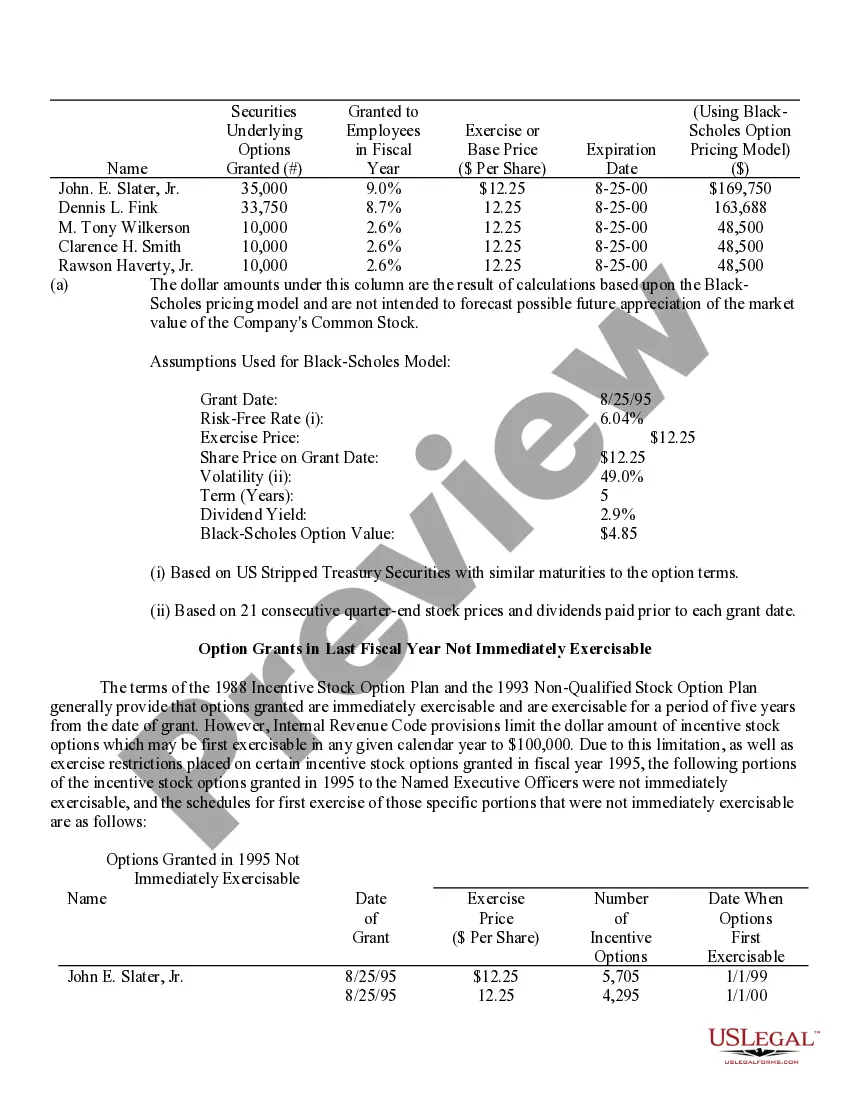
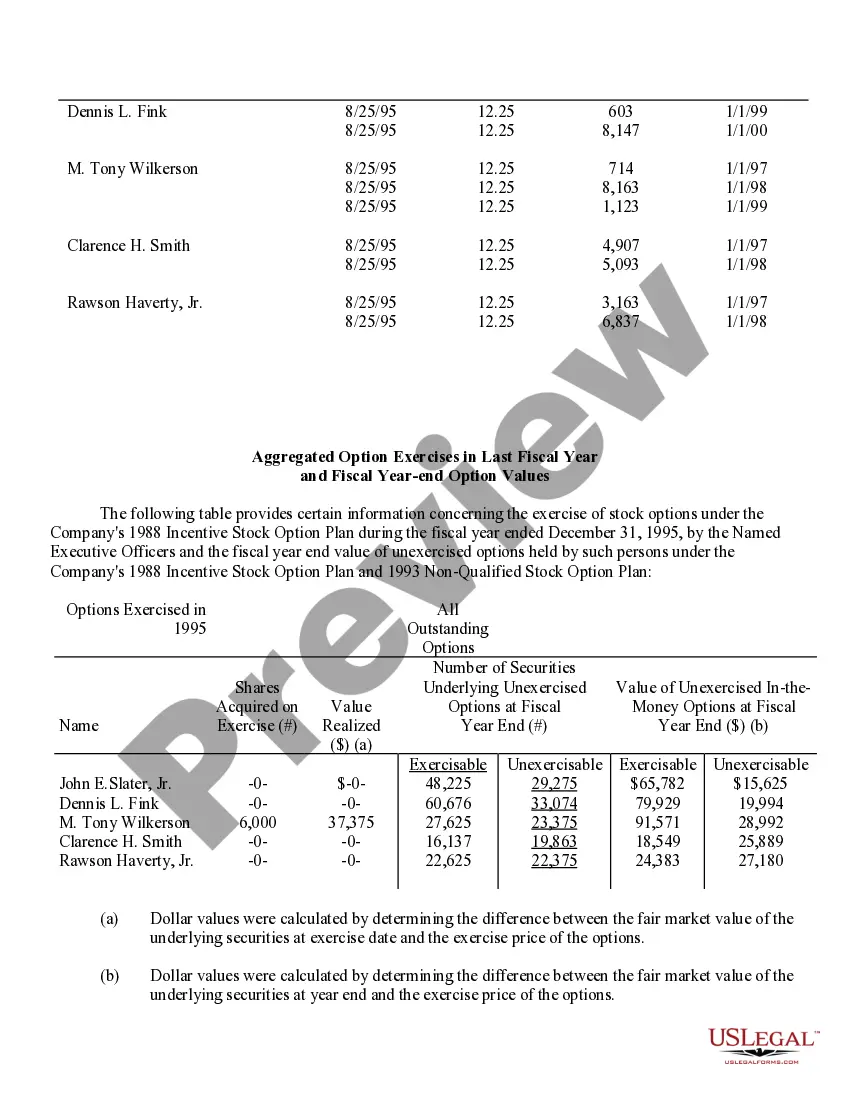
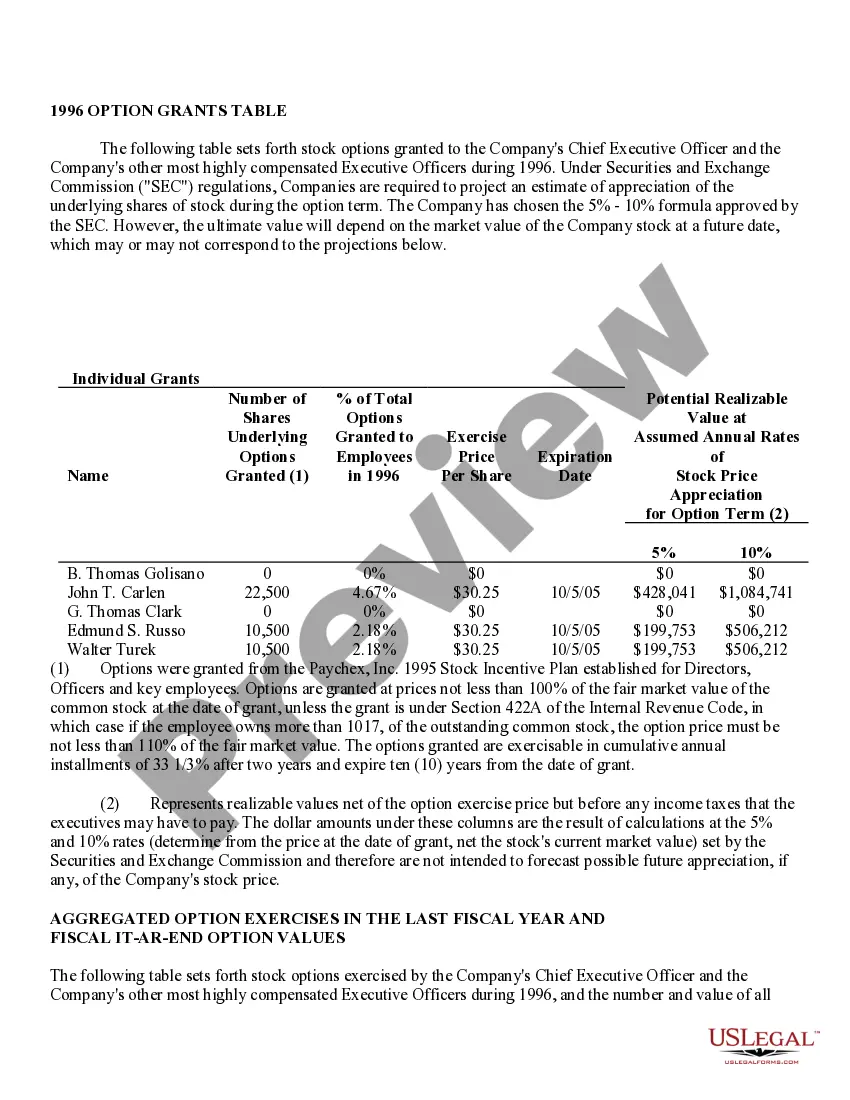
