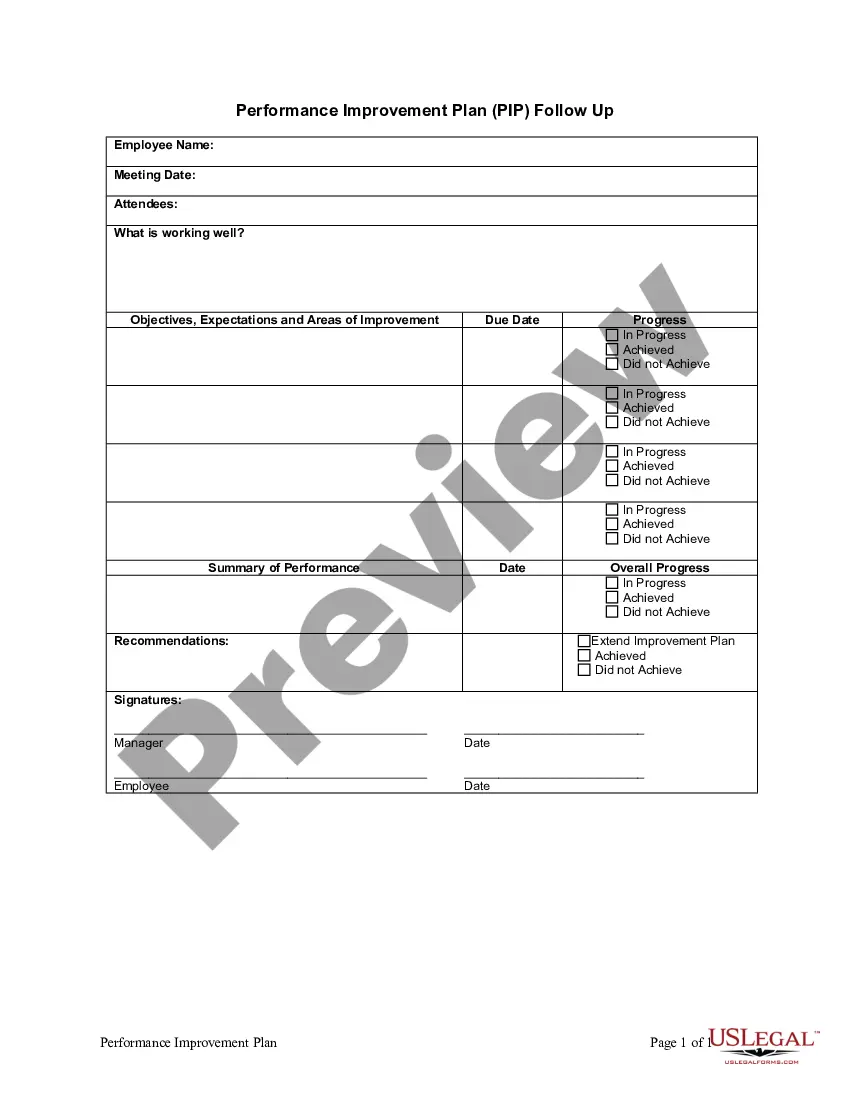
High Risk For Activity Intolerance In King
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
The nursing diagnosis Sedentary lifestyle (SL) was included in the NANDA-International in 2004.
Encourage gradual increase of activity as condition improves. Position for optimal comfort and activity tolerance (e.g., sitting for self-care). Monitor physiologic response to activity; adjust ingly. Provide range of motion actions (active, passive or assistive) per prescribed limitations.
Activity intolerance is a hallmark symptom of heart failure, and it can also appear after having a heart attack. Other medical conditions, such as COPD and hypothyroidism may also lead to activity intolerance.
Optimize Activity Tolerance Preplan and pace activity; balance activity with periods of rest; allow for uninterrupted sleep. Support coping and manage anxiety to minimize energy expenditure. Encourage gradual increase of activity as condition improves.
Follow your provider's instructions for building your tolerance to exercise. That will likely mean getting a certain amount of physical activity at a set level of effort. It could mean eating more protein or making sure you manage the condition that caused your intolerance to exercise.
There are various physical factors that can reduce activity tolerance, including advanced age, pain, bone and joint problems, heart disease, and dementia. Psychological factors, such as stress and depression, can also decrease the ability to endure daily activities.
Management and Treatment For many people, a program of physical activity (exercise training) is the best treatment for exercise intolerance. Exercise training means performing a physical activity at a moderate intensity for up to an hour three times a week. A provider may make a custom exercise training plan for you.