Trust And Corporation
Description
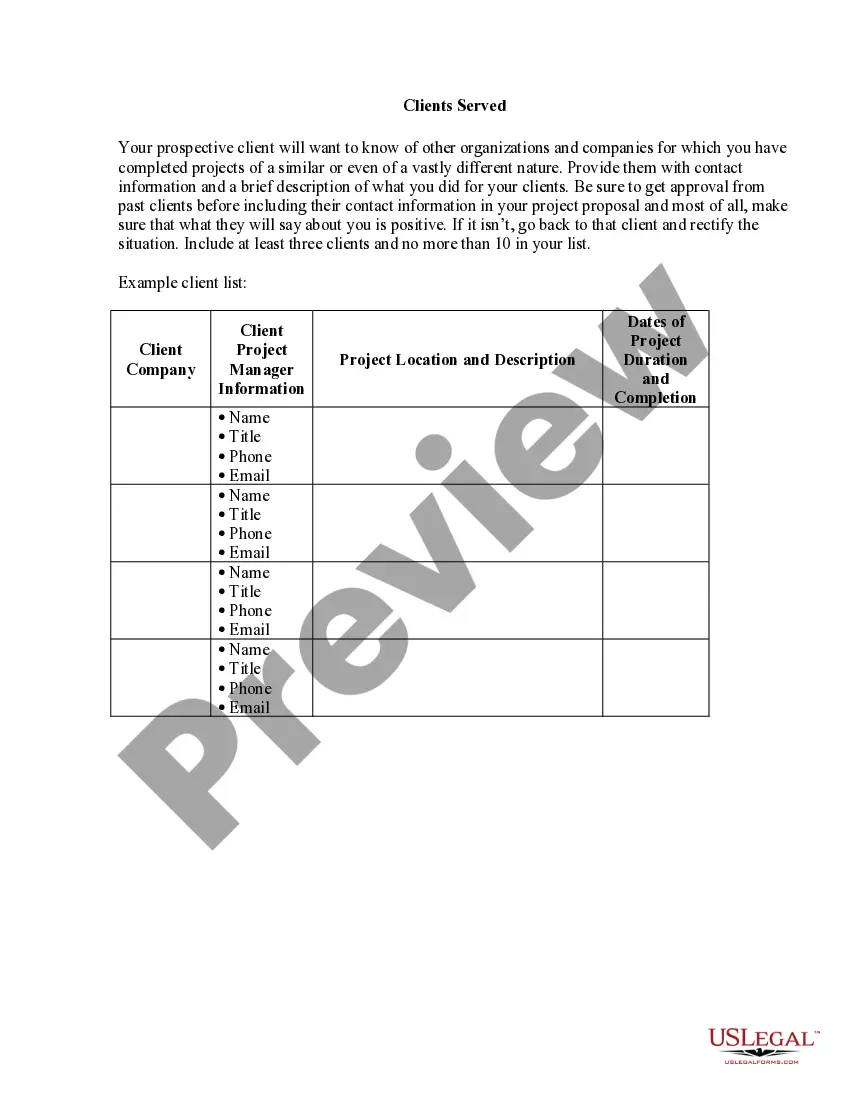
Form popularity
FAQ
A trust in a corporation often acts as a holder of shares or assets on behalf of the company's beneficiaries. This arrangement can provide tax benefits and liability protection. By utilizing a trust within a corporation, you can ensure that the interests of the beneficiaries are safeguarded while efficiently managing corporate assets.
The main purpose of a trust is to manage and protect assets for beneficiaries. Trusts also serve to streamline the transfer of wealth and minimize estate taxes. Establishing a trust can offer peace of mind, knowing that your assets will be handled according to your wishes.
A trust focuses on managing assets for beneficiaries, while a corporation is primarily concerned with running a business. Moreover, a trust does not have a board of directors or shareholders, unlike a corporation which has these governance structures in place. Understanding these differences is vital for asset and liability management.
Trust in a company signifies a relationship where one party relies on another to manage assets responsibly. This trust can establish credibility and stability within business operations. Companies that uphold trust enhance their reputation and foster better relationships with clients and partners.
The purpose of a corporate trust typically involves holding and managing assets for a corporation. This includes acting as a broker or financial intermediary. Corporate trusts facilitate smoother operations while protecting the interests of stakeholders and ensuring compliance with applicable laws.
Yes, a trust can own a corporation. When a trust holds shares in a corporation, it benefits the trust's beneficiaries. This arrangement can provide various legal and tax advantages, making it a strategic choice for managing your business and assets.
A trust and a company can work together in a complementary manner. A trust is a legal arrangement where one party holds property for the benefit of another. In contrast, a corporation is a legal entity that operates a business. Understanding the dynamics between a trust and corporation can help you structure your assets efficiently.
Filing taxes for a trust involves several steps, including gathering all income documents and determining the trust's tax classification. Typically, you'll need to file IRS Form 1041 along with any supporting schedules. It's important to keep accurate records of income, expenses, and distributions. Utilizing resources such as UsLegalForms can simplify the tax filing process for your trust.
To avoid capital gains tax in an irrevocable trust, consider strategies such as maximizing deductions through losses or distributions. You may also explore reallocating assets within the trust to minimize taxable events. It's crucial to evaluate your specific situation carefully. A professional familiar with trust and corporation tax law can guide you in this process.
The new IRS law for irrevocable trusts introduces requirements for reporting, disclosures, and permissible distributions. It impacts how income generated by the trust is taxed and may affect beneficiaries. Staying informed about these changes can help you manage your irrevocable trust more effectively. Platforms like UsLegalForms can provide valuable resources for navigating these new regulations.