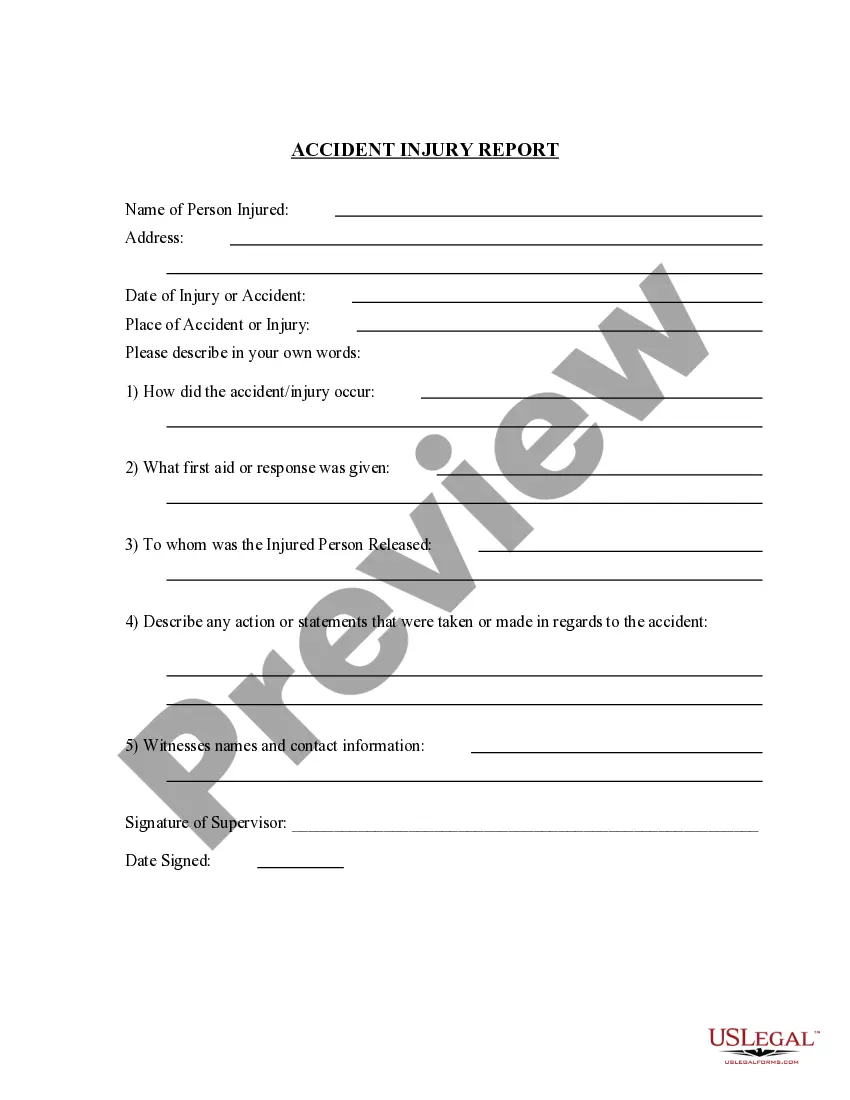
Montana Job Safety Recommendation
Description
How to fill out Job Safety Recommendation?
Are you currently in a situation where you frequently require documents for both corporate or personal purposes.
There are numerous legitimate template documents available online, but finding reliable ones can be challenging.
US Legal Forms offers thousands of form templates, such as the Montana Job Safety Recommendation, designed to comply with federal and state regulations.
Once you locate the right form, simply click Purchase now.
Select the pricing plan you desire, enter the required information to create your account, and pay for your order using your PayPal or credit card.
- If you are already familiar with the US Legal Forms website and have an account, simply Log In.
- Then you will be able to download the Montana Job Safety Recommendation template.
- If you do not have an account and wish to start using US Legal Forms, follow these steps.
- Obtain the form you need and ensure it is for the correct region/area.
- Utilize the Review option to scrutinize the form.
- Check the description to confirm you've selected the appropriate form.
- If the form is not what you are seeking, use the Search field to find the form that meets your needs.
Form popularity
FAQ
State Plans are OSHA-approved workplace safety and health programs operated by individual states or U.S. territories. There are currently 22 State Plans covering both private sector and state and local government workers, and there are six State Plans covering only state and local government workers.
Those not covered by the OSH Act include: self-employed workers, immediate family members of farm employers, and workers whose hazards are regulated by another federal agency (for example, the Mine Safety and Health Administration, the Department of Energy, Federal Aviation Administration, or Coast Guard).
The following 22 states or territories have OSHA-approved State Plans that cover both private and state and local government workers:Alaska.Arizona.California.Hawaii.Indiana.Iowa.Kentucky.Maryland.More items...
What is the minimum standard on safety and health in the workplace? The OSH Standards provide that every company shall keep and maintain its workplace free from work hazards that are likely to cause physical harm to the workers or damage to property.
OSHA standards are rules that describe the methods that employers must use to protect their employees from hazards. There are four groups of OSHA standards: General Industry, Construction, Maritime, and Agriculture. (General Industry is the set that applies to the largest number of workers and worksites).
Federal OSHA has no jurisdiction over State, municipal, or volunteer fire departments.
Montana is not a state plan state; that is, it does not have a federally approved occupational safety and health regulatory program. Therefore, the federal OSH Act governs occupational safety and health in the private sector (private businesses and nonprofit organizations) workplace in Montana.
With the RA 11058, employers are now required to comply with occupational safety and health standards including informing workers on all types of hazards in the workplace and having the right to refuse unsafe work, as well as providing facilities and personal protective equipment for the workers, among others.
The OSHA recommendations include seven core elements for a safety and health program: management leadership; worker participation; hazard identification and assessment; hazard prevention and control; education and training; program evaluation and improvement; and communication and coordination for host employers,
As indicated in Question and Answer #50 of OSHA's compliance directive CPL 2-1.34 (copy attached), OSHA standards are minimum safety requirements; employers may apply more protective requirements.