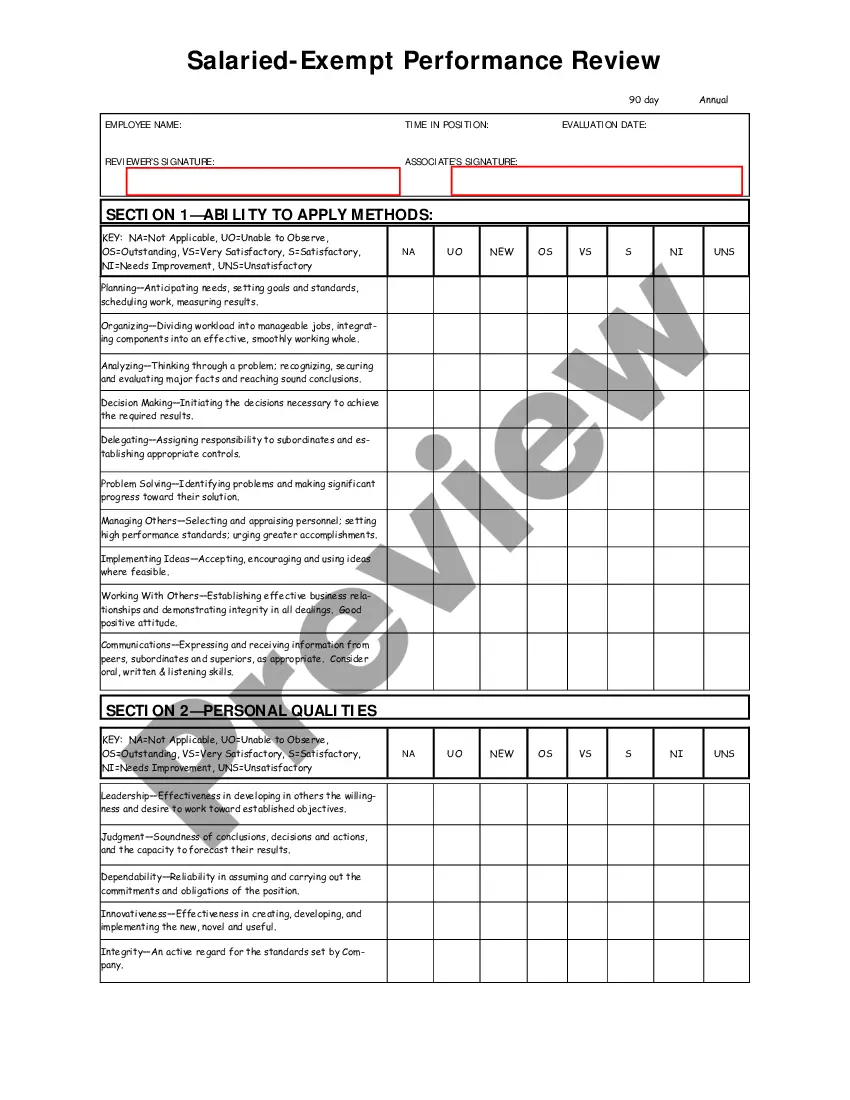
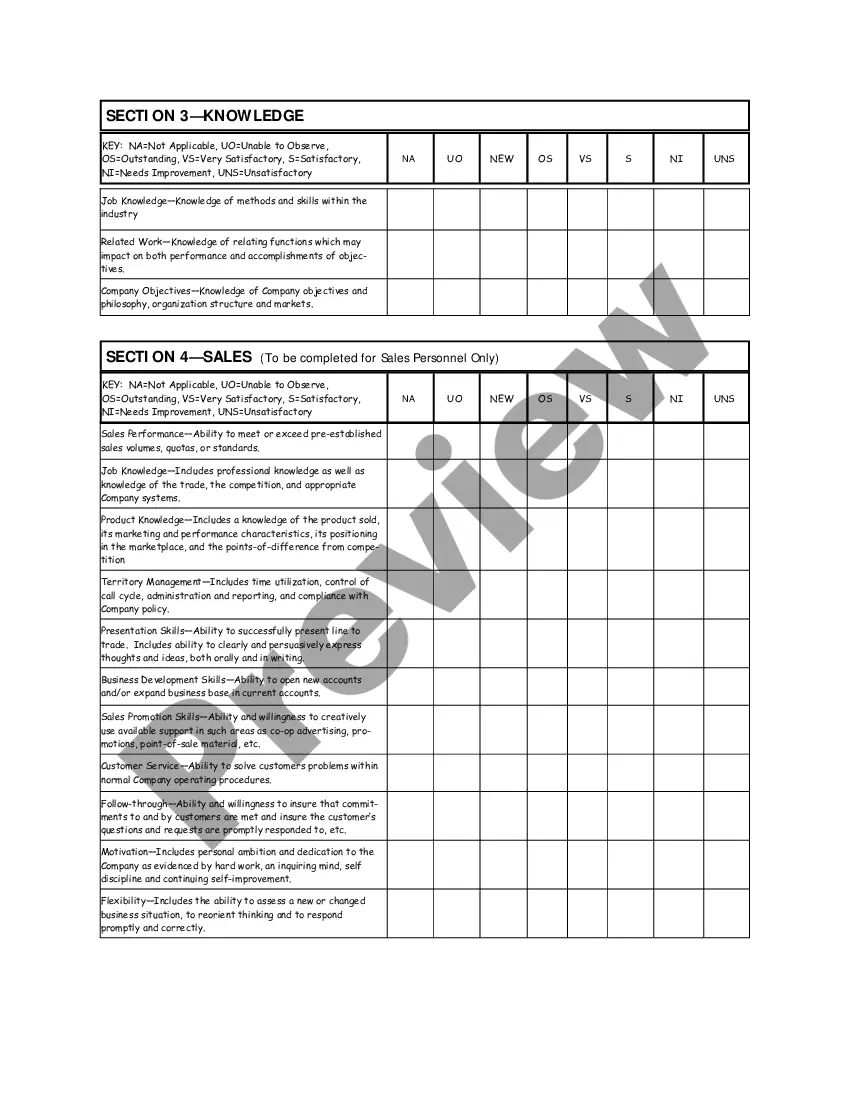
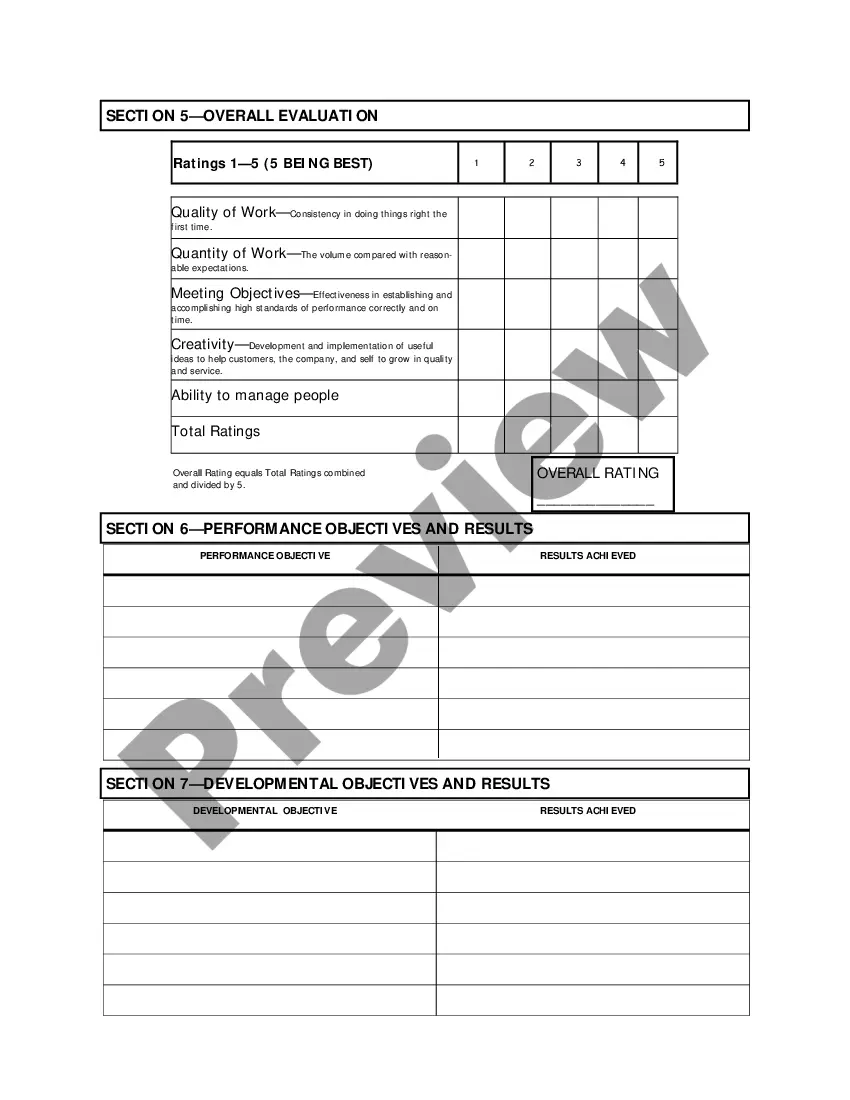
Indiana Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form
Description
How to fill out Salary - Exempt Employee Review And Evaluation Form?
