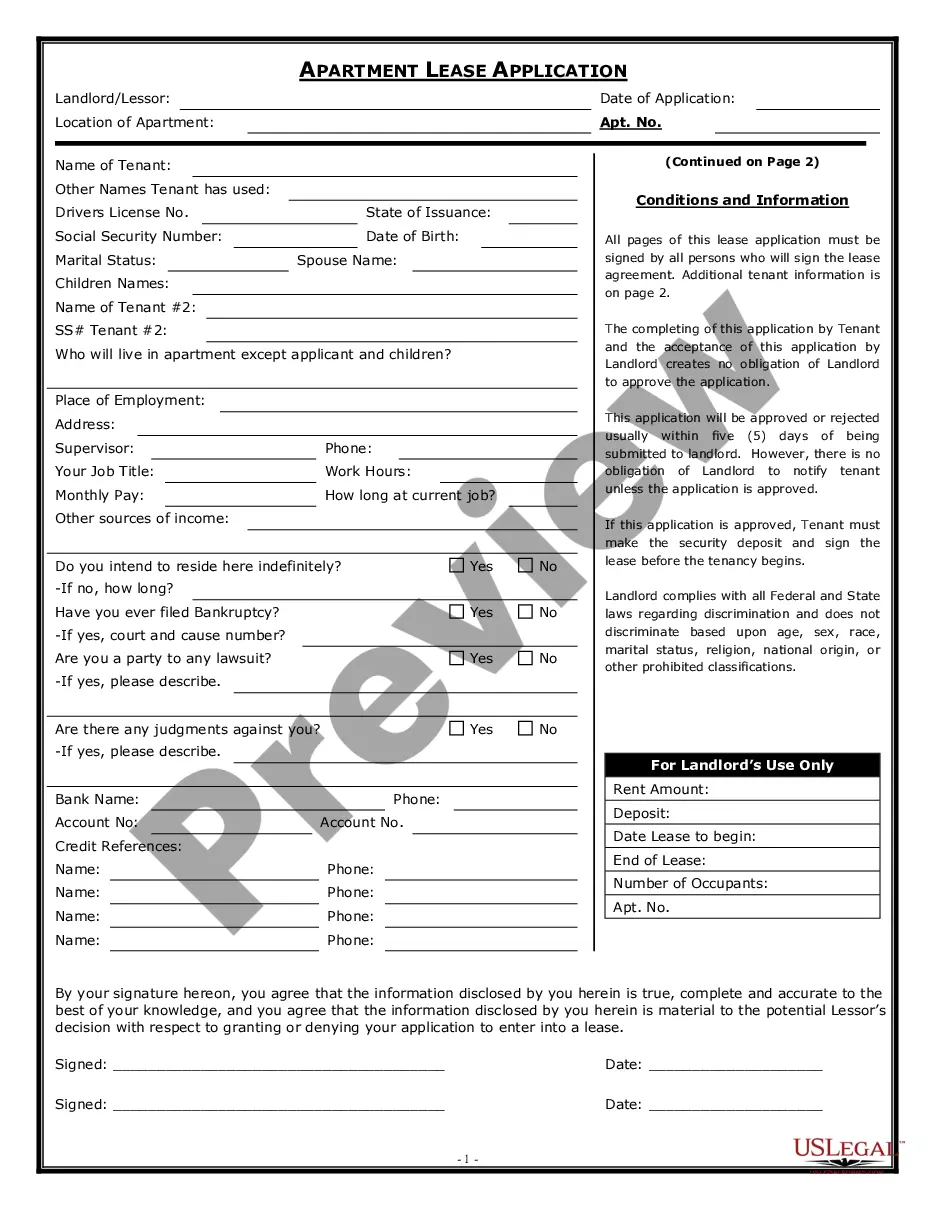
Non-disclosure Of Confidential Information In Fairfax
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
NDAs often include broad confidentiality clauses, covering general business information like financial data, trade secrets, and strategies. CDAs typically include clauses that address precise technical or scientific data, experimental methods, and intellectual property ownership.
A Confidential Disclosure Agreement (CDA), also referred to as non-disclosure agreement (NDA) or secrecy agreement, is a legal agreement between a minimum of two parties which outlines information the parties wish to share with one another for certain evaluation purposes, but wish to restrict from wider use and ...
Whereas confidentiality agreements are typically devised in employment or personal situations to protect sensitive information, NDAs are often used in business and legal settings to protect trade secrets, client lists, and financial data.
A Confidential Disclosure Agreement (CDA), also referred to as non-disclosure agreement (NDA) or secrecy agreement, is a legal agreement between a minimum of two parties which outlines information the parties wish to share with one another for certain evaluation purposes, but wish to restrict from wider use and ...
Return of Information: After the conclusion of business between the parties, an NDA may require that the recipient confirm that sensitive information has been returned or destroyed.
An NDA creates a confidential relationship between the parties, typically to protect any type of confidential and proprietary information or trade secrets. As such, an NDA protects non-public business information. Like all contracts, they cannot be enforced if the contracted activities are illegal.
Conditions of Disclosure to Third Parties. The general rule under the Privacy Act is that an agency cannot disclose a record contained in a system of records unless the individual to whom the record pertains gives prior written consent to the disclosure. There are twelve exceptions to this general rule.