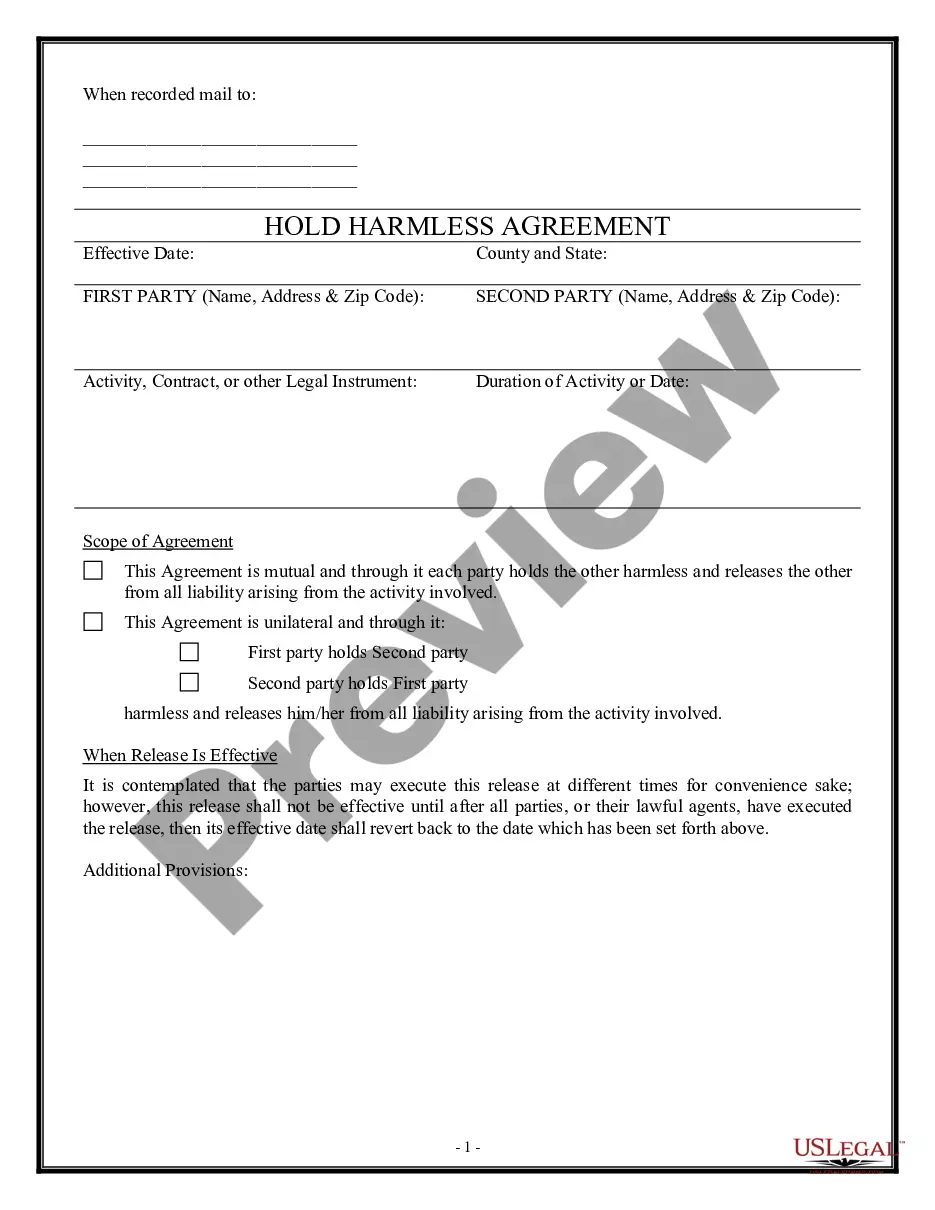
Contract Law Formalities In Alameda
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
Discover the 3 elements of contract law: offer, acceptance, and consideration. Ensure legal protection and clarity in your agreements. Understanding the 3 elements of contract law is crucial for anyone involved in business transactions.
Contracts are made up of three basic parts – an offer, an acceptance and consideration. The offer and acceptance are what the purpose of the agreement is between the parties. A public relations firm offers to provide its services to a potential client. An electrician offers to wire a new home.
A contract is an agreement between parties, creating mutual obligations that are enforceable by law. The basic elements required for the agreement to be a legally enforceable contract are: mutual assent, expressed by a valid offer and acceptance; adequate consideration; capacity; and legality.
In order for a contract to be valid, there must be an offer, an acceptance of the offer, an exchange between the parties of something of value, and an agreement to the terms.
Rule 3.31. Unless otherwise authorized by the court, discovery meet and confer obligations require an in-person, telephonic, or video conference between parties.
There are four essential elements of forming a contract: offer, acceptance, consideration, and intention to create legal relations. Beyond this, the terms of the contract must also be unambiguous, and the parties must have the mental capacity to agree.
There are three essential components of any contract: the offer, the acceptance, and the consideration. If all three of these characteristics aren't present, a document is not considered a contract.
Sources of contract law are grouped into four: the Constitution, federal and state statutes, federal and state case law, and administrative law. There are different elements of contract law, namely certainty, offer consideration, Mutuality, signatures, Capacity, and legally accepted terms.
Rule 3.31. Unless otherwise authorized by the court, discovery meet and confer obligations require an in-person, telephonic, or video conference between parties.
In every case, to present an ex parte application to the court, a party must: reserve a hearing date with the applicable department (for applications that require a hearing.) ... file the motion with the court, and. give notice of the hearing date as required by law.