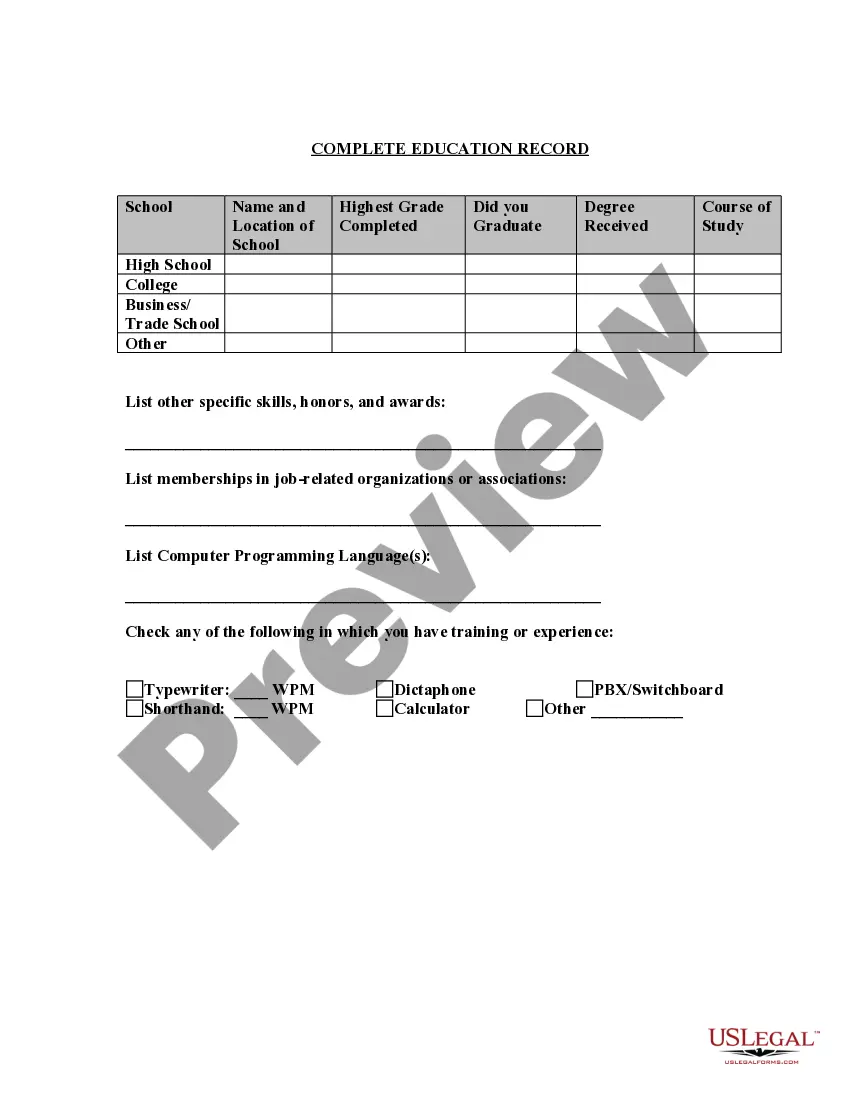
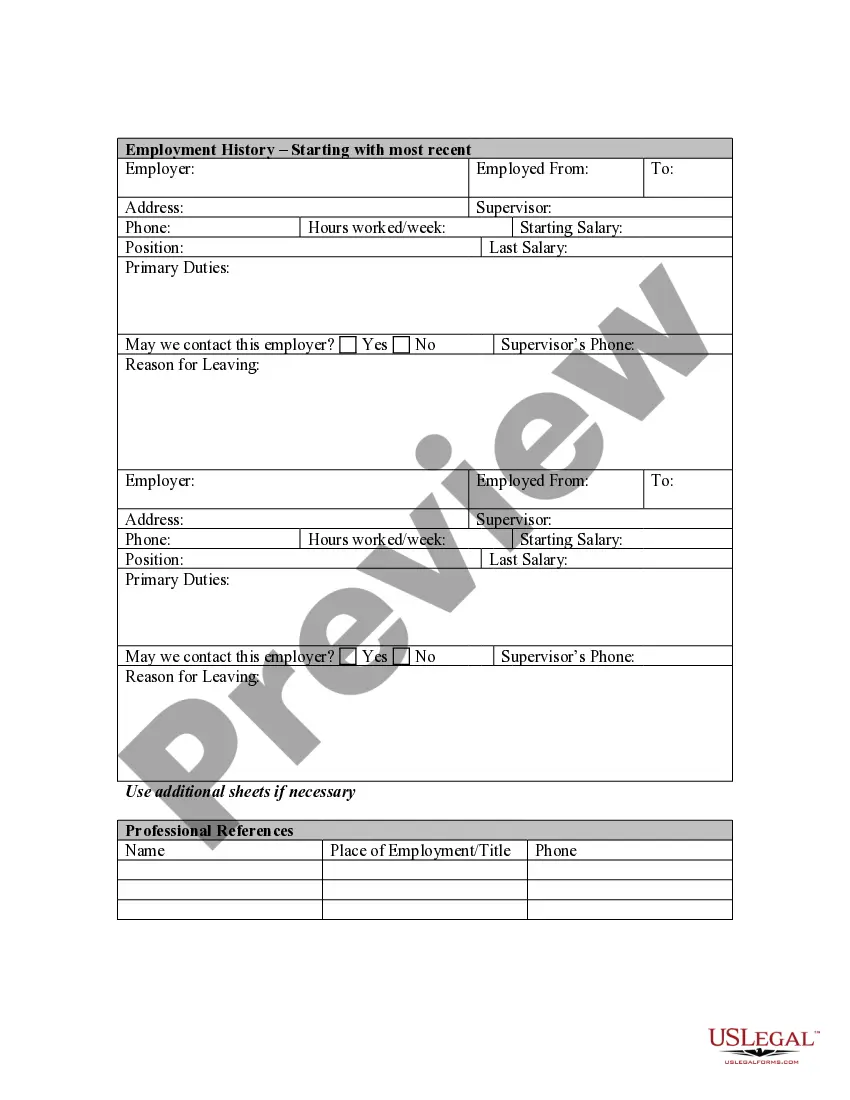
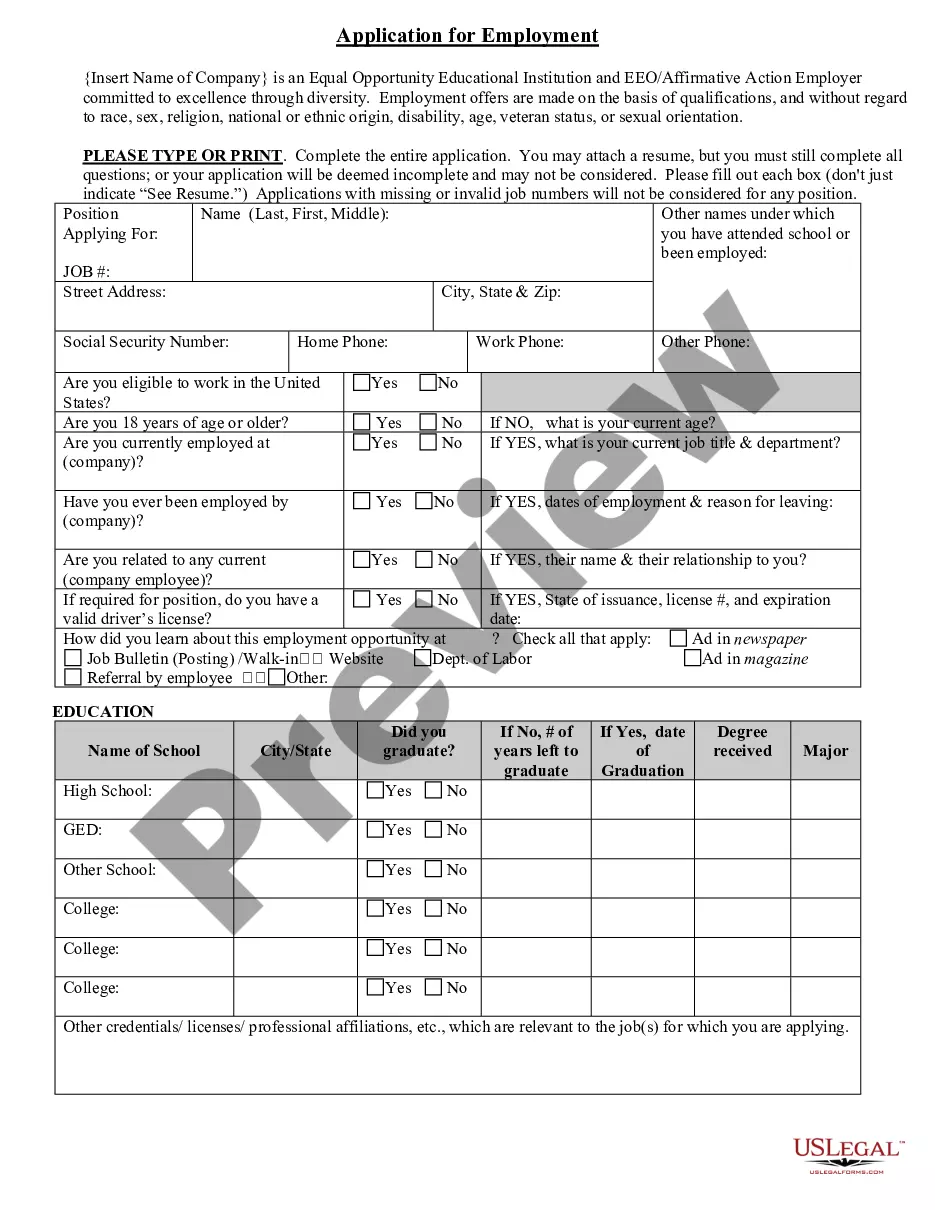
Maryland Application for Work or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position
Description
How to fill out Application For Work Or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, Or Nonexempt Position?
