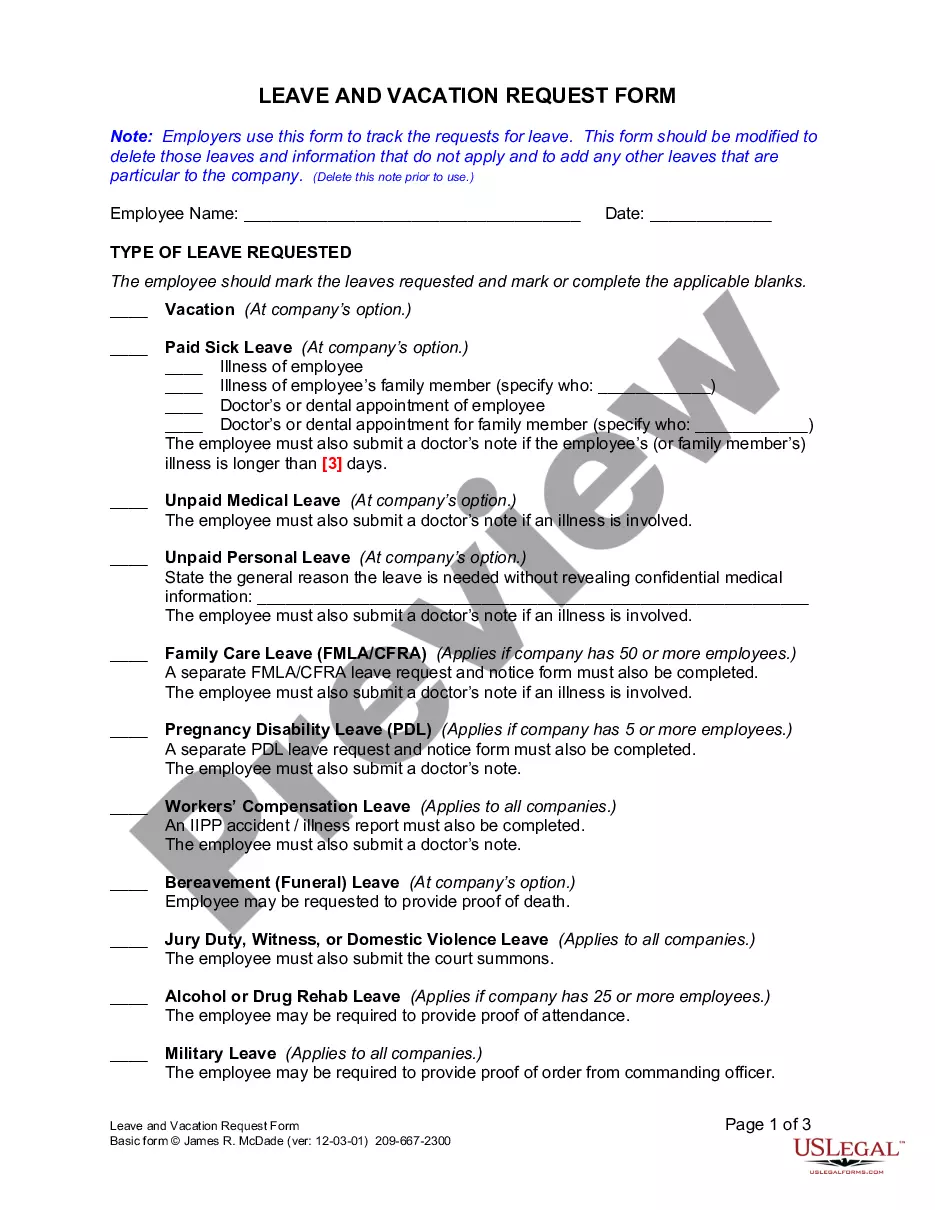
4th Amendment Us Constitution With Case Laws In Pennsylvania
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
The Fourth Amendment states that “no warrants shall issue, but upon probable cause.” This means that any search and seizure conducted without a warrant has the potential to be unconstitutional.
MAPP V. OHIO, decided on 20 June 1961, was a landmark court case originating in Cleveland, in which the U.S. Supreme Court ruled that under the 4th and 14th Constitutional amendments, illegally seized evidence could not be used in a state criminal trial.
Exceptions to the Warrant Requirement These include: Exigent circumstances. Plain view. Search incident to arrest.
Brendlin v. California. This Fourth Amendment activity is based on the landmark Supreme Court case Brendlin v. California, dealing with search and seizure during a traffic stop.
Brendlin v. California | United States Courts.
To claim a violation of Fourth Amendment rights as the basis for suppressing relevant evidence, courts have long required that the claimant must prove that they were the victim of an invasion of privacy to have a valid standing.
In a juvenile court, T.L.O. argued that her Fourth Amendment rights against unreasonable searches and seizures had been violated. The court sided with the school, and T.L.O. took her case to the New Jersey Supreme Court, which later found that the search was unreasonable and the evidence could not be used.
Brendlin v. California. This Fourth Amendment activity is based on the landmark Supreme Court case Brendlin v. California, dealing with search and seizure during a traffic stop.
The Fourth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution protects individuals from unreasonable searches and seizures. Generally, evidence found through an unlawful search cannot be used in a criminal proceeding.
This Fourth Amendment activity is based on the landmark Supreme Court case Brendlin v. California, dealing with search and seizure during a traffic stop.