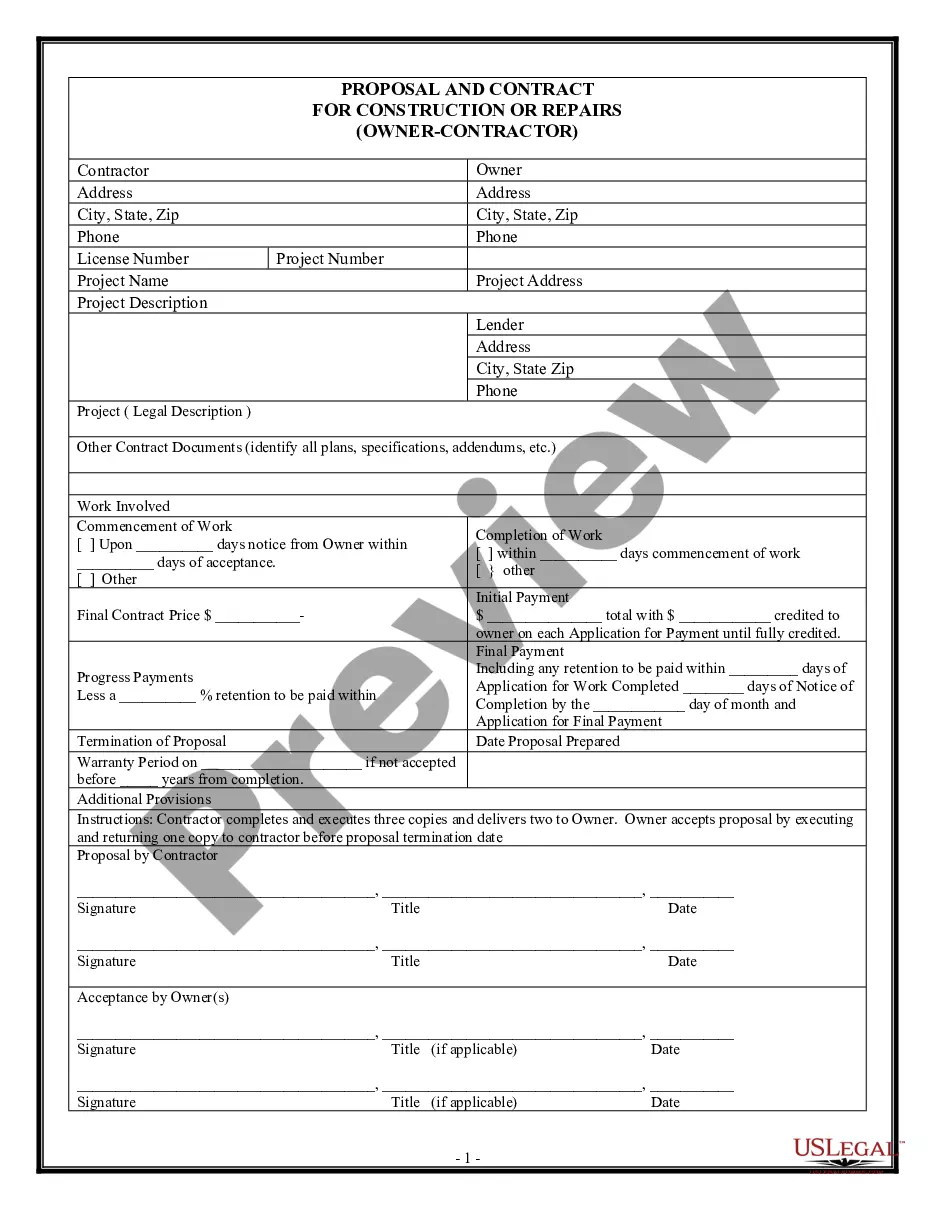
Contingency Agreement Sample For Drrm In Maryland
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Steps of a disaster recovery plan Establish downtime impact parameters. Identify critical operations. Plan initiation. Risk assessment. Response. Recovery. Plan evaluations and testing. Disaster recovery plans and remote team considerations for MSPs.
A good disaster recovery plan is both proactive and reactive and has four components: equipment, data, facilities, and personnel. Equipment includes the hardware and software used to maintain and protect your system, as well as restore functionality in the event of a disaster.
What should a disaster recovery plan include? Goals. Personnel. IT inventory. Backup procedures. Disaster recovery procedures. Disaster recovery sites. Restoration procedures.
Typically, the following steps are involved in creating a DRP: Conduct a BIA. Create a risk analysis. Develop a goals statement. Identify the DRP team. Take inventory of IT. Create an internal communication strategy. Create an external communication strategy. Develop a data backup, recovery and redundancy plan.
Although these may vary somewhat based on the organization, here are the basic disaster recovery plan steps: Risk assessment. Evaluate critical needs. Set disaster recovery plan objectives. Collect data and create the written document. Test and revise.
5 Disaster Recovery Policy (DRP) Best Practices Prepare for physical disasters. Protect against cyber disasters. Redundancy is critical. Assign responsibilities. Test and review your disaster recovery plan.
An IT disaster recovery plan template is a crucial runbook that outlines the end-to-end process and sequence of steps your organization will take to recover applications from a disruptive event, such as a power outage, cyber attack, or hardware failure.