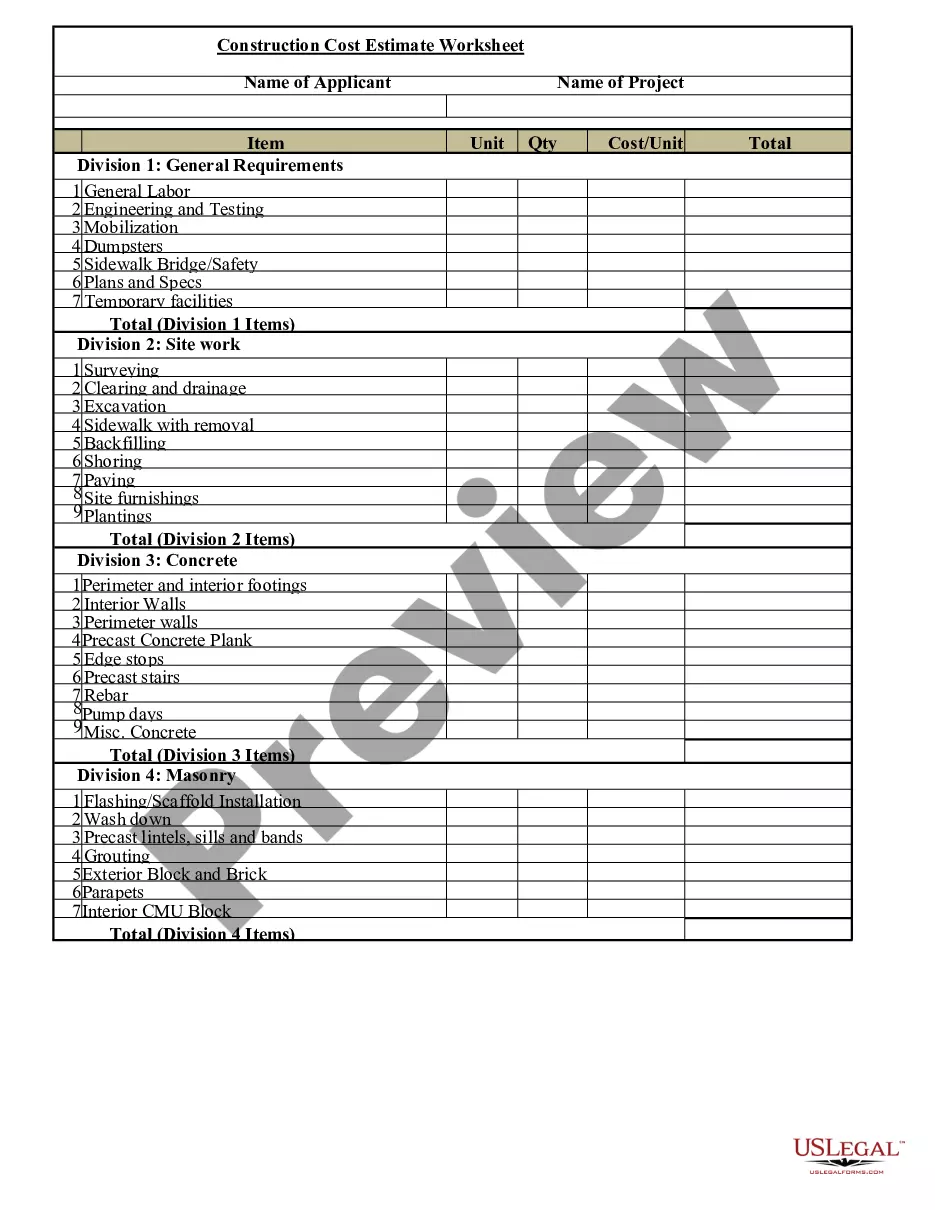
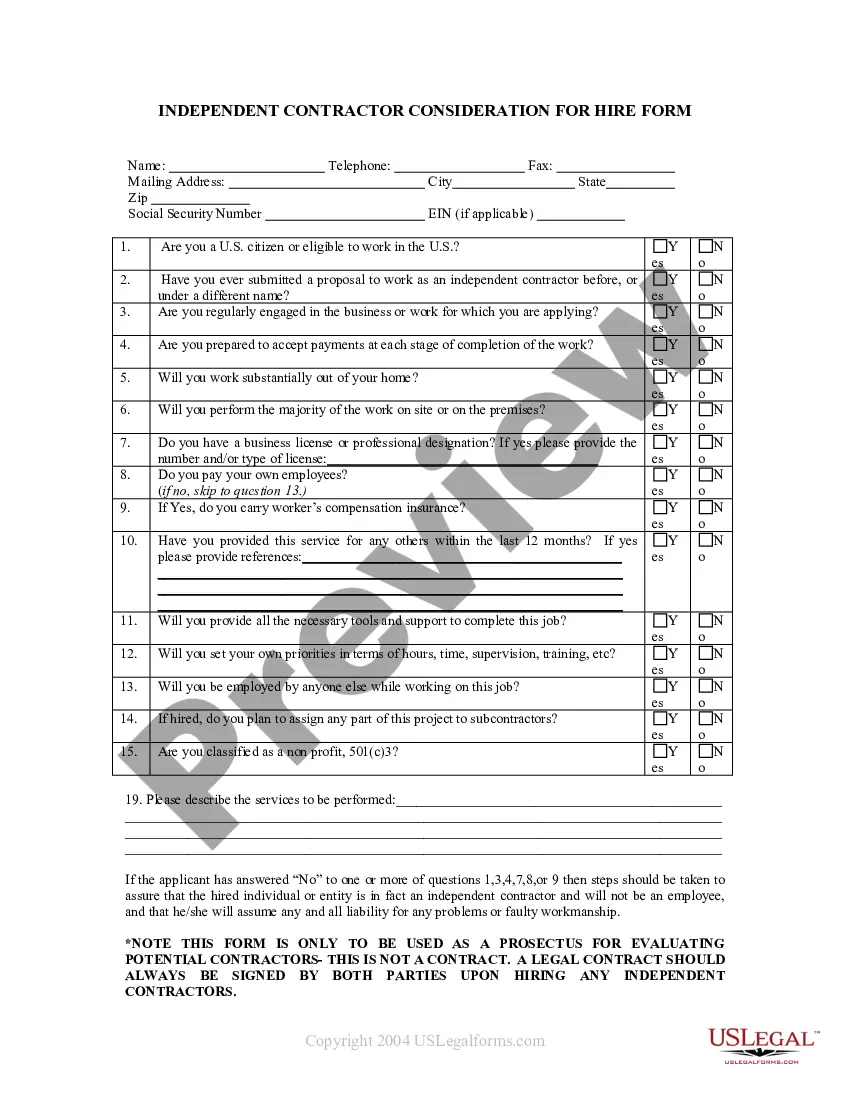
Assets Asset Purchase With Lease In California
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
With leasing the asset isn't yours during the leasing agreement. You can use it as if it was yours, but you are not the legal owner of the asset until the end of the contract, and when all outstanding payments have been made to the leasing company.
The right of use asset will be recorded as the lease liability plus initial direct costs plus prepayments less any lease incentives. Therefore, the right-of-use asset would be calculated as $179,437 (lease liability) +1,000 (lease incentives) = $180,437 (Note there are no prepayments or lease incentives in this example ...
The lessor is the owner of the asset in the lease agreement.
Lessor meaning A lessor is an individual or entity that owns property or an asset and grants another party (the lessee) the right to use it through a lease agreement. The lessor retains ownership while providing temporary usage rights in exchange for regular payments.
Leased Asset on the Balance Sheet: The value of the leased asset is recorded as a fixed asset on the balance sheet. The amount recorded is generally the present value of the minimum lease payments or the fair market value of the leased asset, whichever is lower.
In an operating lease, the ownership remains with the lessor, the entity that leased the asset to the lessee.
The lessor in a lease agreement is the person or legal entity who grants a lease to an individual or family. The lessor is the owner of the asset in the lease agreement.
An operating lease is an agreement to use and operate an asset without the transfer of ownership. Common assets that are leased include real estate, automobiles, aircraft, or heavy equipment.
A right of use asset, or ROU, is a lessee's right to use an asset over the course of a lease. More formally, an ROU asset is an identified property or plant of equipment—in other words, an identified asset—that is leased by an entity.