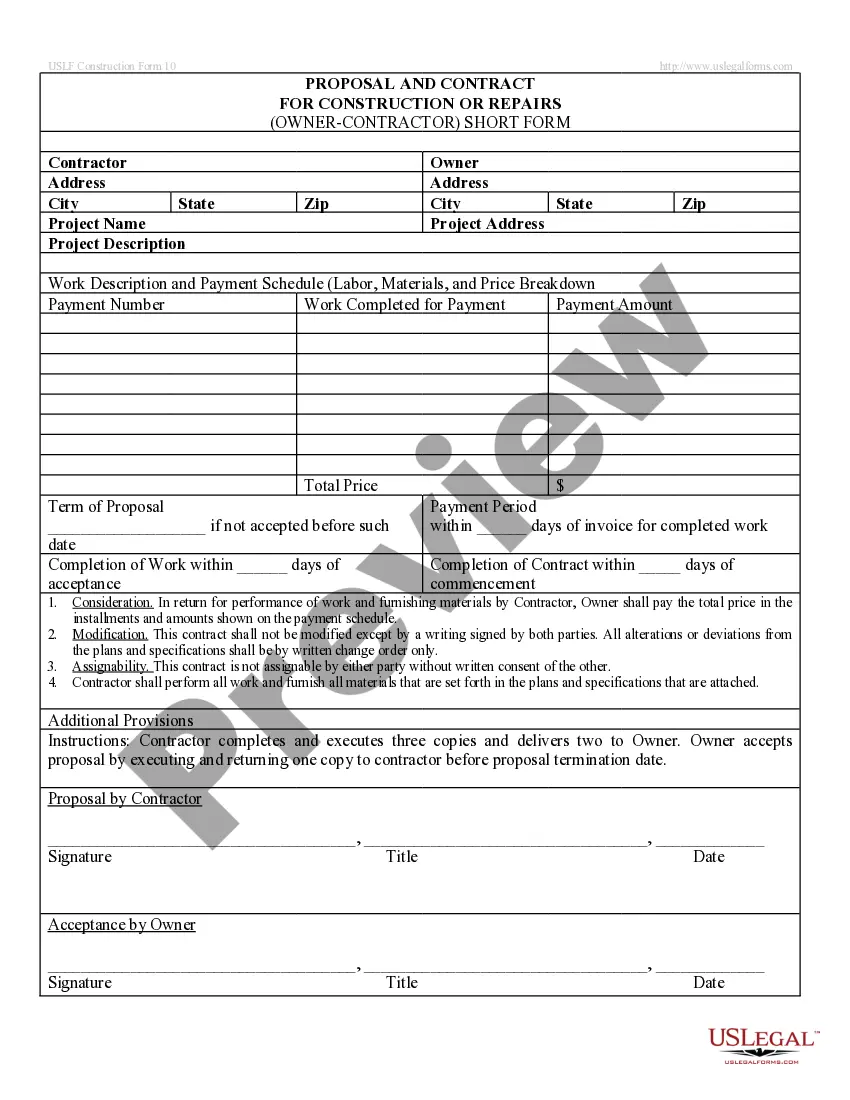
Contingent Contract With Case Law In Tarrant
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Contingency clauses help parties find common ground when they have divergent future expectations. However, they come with complexities and potential drawbacks, such as increased administrative overhead and the need for careful negotiation and drafting.
In the case of conditional contracts, conditions that need to be fulfilled are certain, i.e., bound to happen, which is not the case with contingent contracts, as such conditions may or may not happen.
Conditions are requirements set by lenders that must be met for the approval to move forward. Contingencies, on the other hand, are provisions that allow you to back out of the mortgage agreement under specific circumstances.
A "contingent contract" is a contract to do or not to do something, if some event, collateral to such contract, does or does not happen.
In the case of conditional contracts, conditions that need to be fulfilled are certain, i.e., bound to happen, which is not the case with contingent contracts, as such conditions may or may not happen.
Contingent contracts to do or not to do anything if a specified uncertain event does not happen within a fixed time may be enforced by law when the time fixed has expired and such event has not happened or, before the time fixed has expired, if it becomes certain that such event will not happen.