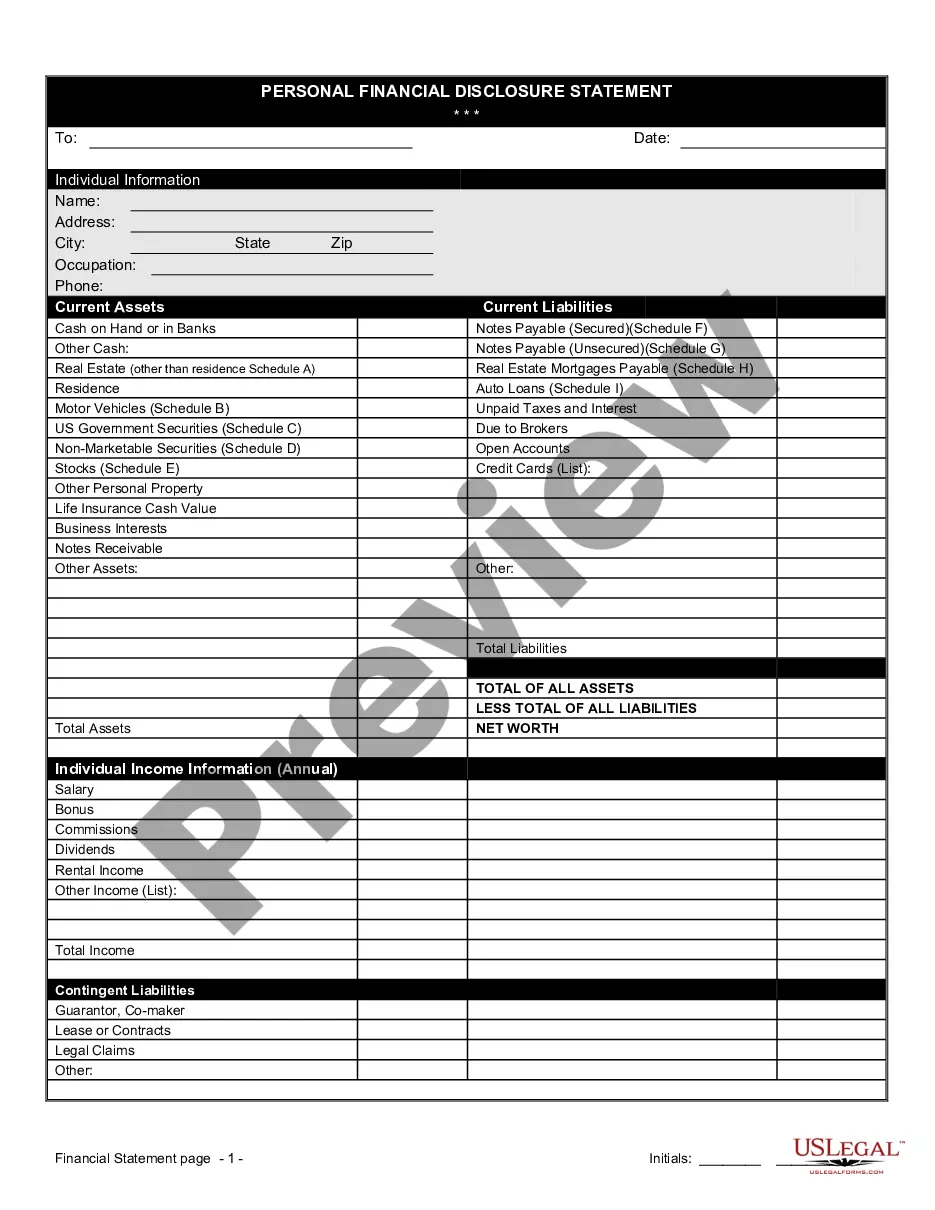
Contract Management With Example In Maricopa
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
The stages of contract management can be broken down into pre-signature (creation, negotiation/collaboration, and review/approval) and post-signature (administration/execution, renewal/termination, and reporting/tracking).
There are five elements which, taken together, make a contract valid: offer; acceptance; consideration; capacity; and. intention to create legal relations.
Contract management software is a digital platform designed to automate and streamline all stages of contract management—from drafting and negotiation to execution and ongoing maintenance. It is designed to help lawyers and other professionals create, negotiate, renew, and collect data on existing business contracts.
Exploring the key stages of the contract management lifecycle Stage 1: Contract Initiation. Stage 2: Contract Creation and Negotiation. Stage 3: Contract Approval. Stage 4: Contract Execution. Stage 5: Contract Monitoring and Management. Stage 6: Contract Renewal or Termination.
Contract management is the process of managing legally-binding agreements from initiation through to execution. Contract management activities include creation and negotiation, execution, compliance monitoring and renewal or close out.
This good practice framework defines the four blocks – structure and resources, delivery, development, and strategy – comprising 11 areas (Figure 1) that organisations should consider when planning and delivering contract management.
To be legally enforceable, an agreement must contain all of the following criteria: An offer and acceptance; Certainty of terms; Consideration; An intention to create legal relations; Capacity of the parties; and, Legality of purpose.
To understand that, you need to know about the 5 essential elements of a valid contract: offer, acceptance, consideration, mutual intent, capacity and legality. Understanding these 5 fundamental elements of a contract can help you protect your interests and avoid potential legal disputes.
Some examples of Contract Management activities are: Phone calls with suppliers; Meetings with suppliers; Score carding of suppliers; Site visits; Analysing performance information; Problem solving; Benchmarking against other similar contracts/suppliers; Analysing management information.