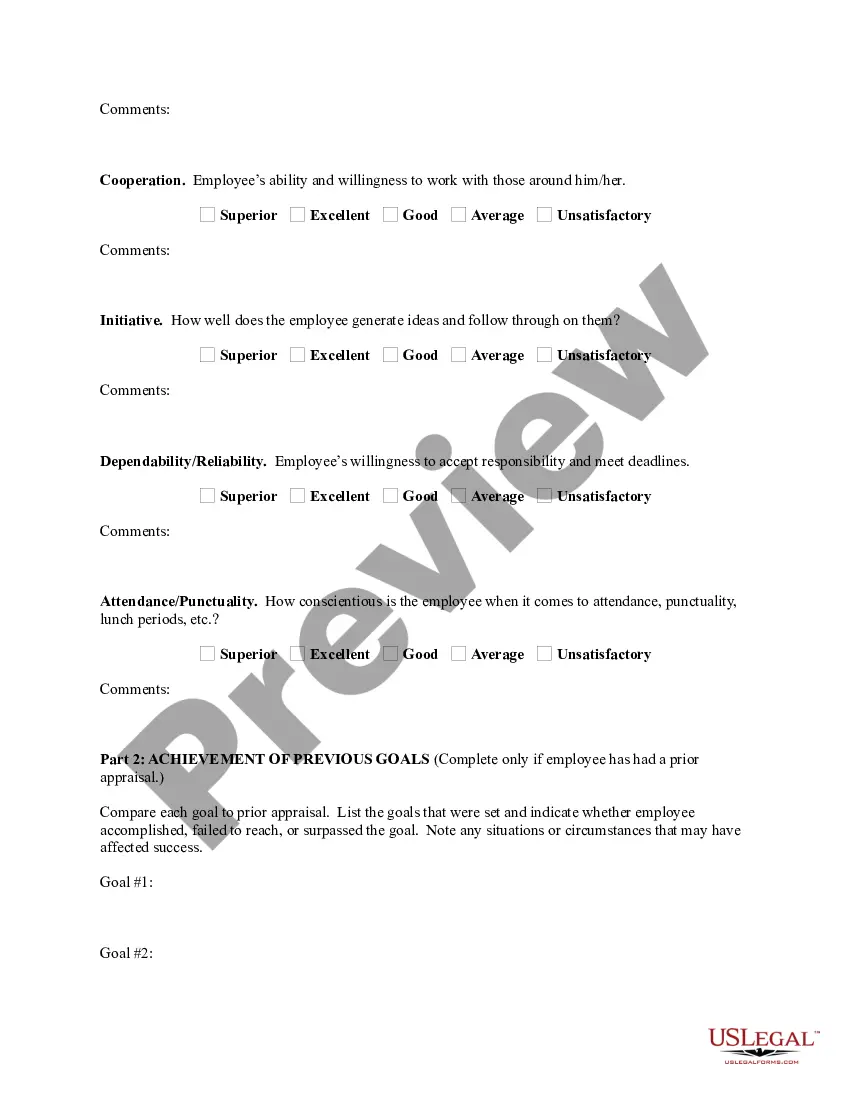
Software developer performance review examples are a useful tool to evaluate and assess the performance of software developers within an organization. These reviews help identify strengths and weaknesses and establish goals for professional growth. Here are some detailed examples of software developer performance review that can be adapted to various types of software development roles: 1. Technical Skills Assessment: a. Proficiency in programming languages such as Java, JavaScript, Python, etc. b. Ability to understand and implement algorithms efficiently. c. Capability to develop scalable and reliable code. d. Knowledge of different software development frameworks and libraries. e. Expertise in using development tools and integrated development environments (IDEs). 2. Project Management: a. Meeting project deadlines consistently. b. Successfully handling multiple projects/tasks simultaneously. c. Demonstrating effective time management skills. d. Proactively identifying and resolving project bottlenecks. e. Collaborating and communicating with cross-functional teams effectively. 3. Problem-Solving and Analytical Abilities: a. Aptitude for analyzing complex problems and proposing innovative solutions. b. Demonstrating logical reasoning and critical thinking skills. c. Showing creativity in designing robust algorithms and data structures. d. Identifying and debugging software defects efficiently. e. Ability to learn and adapt to new technologies quickly. 4. Collaboration and Teamwork: a. Actively participating in team discussions and decision-making processes. b. Supporting team members and providing constructive feedback. c. Demonstrating flexibility and adaptability in a team environment. d. Efficiently sharing knowledge and skills with colleagues. e. Contributing to a positive and collaborative work atmosphere. 5. Communication Skills: a. Ability to clearly articulate technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders. b. Active listening skills and openness to feedback and suggestions. c. Effective written communication for documentation and reporting. d. Demonstrating empathy and professionalism when interacting with team members. e. Providing timely and comprehensive updates on project progress. 6. Leadership and Initiative: a. Taking ownership of assigned tasks and projects. b. Demonstrating leadership skills by guiding and mentoring junior developers. c. Proactively suggesting process improvements and implementing them. d. Showing willingness to take on challenging responsibilities. e. Exhibiting a growth mindset and continuously updating skills. While these examples cover various aspects of software developer performance evaluation, it is important to tailor them according to the organization's specific requirements and job responsibilities.
Software Developer Performance Review Examples
Description
How to fill out Software Developer Performance Review Examples?