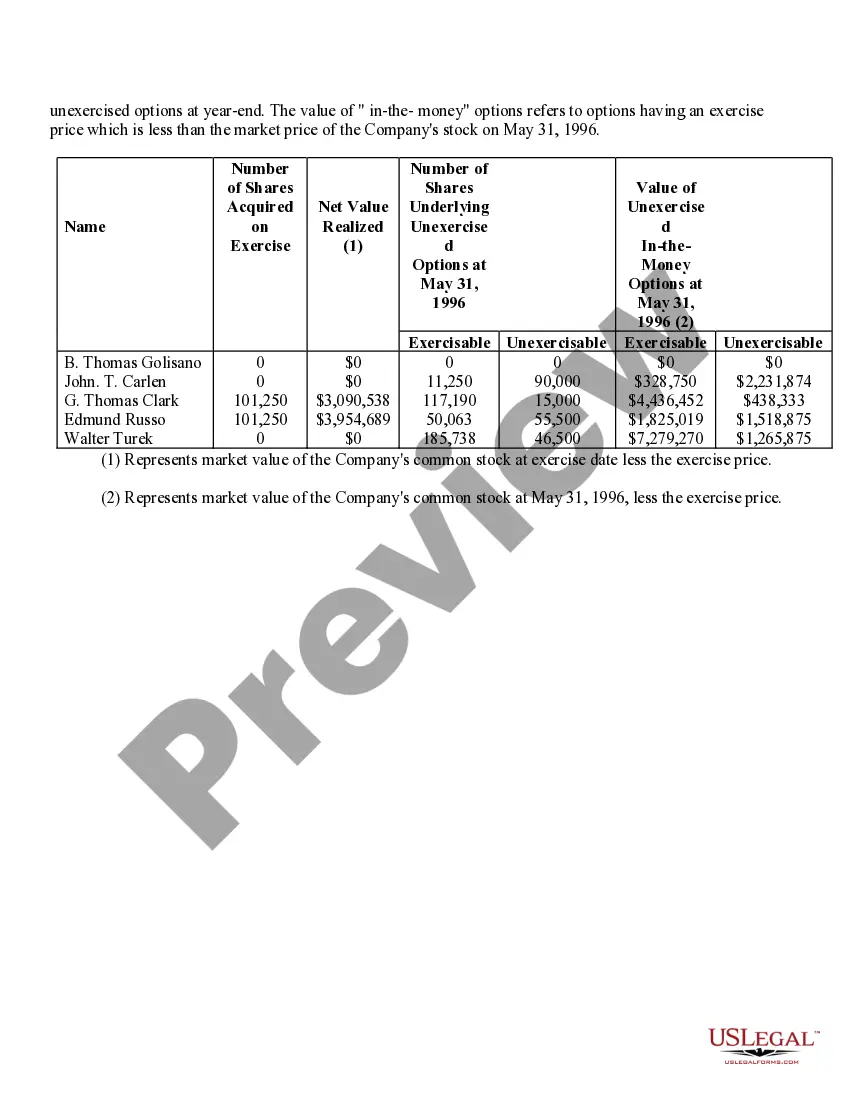
Nevada Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values
Description
How to fill out Stock Option Grants And Exercises And Fiscal Year-End Values?
