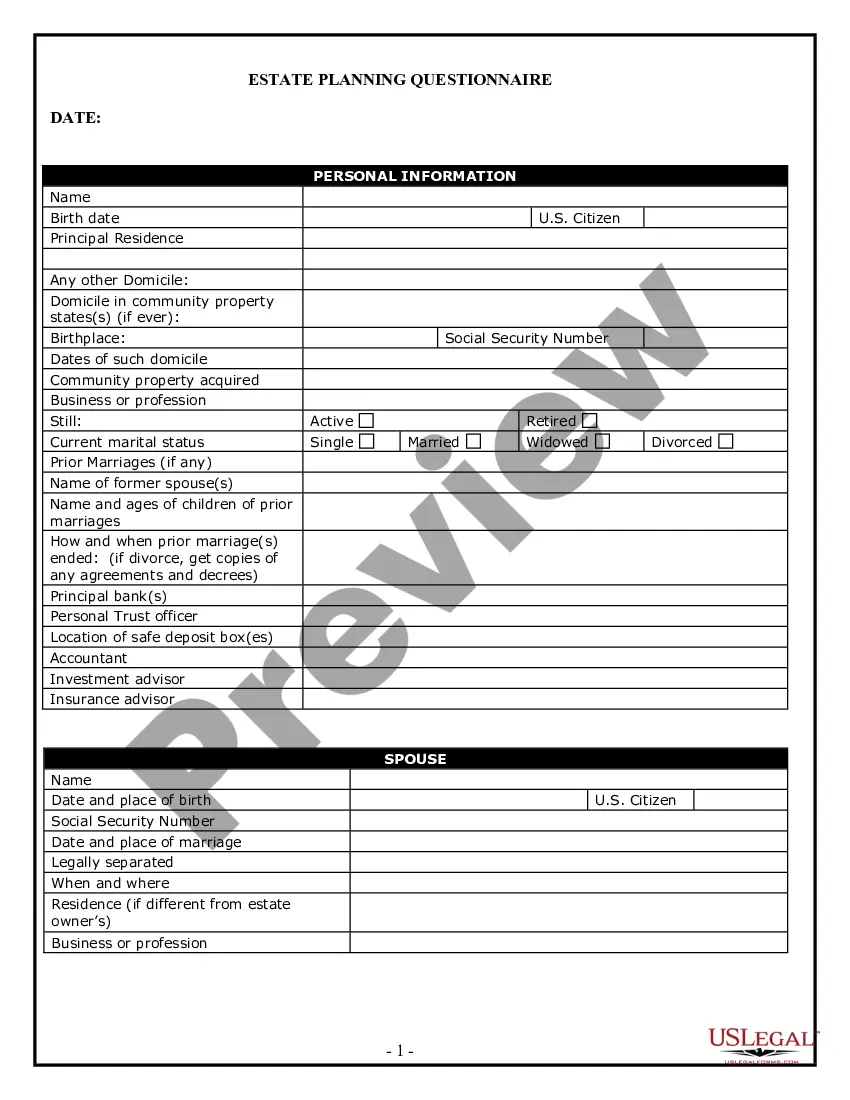
Montana Reservations of Other Interests
Description
How to fill out Reservations Of Other Interests?
If you need to full, down load, or produce legal document themes, use US Legal Forms, the largest assortment of legal forms, that can be found on-line. Make use of the site`s simple and practical look for to obtain the files you need. Various themes for enterprise and specific reasons are categorized by types and says, or keywords and phrases. Use US Legal Forms to obtain the Montana Reservations of Other Interests in a handful of click throughs.
Should you be presently a US Legal Forms client, log in in your accounts and click the Down load option to get the Montana Reservations of Other Interests. You can even access forms you previously saved from the My Forms tab of your accounts.
If you are using US Legal Forms the very first time, follow the instructions under:
- Step 1. Be sure you have chosen the shape for the appropriate metropolis/nation.
- Step 2. Take advantage of the Preview choice to look through the form`s content. Do not forget about to see the outline.
- Step 3. Should you be unsatisfied with the form, make use of the Research field near the top of the monitor to get other versions in the legal form web template.
- Step 4. When you have found the shape you need, click the Purchase now option. Pick the prices strategy you choose and put your accreditations to sign up on an accounts.
- Step 5. Process the transaction. You should use your Мisa or Ьastercard or PayPal accounts to finish the transaction.
- Step 6. Select the structure in the legal form and down load it on your system.
- Step 7. Total, modify and produce or signal the Montana Reservations of Other Interests.
Each legal document web template you get is your own eternally. You have acces to each form you saved with your acccount. Select the My Forms portion and pick a form to produce or down load again.
Compete and down load, and produce the Montana Reservations of Other Interests with US Legal Forms. There are thousands of expert and condition-certain forms you may use for the enterprise or specific requirements.
Form popularity
FAQ
Montana has eleven Indian tribes living on seven reservations. Together they make up about six percent of Montana's population. Before trappers and settlers came west, Indian people roamed freely across the state, following the huge buffalo herds that once covered the plains.
Montana is also home to many Indians of other tribes living on and off the reservations. Each of these tribal nations has its own culture, language, identity, and history which continue to be important to their individual and collective identity today despite many changes over the last two centuries.
(EU1) ? There are seven Indian reservations in Montana; Crow, Northern Cheyenne, Fort Peck, Fort Belknap, Rocky Boy's, Blackfeet, Flathead. (EU4) ? The Little Shell Chippewa do not have a reservation. What are reservations?
You can live on a reservation but you can't become a tribal member. In order to become a member of a tribe, you must be at least 1/8% Native American, for some of the Native American tribes, other tribes require 1/4% Native American.
You may own a combination of trust lands and fee lands on one or more reservations. The General Allotment Act of 1887 divided American Indian treaty lands into individually owned parcels of land known as allotments.
The Crow Indian Reservation, headquartered in Crow Agency, is the largest reservation in Montana encompassing approximately 2.2 million acres. The Crow Tribe has a membership of 11,000, of whom 7,900 reside on the Crow Indian Reservation.
Introduction. About four percent of the present population of Montana is indigenous. The major groups include the Assiniboin, Blackfeet, Chippewa-Cree, Crow, Flathead, Grosventres, Kalispel, Kootenai, Little Shell Band of Chippewa, Northern Cheyenne, Piegan, Salish, and Spokane.
Where Are Reservations Located? The highest concentration of Native American reservations can be found in the western United States. California alone has 103 reservations that are recognized by the federal government.