Drafting legal paperwork from scratch can sometimes be daunting. Certain scenarios might involve hours of research and hundreds of dollars invested. If you’re looking for a a simpler and more cost-effective way of creating Software Developer Performance Review Examples or any other forms without the need of jumping through hoops, US Legal Forms is always at your fingertips.
Our virtual library of over 85,000 up-to-date legal documents addresses virtually every aspect of your financial, legal, and personal affairs. With just a few clicks, you can instantly access state- and county-compliant templates diligently put together for you by our legal specialists.
Use our platform whenever you need a trustworthy and reliable services through which you can quickly find and download the Software Developer Performance Review Examples. If you’re not new to our services and have previously set up an account with us, simply log in to your account, select the form and download it away or re-download it at any time in the My Forms tab.
Don’t have an account? No worries. It takes minutes to set it up and navigate the catalog. But before jumping straight to downloading Software Developer Performance Review Examples, follow these recommendations:
- Review the document preview and descriptions to make sure you have found the form you are searching for.
- Make sure the template you select complies with the regulations and laws of your state and county.
- Choose the right subscription option to buy the Software Developer Performance Review Examples.
- Download the file. Then fill out, certify, and print it out.
US Legal Forms has a spotless reputation and over 25 years of experience. Join us now and turn document execution into something simple and streamlined!
Form popularity
FAQ
Tips for Conducting an Effective Software Engineer Performance Review Define clear objectives. Start with a clear vision of the software engineering performance review. ... Learn programmers' aspirations. ... Plan for growth. ... Look at past reviews. ... Clarify roles. ... Guide, don't just review. ... Read between the lines. ... Write notes.
Q: How do I give feedback to developers? Avoid Textual Forms of Communication. Carefully Plan the Meeting. Don't Give Feedback That's Too Indirect or Too Direct. Be Specific, Not Blurry. Apply the Situation, Behavior, Impact (SBI) Framework. End on a Question.
Positive productivity performance review phrases ?Always manages their time well and is extremely well-organized.? ?Displays endless drive to improve productivity, profits, and meet business goals.? ?Your excellent work ethic speaks for itself.? ?Consistently contributes measurable value to company goals and projects.?
How to Write Software Engineer Self-Performance Review Examples Identify Strengths and Weaknesses. ... Set Goals. ... Describe Your Accomplishments. ... Track Progress. ... Code Quality. ... Speed. ... Problem-Solving Skills. ... Collaboration.
How to Write Software Engineer Self-Performance Review Examples Identify Strengths and Weaknesses. ... Set Goals. ... Describe Your Accomplishments. ... Track Progress. ... Code Quality. ... Speed. ... Problem-Solving Skills. ... Collaboration.