Alimony And Child Support In Texas In King
Description
Form popularity
FAQ
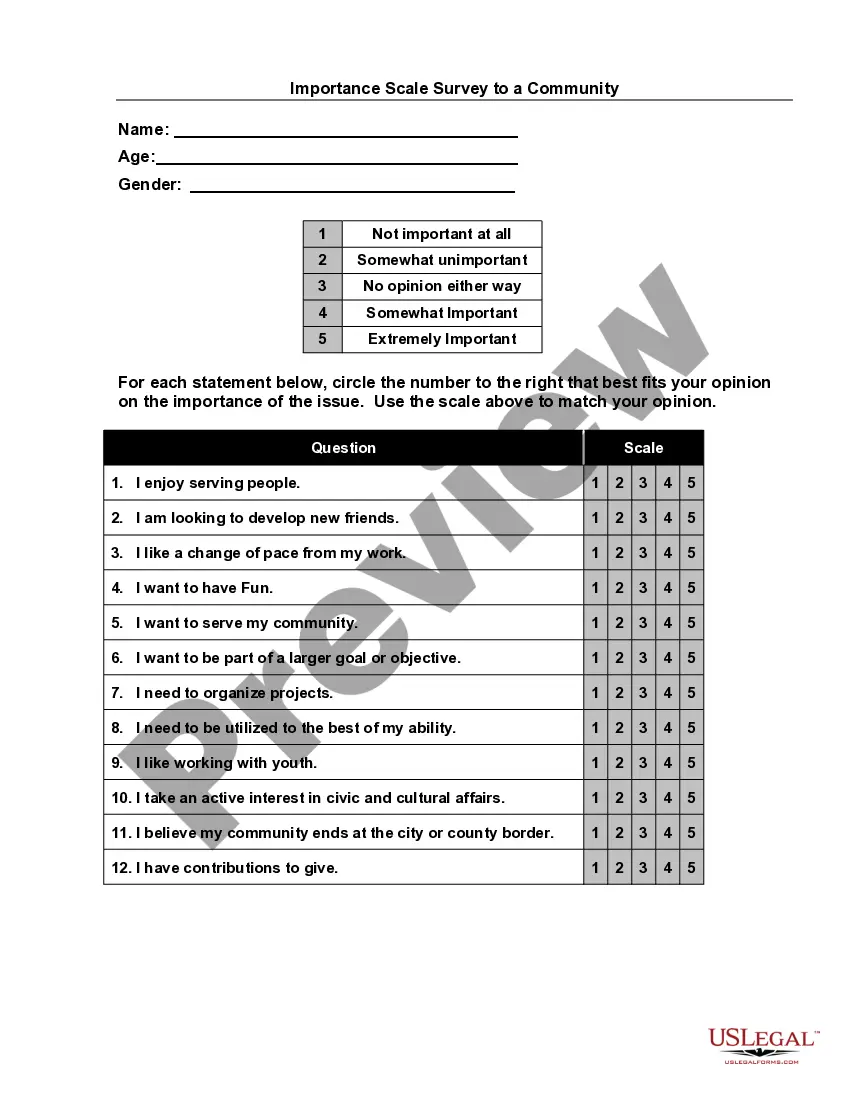
In Texas, some things can disqualify you from spousal support. These include: Cohabitation: If you live with someone else in a marriage-like relationship, you may be disqualified for spousal support. Remarriage: If you remarry before your spousal support obligation ends, you may be disqualified for further payments.
Unlike most other states, Texas law limits the amount of spousal maintenance that judges may award. Monthly payments may not exceed $5,000 or 20% of the supporting spouse's average monthly gross income, whichever is less. Monthly gross income includes income from all sources except: Social Security retirement benefits.
Texas child support law does not take into consideration the payee spouse's (obligee) income or the income of the obligor's spouse.
In short, while there are instances where a remarriage will have an impact on the level of child support, unless your ex's new spouse legally adopts a child, they are not responsible for child support. Furthermore, their income won't have an impact on what is currently agreed upon.
Misconduct: Certain behaviors can also lead to the disqualification of alimony. For instance, if a spouse is found to have engaged in financial misconduct, such as hiding assets or failing to disclose financial information during the divorce proceedings, this can result in disqualification.
After a divorce, it's common for one spouse to make payments to the other as part of the divorce agreement. These payments can be alimony, child support or a mix of both.
Here's how to qualify for alimony in Texas, a couple has to have been married for at least 10 years, and the spouse requesting alimony cannot reasonably meet their needs financial (about $18,0000 per year).
To calculate alimony, the court will divide the paying spouse's annual gross income by 12 to determine their monthly gross income. Then, it will multiply that number by 0.2. If that amount is less than $5,000, that is the monthly amount of alimony you will receive.