Locating the correct legal document template can be a challenge.
Naturally, there are numerous templates accessible online, but how can you find the legal form you require.
Utilize the US Legal Forms website. The service offers thousands of templates, including the Indiana Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form, which can be utilized for both business and personal purposes.
You can preview the form using the Preview button and read the form description to ensure it meets your needs.
- All documents are reviewed by experts and comply with federal and state regulations.
- If you are already registered, Log In to your account and click on the Download button to obtain the Indiana Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form.
- Use your account to look through the legal forms you have acquired previously.
- Visit the My documents tab in your account and download another copy of the document you require.
- If you are a new user of US Legal Forms, here are simple steps you should follow.
- First, make sure you have selected the correct form for your city/state.
Form popularity
FAQ
In Indiana, the salary exempt threshold for employees generally aligns with federal guidelines, which define exempt status primarily for salaried employees. The Indiana Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form provides insights into these standards and helps employers determine who qualifies as exempt. Adhering to these regulations not only enhances workplace fairness but also minimizes the risk of legal challenges. For businesses, using this form can streamline evaluations and ensure that employees are classified correctly.
In 2025, the minimum salary for exempt employees is set to increase, reflecting the evolving standards in employment compensation. Employers in Indiana should prepare for these changes to ensure compliance with state and federal regulations. By reviewing the Indiana Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form, you can navigate these updates effectively and maintain appropriate payroll practices. This form helps ensure that your business remains compliant while treating employees fairly.
Writing an employee evaluation form involves setting clear criteria relevant to job responsibilities. Start with a brief introduction and a list of evaluation points reflecting the company’s goals. By using the Indiana Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form as a model, you can ensure that important factors are covered. Conclude with space for both achievements and areas of improvement to encourage balanced feedback.
Filling out an employee self-evaluation form requires honest reflection on your performance. Begin by reviewing your goals and accomplishments, using metrics where applicable. Consider the format of the Indiana Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form, as it can guide you in structuring your thoughts and highlighting areas for development. Aim for clarity in your explanations to showcase your understanding of your role.
To create an evaluation form, focus on clarity and structure. Start with an introduction explaining the purpose of the form, followed by sections for various performance indicators. Reviews often benefit from a framework like the Indiana Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form, which provides standardized criteria. Ensure the form encourages thoughtful responses to evoke meaningful insights.
Creating an employee evaluation form involves identifying essential performance metrics related to your organizational goals. Begin by outlining the key areas to assess, such as communication skills, teamwork, and problem-solving abilities. Integrating features from the Indiana Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form can enhance its effectiveness. Finally, ensure that the form is user-friendly to facilitate honest employee feedback.
To create an evaluation form in Word, start by opening a new document and organizing your content into sections like employee information, performance criteria, and feedback. Utilizing a template, like those found in the Indiana Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form, can simplify your task. Remember to include both quantitative and qualitative fields to foster comprehensive assessments. Save in a format that allows easy sharing for further use.
A good employee evaluation includes clear criteria related to job performance, goals achieved, and areas for improvement. For instance, using the Indiana Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form can guide you in assessing an employee’s contributions effectively. Providing constructive feedback and actionable suggestions enhances the evaluation process. Always focus on measurable outcomes to ensure clarity.
An employee performance evaluation form is a document used to assess and document an employee’s job performance. It typically includes sections for feedback, ratings, and goal setting. Utilizing the Indiana Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form can streamline this process, ensuring a thorough and standardized review.
Filling out a self-evaluation form involves reflecting on your achievements over the evaluation period. Address your strengths and areas for improvement, using specific examples to illustrate your points. By using the Indiana Salary - Exempt Employee Review and Evaluation Form, you can follow a structured approach that helps guide your reflection.