Difference Between Asset Sale And Stock Sale Without Tax Implications In Washington
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Stocks are financial assets. They're not real assets. A financial asset is a liquid asset that gets its value from a contractual right or ownership claim.
In addition to the $270,000 standard deduction detailed above, gain on some assets is exempt from the tax altogether, including: Real estate and gains from privately held entities directly attributable to a real estate sale. Retirement accounts. Certain livestock.
Almost everything you own and use for personal or investment purposes is a capital asset. Examples of capital assets include a home, personal-use items like household furnishings, and stocks or bonds held as investments.
You could: Stagger the sale of assets over several tax years to make the most of using your CGT allowance over several years. You could sell part of a share portfolio on 3 April and the rest on 6 April to take advantage of two years' CGT allowance. Offset any losses you've made on other assets.
For the target, a stock sale is usually a nonevent from a tax perspective. The buyer in a stock sale does not get a step-up in tax basis in the assets that comprise the target company, and thus is not able to increase their depreciation and amortization deductions in the same way as in an asset sale.
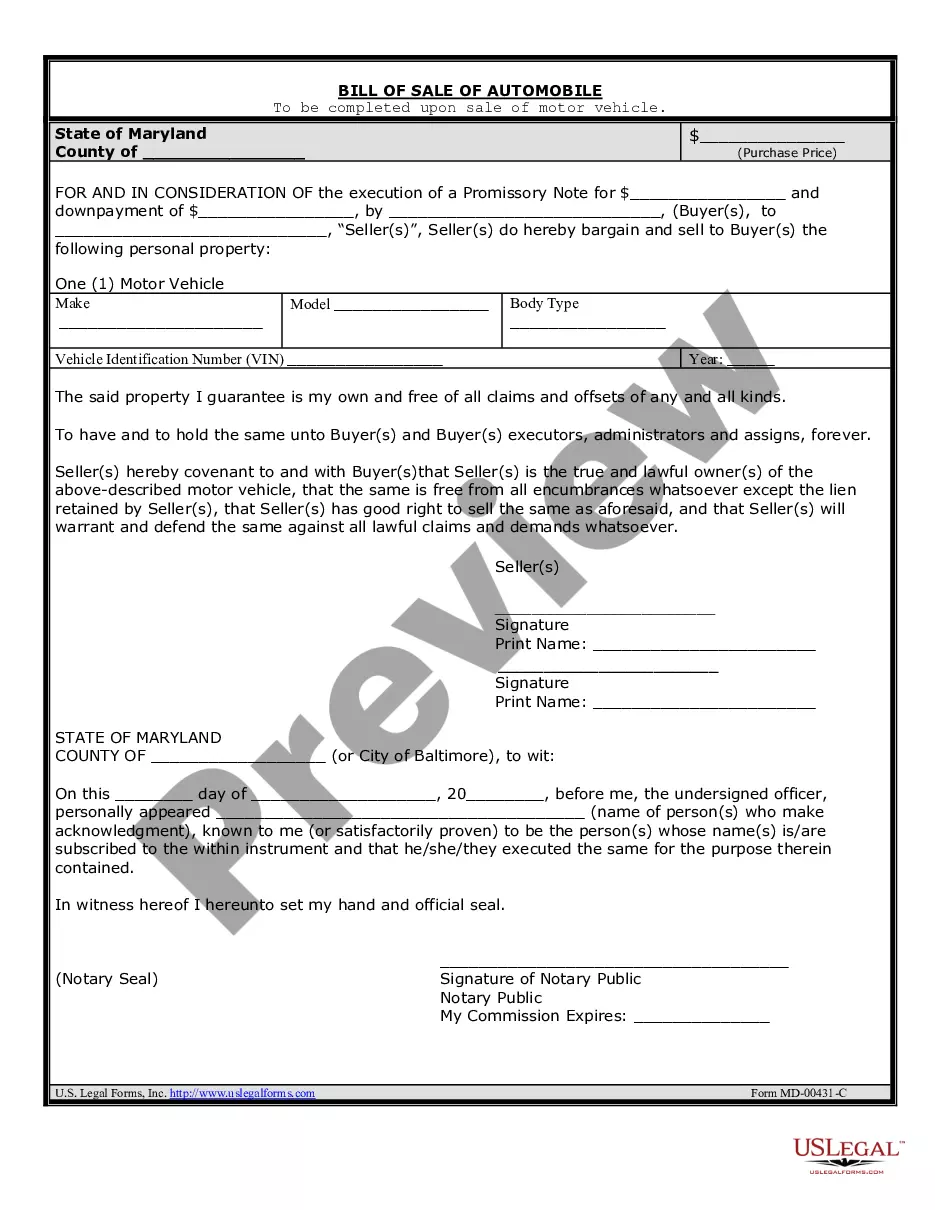
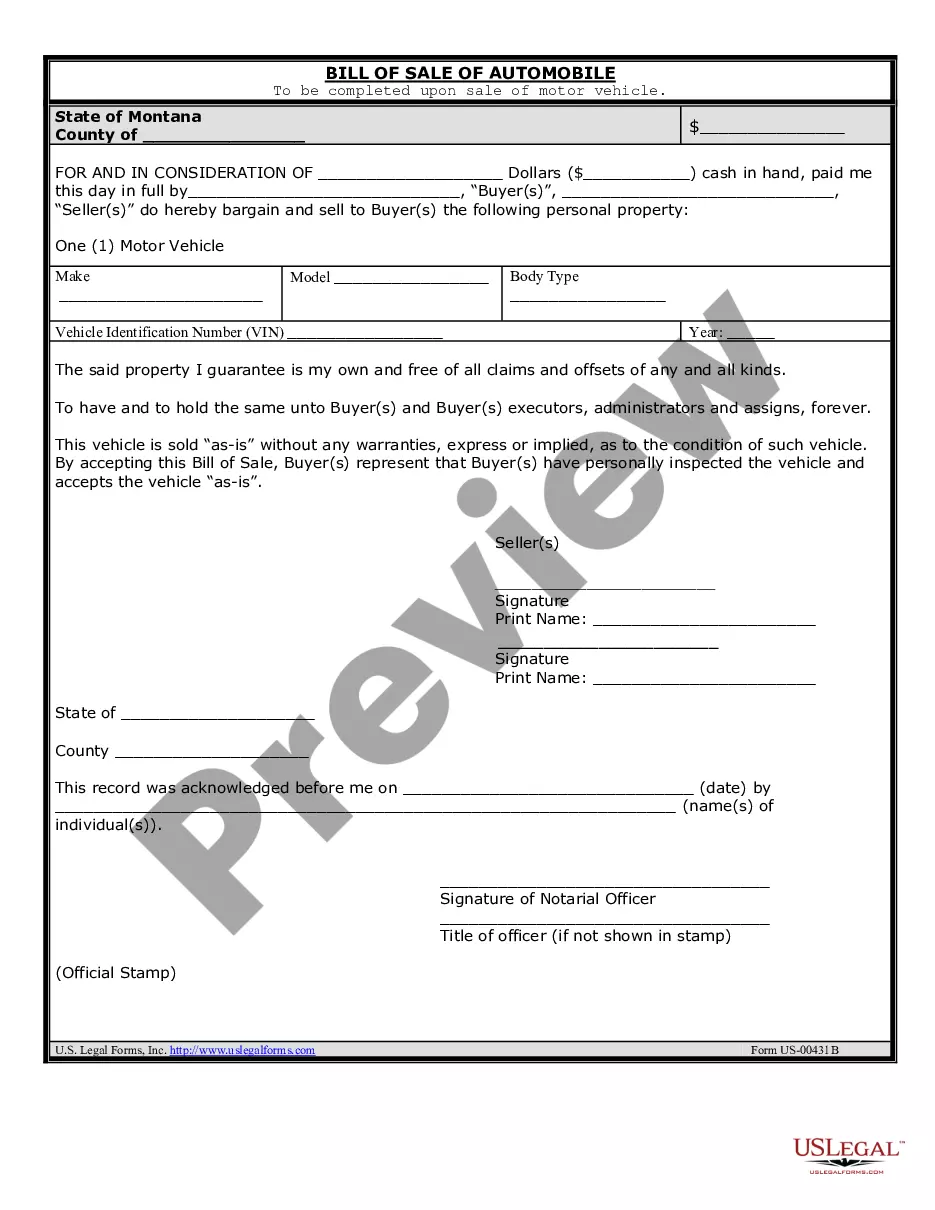
In an asset sale, the ownership of these acquired assets would change hands, with the buyer negotiating separately for each asset. In a stock sale, ownership of such assets does not change hands in the same way. The target still retains its ownership typically, even if the target has a new owner.
Investing in retirement accounts eliminates capital gains taxes on your portfolio. You can buy and sell stocks, bonds and other assets without triggering capital gains taxes. Withdrawals from Traditional IRA, 401(k) and similar accounts may lead to ordinary income taxes.
For 2025, that threshold for individuals rises to $48,350. Those with the married filing jointly status get double these amounts, while married filing separately and head of household each have their own levels, too. Earn up to this level in taxable income, and you'll enjoy that 0 percent rate on long-term gains.
What is the Current Washington Capital Gains Tax? The capital gains tax in Washington state is a 7% tax on profits from the sale of long-term assets (owned for over a year before selling them) over $270k for the 2024 tax year. For 2023, this number was $262,000.
Common strategies to avoid paying CGT, include: Main residence exemption. Temporary absence rule. Investing in superannuation. Timing capital gain or loss. Partial exemptions.