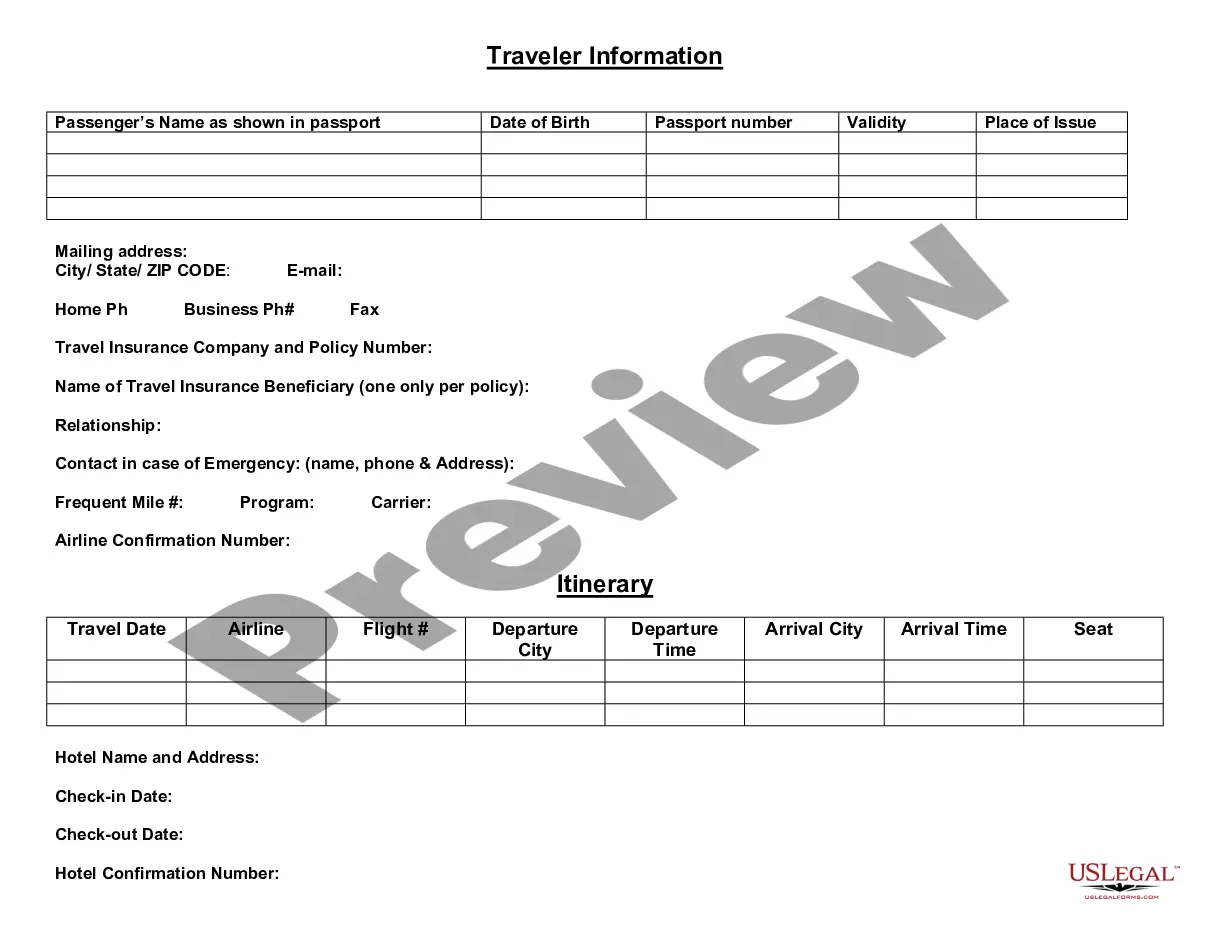
North Dakota Covenant Not to Sue by Husband and Wife for Accidental Injuries
Description
How to fill out Covenant Not To Sue By Husband And Wife For Accidental Injuries?
US Legal Forms - one of the largest collections of legal documents in the United States - offers a diverse selection of legal form templates that you can download or print.
By using the website, you can access numerous forms for both business and personal purposes, categorized by type, location, or keywords. You can obtain the latest versions of forms like the North Dakota Covenant Not to Sue by Husband and Wife for Accidental Injuries in moments.
If you have a subscription, Log In to download the North Dakota Covenant Not to Sue by Husband and Wife for Accidental Injuries from the US Legal Forms library. The Download button will appear on every form you view. You can find all previously downloaded forms in the My documents tab of your profile.
Proceed with the transaction. Use your credit card or PayPal account to finalize the payment.
Select the format and download the form to your device. Edit. Complete, modify, print, and sign the downloaded North Dakota Covenant Not to Sue by Husband and Wife for Accidental Injuries. Each template you added to your account has no expiration date and is yours indefinitely. So, if you wish to download or print another copy, simply navigate to the My documents section and click on the form you need. Access the North Dakota Covenant Not to Sue by Husband and Wife for Accidental Injuries with US Legal Forms, the largest collection of legal document templates. Utilize thousands of professional and state-specific templates that fulfill your business or personal needs and requirements.
- Make sure you have selected the correct form for your city/state.
- Click the Preview button to review the form's content.
- Review the form details to ensure you have chosen the right document.
- If the form does not meet your needs, utilize the Search field at the top of the screen to find the one that does.
- Once satisfied with the form, confirm your choice by clicking on the Buy Now button.
- Then, choose the payment plan you prefer and provide your information to register for an account.
Form popularity
FAQ
Rule 32 in North Dakota pertains to the admissibility of evidence during legal proceedings, focusing on the standard for what can be considered in court. This rule exists to ensure fairness and clarity in trials, allowing both parties to present relevant information effectively. When navigating legal issues, including those related to the North Dakota Covenant Not to Sue by Husband and Wife for Accidental Injuries, understanding these rules can support the outcome of your case. For legal forms relating to this matter, USLegalForms is a valuable resource.
If you're wondering about how to stop most frivolous lawsuits, you must contact an experienced attorney who can advise you on the best course of action to take. Very often, a wise option is to settle out of court by apologizing or offering a small compensation to resolve the issue even if you were not at fault.
Promise. 1) n. a firm agreement to perform an act, refrain from acting or make a payment or delivery. In contract law, if the parties exchange promises, each promise is "consideration" (a valuable item) for the other promise.
Covenant Not to Sue.A "covenant not to sue" is a legal term which means you promise not to file a lawsuit in court.It is different from the general release of claims covered above.
A promise is not legally binding, but a contract is. While people of honor and strong moral character strive to keep promises whenever possible, there are no legal repercussions for breaking one the way there are for breaching a contract.
An agreement not to sue, also called a covenant not to sue, in which the party seeking damages agrees not to sue the party that it has cause against. A covenant not to sue may indicate that the potential claimant will never sue or it may indicate that the claimant will postpone a lawsuit for a defined period of time.
A covenant not to sue legally obliges a party that could initiate a lawsuit not to do so. The covenant is made explicitly between two parties, and any third party that wants to make a claim is legally allowed to do so. Covenants not to sue are used to settle specific legal issues outside of the court system.
If the occupier is the owner of the property, then they will be the defendant in any claim. If the current occupier is a renter of the property, it may be the occupier or landlord liable. The ultimate answer will depend on the specific circumstances surrounding your accidents on private property.
assertion covenant (nonassert for short) is an agreement by a party not to seek to enforce patent or other intellectual property rights it may have against another party or parties.