If you want to total, acquire, or produce legitimate record web templates, use US Legal Forms, the largest variety of legitimate types, which can be found on the Internet. Use the site`s simple and easy handy look for to find the paperwork you need. A variety of web templates for company and person uses are sorted by groups and claims, or key phrases. Use US Legal Forms to find the Nevada Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values with a couple of mouse clicks.
In case you are previously a US Legal Forms customer, log in in your accounts and click the Down load option to have the Nevada Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values. You can also accessibility types you in the past downloaded in the My Forms tab of your respective accounts.
If you are using US Legal Forms the very first time, refer to the instructions beneath:
- Step 1. Be sure you have selected the shape for your appropriate city/country.
- Step 2. Make use of the Preview choice to examine the form`s content. Do not forget to learn the explanation.
- Step 3. In case you are not satisfied with all the develop, utilize the Lookup field at the top of the screen to locate other variations from the legitimate develop format.
- Step 4. Upon having identified the shape you need, click the Buy now option. Pick the costs strategy you like and put your accreditations to sign up for the accounts.
- Step 5. Process the deal. You can utilize your credit card or PayPal accounts to complete the deal.
- Step 6. Find the file format from the legitimate develop and acquire it in your device.
- Step 7. Comprehensive, modify and produce or sign the Nevada Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values.
Every legitimate record format you buy is the one you have forever. You have acces to each and every develop you downloaded in your acccount. Click on the My Forms section and choose a develop to produce or acquire once again.
Remain competitive and acquire, and produce the Nevada Stock Option Grants and Exercises and Fiscal Year-End Values with US Legal Forms. There are thousands of specialist and state-specific types you can utilize for your company or person requirements.
Form popularity
FAQ
You can calculate the aggregate exercise price by taking the strike price of the option and multiplying it by its contract size. In the case of a bond option, the exercise price is multiplied by the face value of the underlying bond.
Both call and put options have an exercise price. Investors also refer to the exercise price as the strike price. The difference between the exercise price and the underlying security's price determines if an option is ?in the money? or ?out of the money."
FMV influences the price employees, contractors, and other common stock option recipients must pay to purchase their stock options (also known as the strike price). The strike price must be greater than or equal to the FMV stated in the 409A valuation.
A strike price, also known as a grant price or exercise price, is the fixed cost that you'll pay per share in order to exercise your stock options so you can own them.
Exercise Price ? Also known as the strike price, the grant price is the price at which you can buy the shares of stock. Regardless of the future value of that particular stock, the option holder will have the right to buy the shares at the grant price rather than the current, actual price.
Every stock option has an exercise price, also called the strike price, which is the price at which a share can be bought. In the US, the exercise price is typically set at the fair market value of the underlying stock as of the date the option is granted, in order to comply with certain requirements under US tax law.
You have taxable income or deductible loss when you sell the stock you bought by exercising the option. You generally treat this amount as a capital gain or loss. However, if you don't meet special holding period requirements, you'll have to treat income from the sale as ordinary income.
Exercising a stock option means purchasing the issuer's common stock at the price set by the option (grant price), regardless of the stock's price at the time you exercise the option.