You may spend time on the web trying to locate the valid file format that meets the federal and state requirements you are looking for.
US Legal Forms provides a vast array of valid forms that have been reviewed by experts.
You can easily obtain or print the Maryland Application for Work or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position from our services.
If available, use the Review button to navigate through the file format as well.
- If you have a US Legal Forms account, you may Log In and then click the Obtain button.
- Afterward, you can fill out, edit, print, or sign the Maryland Application for Work or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position.
- Each valid file format you purchase is yours forever.
- To get an additional copy of any purchased form, go to the My documents tab and click the corresponding button.
- If you are visiting the US Legal Forms site for the first time, follow the simple instructions listed below.
- First, ensure you have selected the correct file format for the county/city of your choice.
- Review the form details to make sure you have selected the appropriate type.
Form popularity
FAQ
The answer to whether it is better to be an exempt or non-exempt employee depends on individual circumstances and career goals. Exempt employees often have a fixed salary and may enjoy greater job flexibility, while non-exempt employees can earn more through overtime. When navigating career options, consider how each classification aligns with your personal and financial needs while completing the Maryland Application for Work or Employment - Clerical, Exempt, Executive, or Nonexempt Position.
Tips For Drafting Job Descriptions for Exempt EmployeesAccuracy is King. The job description must be accurate.Accuracy Does Not Mean Exhaustion.Strong Verbs, Clear Impact.Focus on Exempt Functions.Don't Shy Away From Degree Requirements.Assist With Can Diminish a Role.Consider Requiring Acknowledgement.
Simply put, an exempt employee is someone exempt from receiving overtime pay. It is a category of employees who do not qualify for minimum wage or overtime pay as guaranteed by Fair Labor Standard Act (FLSA). Exempt employees are paid a salary instead of hourly wages and their work is professional in nature.
Who is eligible for overtime pay? To qualify as an exempt employee one who does not receive overtime pay staff members must meet all the requirements under the duties and salary basis tests.
An exempt employee is not entitled overtime pay by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). These salaried employees receive the same amount of pay per pay period, even if they put in overtime hours. A nonexempt employee is eligible to be paid overtime for work in excess of 40 hours per week, per federal guidelines.
Exempt employees do not receive overtime pay, nor do they qualify for minimum wage. When an employee is exempt, it primarily means that they are exempt from receiving overtime pay. Exempt employees stand in contrast to nonexempt employees.
Salaried employees, who fit the description of "Executive," "Administrative" or "Professional," are generally exempt under the law from receiving overtime, regardless of the number of hours they are required to work in a week.
With few exceptions, to be exempt an employee must (a) be paid at least $23,600 per year ($455 per week), and (b) be paid on a salary basis, and also (c) perform exempt job duties. These requirements are outlined in the FLSA Regulations (promulgated by the U.S. Department of Labor).
In short, the executive exemption means employees whose primary duties comprise managerial tasks are not eligible for FLSA coverage like overtime pay. The roles that typically fall under the executive exemption include CEOs, mid-level managers, and shift managers.
Exempt employees refer to workers in the United States who are not entitled to overtime pay. This simply implies that employers of exempt employees are not bound by law to pay them for any extra hours of work. The federal standard for work hours in the United States is 40 hours per workweek.